A) decreases;increases
B) increases;stays the same
C) decreases;decreases
D) stays the same;increases
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Positive externalities:
A) are similar to negative externalities in their ease of measuring marginal benefits.
B) are likely to be solved with the use of a Pigouvian tax.
C) are difficult to measure since marginal social benefits are hard to observe.
D) result from greater than optimal production of a good.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question: 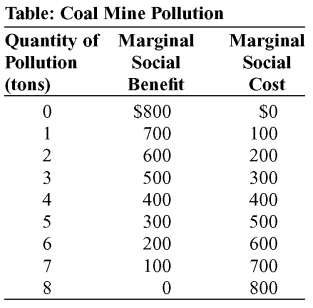 -(Table: Coal Mine Pollution) Use Table: Coal Mine Pollution.The table shows the marginal social benefit and cost of various amounts of pollution from a coal mine.Suppose that the marginal cost from the production process itself (to the producer) is 0.At the market-determined quantity of pollution,the marginal social cost of pollution is:
-(Table: Coal Mine Pollution) Use Table: Coal Mine Pollution.The table shows the marginal social benefit and cost of various amounts of pollution from a coal mine.Suppose that the marginal cost from the production process itself (to the producer) is 0.At the market-determined quantity of pollution,the marginal social cost of pollution is:
A) $800.
B) $400.
C) $200.
D) $0.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
According to the Coase theorem,the inefficiencies caused by externalities can be removed by the private sector if individuals enter into appropriately structured deals,provided that the transaction costs of such deals are sufficiently low.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Taxes on sulfur dioxide emissions,excise taxes on gas,and sales taxes are all examples of Pigouvian taxes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question:
Figure: Efficiency and Pollution 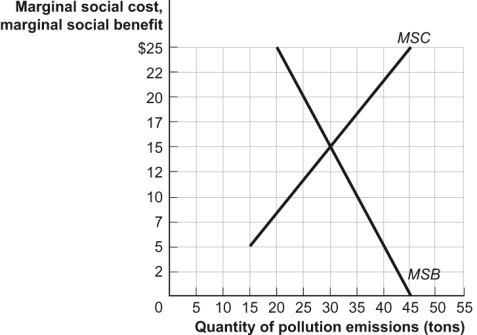 -(Figure: Efficiency and Pollution) Use Figure: Efficiency and Pollution.Assume that firms are the only beneficiaries of pollution and that costs are borne solely by others in the society.If this market produced _____ tons of pollution,then _____.
-(Figure: Efficiency and Pollution) Use Figure: Efficiency and Pollution.Assume that firms are the only beneficiaries of pollution and that costs are borne solely by others in the society.If this market produced _____ tons of pollution,then _____.
A) 30;it would be efficient
B) 45;marginal social cost would be less than marginal social benefit
C) 20;marginal social benefit would be less than marginal social cost
D) 20;the marginal social benefit would be $7.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An industry with production that generates external costs produces a quantity of output that is:
A) socially optimal.
B) smaller than the socially optimal quantity.
C) larger than the socially optimal quantity.
D) socially optimal if a specific subsidy is given to buyers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Externalities exist when individuals impose costs or confer benefits on others but don't have an incentive to take those costs or benefits into account.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question:
Figure: Efficiency and Pollution  -(Figure: Efficiency and Pollution) Use Figure: Efficiency and Pollution.Assume that firms are the only beneficiaries of pollution and that costs are borne solely by others in the society.A Pigouvian tax of $10 per acre of pollution will result in a quantity of pollution for which the:
-(Figure: Efficiency and Pollution) Use Figure: Efficiency and Pollution.Assume that firms are the only beneficiaries of pollution and that costs are borne solely by others in the society.A Pigouvian tax of $10 per acre of pollution will result in a quantity of pollution for which the:
A) marginal social benefit is less than the marginal social cost.
B) marginal social benefit exceeds the marginal social cost.
C) marginal social benefit equals the marginal social cost.
D) resources are allocated efficiently.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the same amount of pollution emitted,an emissions tax is said to be more efficient than is an environmental standard because all polluters:
A) emit pollution up to the point at which the marginal benefit of polluting is equal to the emissions tax.
B) emit the same amount of pollution,regardless of the marginal benefit of polluting.
C) pay the same total tax bill for their pollution.
