A) MnO2(s)
B) Cl⁻(aq)
C) Cu⁺(aq)
D) SO42-(aq)
E) MnO4⁻(aq)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The electrolysis of molten 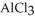 for 4.25 hr with an electrical current of 25.0 A produces
for 4.25 hr with an electrical current of 25.0 A produces  of aluminum metal.
of aluminum metal.
A) 9.90 × 10-3
B) 107
C) 321
D) 1.32
E) 35.7
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the standard half-cell potentials listed below to calculate the standard cell potential for the following reaction occurring in an electrochemical cell at 25°C. (The equation is balanced.) Pb2+(aq) + Mg(s) → Pb(s) + Mg2+(aq) Mg2+(aq) +2 e- →Mg(s) E°= -2.37 V Pb2+(aq) + 2e- → Pb(s) E°= -0.13 V
A) +0.93 V
B) +2.24 V
C) -5.32 V
D) +5.47 V
E) +0.67 V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the cell potential for the following unbalanced reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25 °C when [ ![Calculate the cell potential for the following unbalanced reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25 °C when [ ] = 0.500 M and [ ] = 2.00 M Mg(s) + (aq) → (aq) + Fe(s) E°(Mg<sup>2+</sup>/Mg) = -2.37 V and E°(Fe<sup>3+</sup>/Fe) = -0.036 V A) +2.09 V B) -3.18 V C) +2.35 V D) +0.36 V E) -1.51 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7901/11eacb30_68cf_3555_b5a4_6b5bc377bc77_TB7901_11_TB7901_11.jpg) ] = 0.500 M and [
] = 0.500 M and [ ![Calculate the cell potential for the following unbalanced reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25 °C when [ ] = 0.500 M and [ ] = 2.00 M Mg(s) + (aq) → (aq) + Fe(s) E°(Mg<sup>2+</sup>/Mg) = -2.37 V and E°(Fe<sup>3+</sup>/Fe) = -0.036 V A) +2.09 V B) -3.18 V C) +2.35 V D) +0.36 V E) -1.51 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7901/11eacb30_68cf_3556_b5a4_df5f96c4a4ca_TB7901_11_TB7901_11.jpg) ] = 2.00 M Mg(s) +
] = 2.00 M Mg(s) + ![Calculate the cell potential for the following unbalanced reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25 °C when [ ] = 0.500 M and [ ] = 2.00 M Mg(s) + (aq) → (aq) + Fe(s) E°(Mg<sup>2+</sup>/Mg) = -2.37 V and E°(Fe<sup>3+</sup>/Fe) = -0.036 V A) +2.09 V B) -3.18 V C) +2.35 V D) +0.36 V E) -1.51 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7901/11eacb30_68cf_3557_b5a4_cd06cc2d34c6_TB7901_11_TB7901_11.jpg) (aq) →
(aq) → ![Calculate the cell potential for the following unbalanced reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25 °C when [ ] = 0.500 M and [ ] = 2.00 M Mg(s) + (aq) → (aq) + Fe(s) E°(Mg<sup>2+</sup>/Mg) = -2.37 V and E°(Fe<sup>3+</sup>/Fe) = -0.036 V A) +2.09 V B) -3.18 V C) +2.35 V D) +0.36 V E) -1.51 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7901/11eacb30_68cf_3558_b5a4_17f0182e3fe0_TB7901_11_TB7901_11.jpg) (aq) + Fe(s)
E°(Mg2+/Mg) = -2.37 V and E°(Fe3+/Fe) = -0.036 V
(aq) + Fe(s)
E°(Mg2+/Mg) = -2.37 V and E°(Fe3+/Fe) = -0.036 V
A) +2.09 V
B) -3.18 V
C) +2.35 V
D) +0.36 V
E) -1.51 V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the provided reduction potentials to calculate ΔrG° for the following balanced redox reaction: Pb2+(aq) + Cu(s) → Pb(s) + Cu2+(aq) E°(Pb2+/Pb) = -0.13 V and E°(Cu2+/Cu) = +0.34 V
A) -41 kJ mol-1
B) -0.47 kJ mol-1
C) +46 kJ mol-1
D) +91 kJ mol-1
E) -21 kJ mol-1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the standard reduction potential of Zn is -0.76 V, which of the following statements about a cell whose half-cells are Zn2+/Zn and SHE is correct?
A) SHE will be the cell's cathode, Zn(s) will be the cell's anode, and the measured cell potential will be 0.76 V.
