A) shut down.
B) decrease output.
C) increase output.
D) increase the market price.
E) not change output. This firm is at its profit-maximizing position.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following total cost schedule for a perfectly competitive firm producing ball-point pens. 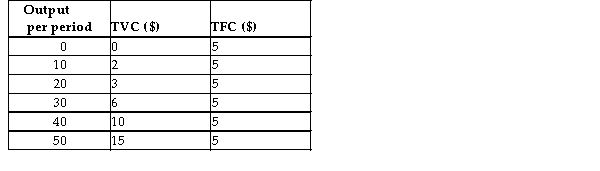 TABLE 9-3
-Refer to Table 9-3. Suppose the prevailing market price for this firmʹs product is $0.14 and the firm is currently producing 20 units of output. This competitive firm wishing to maximize profits would
TABLE 9-3
-Refer to Table 9-3. Suppose the prevailing market price for this firmʹs product is $0.14 and the firm is currently producing 20 units of output. This competitive firm wishing to maximize profits would
A) increase output because marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost.
B) decrease output because marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
C) increase output because marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
D) decrease output because marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost.
E) produce zero output because price is less than the minimum average variable cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the total cost and revenue curves shown below, for two perfectly competitive firms, Firm A and Firm B.
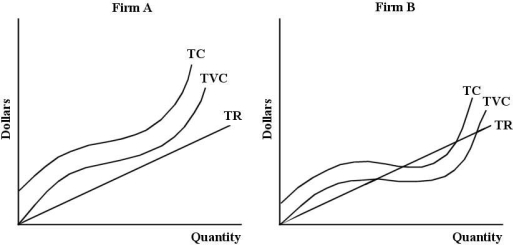 FIGURE 9-4
-The short-run supply curve for a perfectly competitive firm is
FIGURE 9-4
-The short-run supply curve for a perfectly competitive firm is
A) its entire marginal-cost curve.
B) its rising portion of the average-variable-cost curve.
C) its average-revenue curve.
D) its marginal-cost curve above the average-variable-cost curve.
E) the industry supply curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following conditions is true of a perfectly competitive industry when it is in long -run equilibrium?
A) Firms are entering the industry.
B) Firms are exiting the industry.
C) Price equals minimum short-run average total cost for all firms.
D) Accounting profits for all firms are zero.
E) Firms are experiencing increasing returns to scale.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume the following total cost schedule for a perfectly competitive firm. 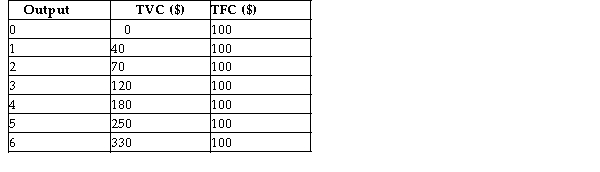 TABLE 9-2
-Refer to Table 9-2. In order to maximize its profits, the firm should continue to produce in the short run even if the market price is less than its ATC as long as the price is greater than or equal to
TABLE 9-2
-Refer to Table 9-2. In order to maximize its profits, the firm should continue to produce in the short run even if the market price is less than its ATC as long as the price is greater than or equal to
A) AVC.
B) MC.
C) AFC.
D) TVC.
E) TC.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that in a perfectly competitive industry, the market price of the product is $27. A firm is producing the output level at which average total cost equals marginal cost, both of which are $25. Average variable cost is $23. To maximize profits in the short run, the firm should
A) reduce its output.
B) increase its output.
C) leave its output unchanged.
D) shut down.
E) change the price of the product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a perfectly competitive market, smaller-than-efficient sized firms can exist in
A) the short run.
B) the long run.
C) both the short and long run.
D) the long run, and they will make positive economic profits.
E) both the short run and the long run, but they must reduce plant size to remain competitive.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Farmer Anna is producing tomatoes in a perfectly competitive market. In Year 1 she sells 4000 bushels of tomatoes at a price of $12.00 each. In Year 2 she sells 4800 bushels at $13.00 each. In Year 2, her average revenue is and her marginal revenue is .
A) $13.00; $1.00
B) $12.50; $12.50
C) $13.00; $13.00
D) $12.00; $12.00
E) $12.00; $1.00
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a perfectly competitive industry in the short-run. When a firm in this industry is at its profit-maximizing level of output, it
A) is doing as well as it can and is making a profit.
B) may be making a profit or incurring a loss.
C) is producing where P = AVC.
D) is producing where MC = AC.
E) is producing where price exceeds marginal cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Average revenue AR) for an individual firm in a perfectly competitive market equals
A) p × q.