D) reduce pollution emissions to zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Scenario: Private and External Benefits) Use Scenario: Private and External Benefits.How many hours of lawn upkeep will occur in this community,and what will be the marginal private benefit of such upkeep? Scenario: Private and External Benefits A small community finds that tidy lawns and neighborhoods provide both private and external benefits.They determine that the marginal private benefit (MPB) of lawns can be represented by the equation MPB = 50 - 0.5Q,where Q is the number of hours spent on keeping lawns tidy.The marginal private cost (MPC) of such lawn upkeep is represented by the equation MPC = 0.5Q,where Q is again the number of hours engaged in lawn upkeep.
A) 50 hours and $50
B) 45 hours and $20
C) 50 hours and $25
D) 100 hours and $50
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The proposition that,if bargaining is costless and property rights are well-defined,the market can achieve an efficient outcome is the:
A) Coase theorem.
B) property rights paradigm.
C) market rights theorem.
D) efficient environment paradigm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The socially optimal amount of pollution occurs where the marginal social benefit of pollution is _____ the marginal social cost of pollution.
A) equal to
B) greater than
C) less than
D) There is no socially optimal amount of pollution.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question: 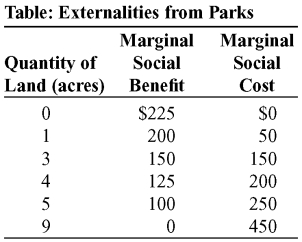 -(Table: Externalities from Parks) Use: Table: Externalities from Parks.The table shows the marginal social benefit and the marginal social cost of preserving various amounts of land in a city for a public park.Suppose that parks result in positive benefits to the community as a whole but that the marginal private benefit that any one individual in the community gets from parks is close to 0.If the government wants to achieve the optimum amount of land for the park,it could use a Pigouvian _____ of _____ per park acre.
-(Table: Externalities from Parks) Use: Table: Externalities from Parks.The table shows the marginal social benefit and the marginal social cost of preserving various amounts of land in a city for a public park.Suppose that parks result in positive benefits to the community as a whole but that the marginal private benefit that any one individual in the community gets from parks is close to 0.If the government wants to achieve the optimum amount of land for the park,it could use a Pigouvian _____ of _____ per park acre.
A) tax;$300
B) tax;$150
C) subsidy;$150
D) subsidy;$450
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question:  -(Table: Coal Mine Pollution) Use Table: Coal Mine Pollution.The table shows the marginal social benefit and cost of various amounts of pollution from a coal mine.If 5 tons of pollution is produced,the outcome is _____ because _____.
-(Table: Coal Mine Pollution) Use Table: Coal Mine Pollution.The table shows the marginal social benefit and cost of various amounts of pollution from a coal mine.If 5 tons of pollution is produced,the outcome is _____ because _____.
A) efficient;MSB = MSC
B) efficient;MSB > MSC
C) inefficient;MSB > MSC
D) inefficient;MSB < MSC
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Markets for the right to pollute are:
A) established by individual firms when they reduce emissions.
B) established by government when it issues tradable pollution permits.
C) likely to result in fewer incentives to develop and implement technology that reduces pollution.
D) a means by which more pollution is encouraged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Since texting while driving generates a negative externality,banning texting while driving would necessarily be economically efficient.
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which example illustrates an environmental policy that uses tradable pollution permits?
A) a charge of $0.10 to automobile drivers for a given level of emitted emissions
B) paying automobile drivers $0.10 for each 10% reduction in automobile emissions
C) allowing automobile drivers to buy and sell the right to emit a certain level of automobile emissions
D) ignoring pollution and letting private markets operate without government interference
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question:  -(Table: Externalities from Parks) Use: Table: Externalities from Parks.The table shows the marginal social benefit and the marginal social cost of preserving various amounts of land in a city for a public park.Suppose that parks result in positive benefits to the community as a whole but the marginal private benefit that any one individual in the community gets from parks is close to 0.Without government intervention,at the amount of land dedicated to the public park the marginal social benefit will be:
-(Table: Externalities from Parks) Use: Table: Externalities from Parks.The table shows the marginal social benefit and the marginal social cost of preserving various amounts of land in a city for a public park.Suppose that parks result in positive benefits to the community as a whole but the marginal private benefit that any one individual in the community gets from parks is close to 0.Without government intervention,at the amount of land dedicated to the public park the marginal social benefit will be:
A) $225.
B) $150.
C) $100.
D) $0.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As the quantity of pollution rises,its marginal social cost:
A) remains constant.
B) falls.
C) rises.
D) rises at first but eventually falls.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 193
Related Exams