B) SHE will be the cell's anode, Zn(s) will be the cell's cathode, and the measured cell potential will be 0.76 V.
C) SHE will be the cell's cathode, Zn(s) will be the cell's anode, and the measured cell potential will be -0.76 V.
D) SHE will be the cell's cathode, Zn2+(aq) will be the cell's anode, and the measured cell potential will be 0.76 V.
E) H+(aq) will be the cell's cathode, Zn2+(aq) will be the cell's anode, and the measured cell potential will be 0.76 V.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What mass of aluminum can be plated onto an object in 755 minutes at 5.80 A of current?
A) 73.5 g
B) 24.5 g
C) 220. g
D) 147 g
E) 8.17 g
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the standard half-cell potentials listed below to calculate the standard cell potential for the following reaction occurring in an electrochemical cell at 25 °C. (The equation is balanced.) Mg(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Cu(s) + Mg2+(aq) Mg2+(aq) + 2 e⁻ → Mg(s) E° = -2.38 V Cu2+(aq) + 2 e⁻ → Cu(s) E° = +0.34 V
A) +2.04 V
B) -2.04 V
C) +2.72 V
D) -1.36 V
E) +1.36 V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the cell notation for the redox reaction given below: Pb(s) + 2H⁺(aq) → Pb2+(aq) + H2(g)
A) H+(aq) ∣ H2(g) ∣ Pt(s) ![]() Pb(s) ∣ Pb2+(aq)
Pb(s) ∣ Pb2+(aq)
B) H2(g) ∣ H+(aq) ∣ Pt(s) ![]() Pb2+(aq) ∣ Pb(s)
Pb2+(aq) ∣ Pb(s)
C) Pb2+(aq) ∣ Pb(s) ![]() H2(g) ∣ H+(aq) ∣ Pt(s)
H2(g) ∣ H+(aq) ∣ Pt(s)
D) Pb(s) ∣ Pb2+(aq) ![]() H+(aq) ∣ H2(g) ∣ Pt(s)
H+(aq) ∣ H2(g) ∣ Pt(s)
E) Pb(s) ∣ H2(g) ![]() Pb2+(aq) ∣ H+(aq) ∣ Pt(s)
Pb2+(aq) ∣ H+(aq) ∣ Pt(s)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Based on the following information, Cl2(g) + 2 e- → 2 Cl-(aq) E° = +1.36 V Mg2+(aq) + 2 e- → 2 Mg(s) E° = -2.37 V Which of the following chemical species is the strongest reducing agent?
A) Cl2(g)
B) Mg2+(aq)
C) Cl-(aq)
D) Mg(s)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is undergoing oxidation in the redox reaction represented by the following cell notation? Pb(s) ∣ Pb2+(aq)  H+(aq) ∣ H2(g) ∣ Pt(s)
H+(aq) ∣ H2(g) ∣ Pt(s)
A) H2(g)
B) H+(aq)
C) Pb2+(aq)
D) Pb(s)
E) Pt(s)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the strongest reducing agent?
A) Al(s)
B) Zn(s)
C) Mg(s)
D) Al3+(aq)
E) Mg2+(aq)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the cell potential for the following unbalanced reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25 °C when [ ![Calculate the cell potential for the following unbalanced reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25 °C when [ ] = 0.914 M and [ ] = 0.0230 M Mg(s) + (aq) → (aq) + Fe(s) E°(Mg<sup>2+</sup>/Mg) = -2.37 V and E°(Fe<sup>3+</sup>/Fe) = -0.036 V A) +2.32 V B) +2.30 V C) -2.32 V D) -2.30 V E) +1.23 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7901/11eacb30_68cf_0e41_b5a4_63c45c3ba0fa_TB7901_11_TB7901_11.jpg) ] = 0.914 M and [