B) p × q) /q.
C) △p × △q.
D) △q/△p.
E) p × q) /△q.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the price and quantity data below for a perfectly competitive firm producing mousetraps.  TABLE 9-1
-Refer to Table 9-1. Suppose this firm is currently selling 1750 mousetraps at the market price of $5. If the firm raises its price to $6, its total revenue will be
TABLE 9-1
-Refer to Table 9-1. Suppose this firm is currently selling 1750 mousetraps at the market price of $5. If the firm raises its price to $6, its total revenue will be
A) $0.
B) greater than or equal to $1750.
C) greater than or equal to $6250.
D) $10 500.
E) greater than $10 500.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If firms in a competitive industry are suffering economic losses, then one would expect that in the long run
A) the demand curve for the product will shift to the left, causing equilibrium output and price to decline.
B) there would be no change in the number of firms in the industry as long as firms are covering their average variable costs.
C) the supply curve for the product will shift to the left as firms leave the industry, causing industry output to fall and price to rise.
D) the supply curve for the product will shift to the right as individual firms lower their prices to increase their sales.
E) each firm would raise its price until it was breaking even.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the usual assumptions about perfect competition, a perfectly competitive firm
A) can set the price it charges.
B) can sell as much of its product as it wishes at the market price.
C) can affect the market conditions in a significant way.
D) is aware of its competitorsʹ costs.
E) competes actively with other sellers in the industry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose ABC Corp. is a firm producing newsprint in a perfectly competitive industry. We have the following information about the firmʹs production: - output Q) = 1500 tonnes per month - average total cost ATC) = $627 per tonne - average variable cost AVC) = $614 per tonne - marginal revenue MR) = $620 per tonne - marginal cost MC) = $620 per tonne In the short run, this firm should
A) reduce output because the price per tonne is less than ATC.
B) shut down because the firm is incurring economic losses.
C) maintain production at the current level.
D) increase output because MR is greater than AVC.
E) Not possible to determine because the price of the product is not known.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
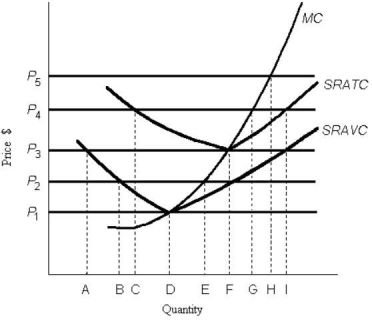 FIGURE 9-1
-Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. The price at which the firm earns zero economic profits is
FIGURE 9-1
-Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. The price at which the firm earns zero economic profits is
A) P1.
B) P2.
C) P3.
D) P4.
E) P5.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The conditions for a perfectly competitive market include which one of the following?
A) Firms behave as price takers.
B) Profits are zero in the short run.
C) New entrants cannot threaten the position of existing firms.
D) Firms can control prices.
E) Firms must employ the newest technologies as soon as they are developed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose ABC Corp. is a firm producing newsprint in a perfectly competitive industry. We have the following information about the firmʹs production: - output Q) = 1500 tonnes per month - average total cost ATC) = $627 per tonne - average variable cost AVC) = $614 per tonne - marginal revenue MR) = $620 per tonne - marginal cost MC) = $620 per tonne At the current level of output, this firm is profit and is earning economic profit of per month.
A) maximizing; $10 500
B) maximizing; -$10 500
C) not maximizing; -$10 500
D) not maximizing; -$9000
E) maximizing; $9000
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a given market price, a perfectly competitive firmʹs total-revenue curve
A) is a positively sloped straight line, starting from the origin.
B) increases to the right and then declines when MC = MR.
C) is a straight line that coincides with the market demand curve.
D) is the same as the firmʹs demand curve.
E) is the same as the firmʹs MR curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Comparing the short-run and long-run profit-maximizing positions of a perfectly competitive firm, which statement is true?
A) Price will equal marginal cost in the short run, but not necessarily in the long run.
B) Economic profit may exist in the short run and in the long run.
C) The firm will produce at minimum average cost in both the short and long run.
D) Price should equal average cost in the long run, but not necessarily in the short run.
E) The firm may have unexploited economies of scale in both the short run and the long run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following total cost schedule for a perfectly competitive firm producing ball-point pens.  TABLE 9-3
-Refer to Table 9-3. This firm would produce no output in the short run if the market price of its output
TABLE 9-3
-Refer to Table 9-3. This firm would produce no output in the short run if the market price of its output
A) dropped below $0.15.
B) dropped below $0.20.
C) dropped below $0.30.
D) dropped below $2.00.
E) dropped below $3.00.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 153
Related Exams