A) Involves one step and occurs with retention of configuration.
B) Involves two steps and occurs with inversion of configuration.
C) Involves one step and occurs with inversion of configuration.
D) Involves one step and occurs with racemization.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reaction of bromoethane with sodium acetate affords the substitution product methyl acetate.What is the effect of doubling the concentration of sodium acetate on the rate of the reaction?
A) The rate remains the same.
B) The rate decreases by a factor of 2.
C) The rate increases by a factor of 2.
D) The rate increases by a factor of 4.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) All good leaving groups are strong bases with weak conjugate acids.
B) Left-to-right across a row of the periodic table,leaving group ability decreases.
C) Down a column of the periodic table,leaving group ability decreases.
D) The conjugate bases of strong acids are good leaving groups.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the product of the nucleophilic substitution reaction shown below? 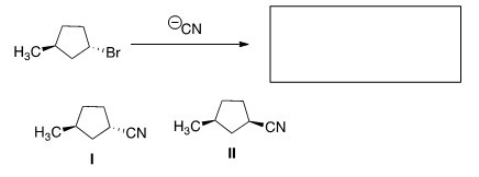
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) I and II
D) None
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reaction of 1-bromobutane with sodium hydroxide affords the substitution product 1-butanol.What would happen to the rate of the reaction if the concentration of both 1-bromobutane and sodium hydroxide were doubled?
A) The rate remains the same.
B) The rate decreases by a factor of 2.
C) The rate increases by a factor of 2.
D) The rate increases by a factor of 4.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following structures have the correct common name? 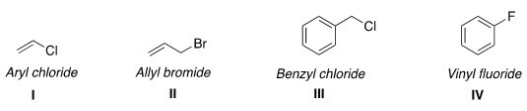
A) I and II
B) II and IV
C) II and III
D) III and IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a characteristic of an SN1 reaction?
A) The rate is proportional to the concentration of substrate.
B) The reaction is favored in polar protic solvents.
C) The rate is independent of the concentration of the nucleophile.
D) The electrophilic carbon undergoes inversion of stereochemistry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the Hammond postulate is not true?
A) The Hammond postulate provides a quantitative estimate of the energy of a transition state.
B) In endothermic reactions,the transition state is closer in energy to the products.
C) In exothermic reactions,the transition state is closer in energy to the reactants.
D) The Hammond postulate provides a qualitative estimate of the energy of a transition state.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which compound is most likely to follow second-order kinetics in a substitution reaction?
A) CH3Br
B) (CH3) 3CCH2Br
C) CH3CH2Br
D) (CH3) 2CHBr
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about an SN1 reaction mechanism is true?
A) The reaction is fastest with primary alkyl halide.
B) The reaction exhibits a one-step mechanism.
C) The reaction rate increases as the leaving group ability increases.
D) The reaction rate increases as the strength of the nucleophile increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following solvents is not a polar protic solvent? 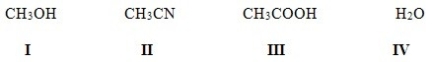
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about carbocation stability is true?
A) Carbocations are stabilized by electron-withdrawing inductive effects only.
B) Carbocations are stabilized by electron-withdrawing inductive effects and hyperconjugation.
C) Carbocations are stabilized by electron-donating inductive effects only.
D) Carbocations are stabilized by electro-donating inductive effects and hyperconjugation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following rate laws describes the kinetics of an SN1 reaction?
A) Rate = k[alkyl halide]
B) Rate = k[alkyl halide][nucleophile]
C) Rate = k[nucleophile]
D) Rate = k[solvent]
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the starting material in the reaction shown below? 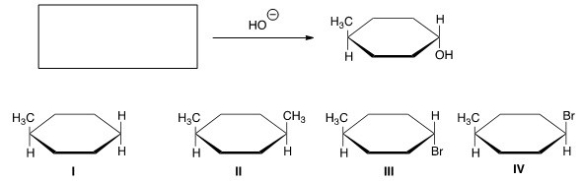
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? 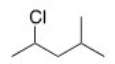
A) 2-Methyl-4-chloropentane
B) 2-Chloro-4-methylpentane
C) 2-Chloro-1-isopropylpropane
D) 2-Chloro-2-methylpentane
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the most nucleophilic?
A) CH4
B) H2O
C) NH3
D) HF
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the reactions of alkyl halides is true?
A) The characteristic reactions of alkyl halides are addition and elimination.
B) The characteristic reactions of alkyl halides are addition and substitution.
C) The characteristic reactions of alkyl halides are elimination and substitution.
D) The characteristic reactions of alkyl halides are oxidation and reduction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following anions is the most nucleophilic in polar aprotic solvents?
A) F-
B) Cl-
C) Br-
D) I-
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rank the following carbocations in order of decreasing stability,putting the most stable first. 
A) I > II > III
B) II > I > III
C) III > I > II
D) III > II > I
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reaction of tert-butyl bromide,(CH3) 3CBr,with ethanol affords the substitution product tert-butyl ethyl ether,(CH3) 3COCH2CH3,in acidic conditions.What would happen to the rate of the reaction if the concentration of ethanol was doubled?
A) The rate remains the same.
B) The rate decreases by a factor of 2.
C) The rate increases by a factor of 2.
D) The rate increases by a factor of 4.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 73
Related Exams