] = 0.914 M and [ ![Calculate the cell potential for the following unbalanced reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25 °C when [ ] = 0.914 M and [ ] = 0.0230 M Mg(s) + (aq) → (aq) + Fe(s) E°(Mg<sup>2+</sup>/Mg) = -2.37 V and E°(Fe<sup>3+</sup>/Fe) = -0.036 V A) +2.32 V B) +2.30 V C) -2.32 V D) -2.30 V E) +1.23 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7901/11eacb30_68cf_0e42_b5a4_b953ab282507_TB7901_11_TB7901_11.jpg) ] = 0.0230 M Mg(s) +
] = 0.0230 M Mg(s) + ![Calculate the cell potential for the following unbalanced reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25 °C when [ ] = 0.914 M and [ ] = 0.0230 M Mg(s) + (aq) → (aq) + Fe(s) E°(Mg<sup>2+</sup>/Mg) = -2.37 V and E°(Fe<sup>3+</sup>/Fe) = -0.036 V A) +2.32 V B) +2.30 V C) -2.32 V D) -2.30 V E) +1.23 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7901/11eacb30_68cf_0e43_b5a4_7917c247e5a7_TB7901_11_TB7901_11.jpg) (aq) →
(aq) → ![Calculate the cell potential for the following unbalanced reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25 °C when [ ] = 0.914 M and [ ] = 0.0230 M Mg(s) + (aq) → (aq) + Fe(s) E°(Mg<sup>2+</sup>/Mg) = -2.37 V and E°(Fe<sup>3+</sup>/Fe) = -0.036 V A) +2.32 V B) +2.30 V C) -2.32 V D) -2.30 V E) +1.23 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7901/11eacb30_68cf_0e44_b5a4_bf76aed2dd5e_TB7901_11_TB7901_11.jpg) (aq) + Fe(s)
E°(Mg2+/Mg) = -2.37 V and E°(Fe3+/Fe) = -0.036 V
(aq) + Fe(s)
E°(Mg2+/Mg) = -2.37 V and E°(Fe3+/Fe) = -0.036 V
A) +2.32 V
B) +2.30 V
C) -2.32 V
D) -2.30 V
E) +1.23 V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following. -Q = K
A) Ecell = E°cell
B) Ecell > 0
C) Ecell = 0
D) E°cell > 0
E) E°cell < 0
F) Ecell < 0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a galvanic cell that uses the following two half-reactions, Cr2O72-(aq) + 14H+(aq) + 6 e- → 2Cr3+(aq) + 7H2O(l) Pb(s) → Pb2+(aq) + 2 e- How many moles of Pb(s) are oxidized by three mol es of Cr2O72-?
A) 3
B) 6
C) 9
D) 18
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine which of the following pairs of reactants will result in a spontaneous reaction at 25 °C.
A) I-(aq) + Zn2+(aq) ; if E°(I2/I-) = + 0.54V and E°(Zn2+/Zn) = -0.76V
B) Ca(s) + Mg2+(aq) ; if E°(Ca2+/Ca) = -2.76V and E°(Mg2+/Mg) = -2.37V
C) H2(g) + Cd2+(aq) ; if E°(Cd2+/Cd) = -0.40V
D) Ag(s) + Sn2+(aq) ; if E°(Ag+/Ag) = + 0.80V and E°(Sn2+/Sn) = -0.14V
E) Ag+(aq) + Mn2+(aq) ; if E°(Ag+/Ag) = + 0.80V and E°(MnO4-/Mn2+) = +1.51V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the tabulated half-cell potentials to calculate the equilibrium constant (K) for the following balanced redox reaction at 25 °C: Pb2+(aq) + Cu(s) → Pb(s) + Cu2+(aq) E°(Pb2+/Pb) = -0.13 V and E°(Cu2+/Cu) = +0.34 V
A) 7.9 × 10-8
B) 8.9 × 107
C) 7.9 × 1015
D) 1.3 × 10-16
E) 1.1 × 10-8
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following reactions would have the smallest value of K at 298 K?
A) A + B → C; E°cell = +1.22 V
B) A + 2 B → C; E°cell = +0.98 V
C) A + B → 2 C; E°cell = -0.030 V
D) A + B → 3 C; E°cell = +0.15 V
E) A + B → C; E°cell = -0.015 V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The standard cell potential (E°) of a voltaic cell constructed using the cell reaction below is 0.76 V: Zn(s) + ![The standard cell potential (E°) of a voltaic cell constructed using the cell reaction below is 0.76 V: Zn(s) + (aq) → (aq) + (g) With = 1.0 atm and [ ] = 1.0 mol L<sup>-1</sup>, the cell potential is 0.45 V. The concentration of in the cathode compartment is ________ mol L<sup>-1</sup>. A) 3.3 × 10<sup>-11</sup> B) 2.4 × 10<sup>-3</sup> C) 1.1 × 10<sup>-2</sup><sup>1</sup> D) 0.73 E) 5.8 × 10<sup>-6</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7901/11eacb30_68d1_7e61_b5a4_d9a699ca9e9a_TB7901_11_TB7901_11.jpg) (aq) →
(aq) → ![The standard cell potential (E°) of a voltaic cell constructed using the cell reaction below is 0.76 V: Zn(s) + (aq) → (aq) + (g) With = 1.0 atm and [ ] = 1.0 mol L<sup>-1</sup>, the cell potential is 0.45 V. The concentration of in the cathode compartment is ________ mol L<sup>-1</sup>. A) 3.3 × 10<sup>-11</sup> B) 2.4 × 10<sup>-3</sup> C) 1.1 × 10<sup>-2</sup><sup>1</sup> D) 0.73 E) 5.8 × 10<sup>-6</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7901/11eacb30_68d1_7e62_b5a4_39b632d2ad5c_TB7901_11_TB7901_11.jpg) (aq) +
(aq) + ![The standard cell potential (E°) of a voltaic cell constructed using the cell reaction below is 0.76 V: Zn(s) + (aq) → (aq) + (g) With = 1.0 atm and [ ] = 1.0 mol L<sup>-1</sup>, the cell potential is 0.45 V. The concentration of in the cathode compartment is ________ mol L<sup>-1</sup>. A) 3.3 × 10<sup>-11</sup> B) 2.4 × 10<sup>-3</sup> C) 1.1 × 10<sup>-2</sup><sup>1</sup> D) 0.73 E) 5.8 × 10<sup>-6</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7901/11eacb30_68d1_7e63_b5a4_0394926c557b_TB7901_11_TB7901_11.jpg) (g)
With
(g)
With ![The standard cell potential (E°) of a voltaic cell constructed using the cell reaction below is 0.76 V: Zn(s) + (aq) → (aq) + (g) With = 1.0 atm and [ ] = 1.0 mol L<sup>-1</sup>, the cell potential is 0.45 V. The concentration of in the cathode compartment is ________ mol L<sup>-1</sup>. A) 3.3 × 10<sup>-11</sup> B) 2.4 × 10<sup>-3</sup> C) 1.1 × 10<sup>-2</sup><sup>1</sup> D) 0.73 E) 5.8 × 10<sup>-6</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7901/11eacb30_68d1_7e64_b5a4_6f976e2a13cd_TB7901_11_TB7901_11.jpg) = 1.0 atm and [
= 1.0 atm and [ ![The standard cell potential (E°) of a voltaic cell constructed using the cell reaction below is 0.76 V: Zn(s) + (aq) → (aq) + (g) With = 1.0 atm and [ ] = 1.0 mol L<sup>-1</sup>, the cell potential is 0.45 V. The concentration of in the cathode compartment is ________ mol L<sup>-1</sup>. A) 3.3 × 10<sup>-11</sup> B) 2.4 × 10<sup>-3</sup> C) 1.1 × 10<sup>-2</sup><sup>1</sup> D) 0.73 E) 5.8 × 10<sup>-6</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7901/11eacb30_68d1_a575_b5a4_fd13dcb85b86_TB7901_11_TB7901_11.jpg) ] = 1.0 mol L-1, the cell potential is 0.45 V. The concentration of
] = 1.0 mol L-1, the cell potential is 0.45 V. The concentration of ![The standard cell potential (E°) of a voltaic cell constructed using the cell reaction below is 0.76 V: Zn(s) + (aq) → (aq) + (g) With = 1.0 atm and [ ] = 1.0 mol L<sup>-1</sup>, the cell potential is 0.45 V. The concentration of in the cathode compartment is ________ mol L<sup>-1</sup>. A) 3.3 × 10<sup>-11</sup> B) 2.4 × 10<sup>-3</sup> C) 1.1 × 10<sup>-2</sup><sup>1</sup> D) 0.73 E) 5.8 × 10<sup>-6</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7901/11eacb30_68d1_a576_b5a4_9db1c1f6ef94_TB7901_11_TB7901_11.jpg) in the cathode compartment is ________ mol L-1.
in the cathode compartment is ________ mol L-1.
A) 3.3 × 10-11
B) 2.4 × 10-3
C) 1.1 × 10-21
D) 0.73
E) 5.8 × 10-6
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the standard half-cell potentials listed below to calculate the standard cell potential for the following reaction occurring in an electrochemical cell at 25 °C. (The equation is balanced.) 2 Ag+(aq) + Pb(s) → 2Ag(s) + Pb2+(aq) Ag+(aq) + e- → Ag(s) E°= 0.80 V Pb2+(aq) + 2 e- → Pb(s) E°= -0.13 V
A) +0.93 V
B) +1.85 V
C) -5.32 V
D) +5.47 V
E) +0.67 V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 122
Related Exams