Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes what occurs when monetary authorities sell government securities?
A) There is a decrease in the size of chartered banks' excess reserves, the money supply increases, and interest rates fall, thereby causing a decrease in investment spending and real GDP.
B) There is a decrease in the size of chartered banks' excess reserves, the money supply decreases, and the interest rates rise, thereby causing a decrease in investment spending and real GDP.
C) There is a decrease in the size of chartered banks' excess reserves, the money supply decreases, and interest rates rise, thereby causing an increase in investment spending and real GDP.
D) There is an increase in the size of chartered bank reserves, the money supply increases, and interest rates fall, thereby causing an increase in investment spending and real GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the dollars held for transactions purposes are, on the average, spent four times a year for final goods and services, then the quantity of money people will wish to hold for transactions is equal to:
A) four percent of nominal GDP.
B) 25 percent of nominal GDP.
C) nominal GDP multiplied times 4.
D) nominal GDP divided by 25.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest rate at which the Bank of Canada lends to chartered banks is called:
A) the prime rate.
B) the short-term rate.
C) the bank rate.
D) the government bonds rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes the cause-effect chain of an expansionary monetary policy?
A) A decrease in the money supply will lower the interest rate, increase investment spending, and increase GDP.
B) A decrease in the money supply will raise the interest rate, decrease investment spending, and decrease GDP.
C) An increase in the money supply will raise the interest rate, decrease investment spending, and decrease GDP.
D) An increase in the money supply will lower the interest rate, increase investment spending, and increase GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bond with no expiration has an original price of $10,000 and a fixed annual interest payment of $1000.If the price of this bond increases by $2500, the interest rate in effect will:
A) decrease by 1 percentage point.
B) decrease by 2 percentage points.
C) increase by 1 percentage point.
D) increase by 2 percentage points.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On a diagram wherein the interest rate and the quantity of money demanded are shown on the vertical and horizontal axes respectively, the total demand for money can be found by:
A) horizontally adding the transactions and the asset demand for money.
B) vertically subtracting the transactions demand from the asset demand for money.
C) horizontally subtracting the asset demand from the transactions demand for money.
D) vertically adding the transactions and the asset demand for money.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The price of a bond with no expiration date is originally $5,000 and it pays an annual interest payment of $500.If the price of the bond falls to $3,000, then the effective interest rate yield to a new buyer of the bond is:
A) 14.4 percent.
B) 16.6 percent.
C) 11.0 percent.
D) 9.0 percent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetary policy is:
A) faster than fiscal policy.
B) slower than fiscal policy.
C) weaker than fiscal policy.
D) stronger than fiscal policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following is a simplified consolidated balance sheet for the chartered banking system and the Bank of Canada.Assume a desired reserve ratio of 5 percent for the chartered banks.All figures are in billions of dollars.CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET: CHARTERED BANKING SYSTEM  BALANCE SHEET: BANK OF CANADA
BALANCE SHEET: BANK OF CANADA
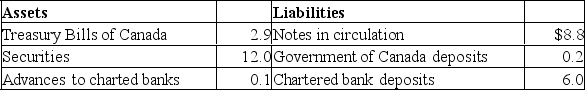 Refer to the above information, suppose the Bank of Canada sells $2 in securities directly to the chartered banks.As a result of this transaction, the supply of money:
Refer to the above information, suppose the Bank of Canada sells $2 in securities directly to the chartered banks.As a result of this transaction, the supply of money:
A) will directly increase by $2 and the money-creating potential of the chartered banking system will increase by $38.
B) will directly decrease by $2 and the money-creating potential of the chartered banking system will decrease by $40.
C) is not directly affected, but the money-creating potential of the chartered banking system will decrease by $40.
D) will decrease by $2, but the money-creating potential of the chartered banking system will not be affected.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in nominal GDP increases the demand for money because:
A) interest rates will rise.
B) more money is needed to finance a larger volume of transactions.
C) bond prices will fall.
D) the opportunity cost of holding money will decline.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Quantitative easing refers to the purchasing of private sector assets by a country's central bank in order to provide liquidity to the financial system.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The bank rate is the rate of interest at which:
A) the Bank of Canada lends to chartered banks.
B) financial institutions lend to some builders.
C) the Bank of Canada lends to large corporations.
D) chartered banks lend to large corporations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correct?
A) The asset demand for money is downward sloping because the opportunity cost of holding money declines as the interest rate rises.
B) The asset demand for money is downward sloping because the opportunity cost of holding money increases as the interest rate rises.
C) The transactions demand for money is downward sloping because the opportunity cost of holding money varies inversely with the interest rate.
D) The asset demand for money is downward sloping because bond prices and the interest rate are directly related.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The job of the monetary authorities in limiting the supply of money may be made more complex if chartered banks initially have substantial excess reserves.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Bank of Canada buys government securities from the chartered banks, which of the following transactions take place?
A) The demand deposits of chartered banks are unchanged, but their reserves increase.
B) The demand deposits and reserves of chartered banks both decrease.
C) The demand deposits of chartered banks are unchanged, but their reserves decrease.
D) The demand deposits and reserves of chartered banks are both unchanged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An important routine function of the Bank of Canada is:
A) to help new chartered banks sell capital stock.
B) to supply the economy with paper currency.
C) to advise chartered banks as to the most profitable ways of reinvesting profits.
D) to help chartered banks develop correspondent relationships with foreign banks.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
By early 2008 it became evident that the Canadian economy was slowing along with the U.S., where housing bubble had created a financial crisis worldwide.The Bank of Canada's response to this crisis was:
A) to increase the overnight rate to 1.5 percent by the end of 2008.
B) to drop the overnight rate to 1.5 percent by the end of 2008, and to lower it even further to a historic low of .25 percent in 2009.
C) to leave the overnight rate at 2 percent.
D) to hike the overnight lending rate in order to avoid inflationary pressures.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A liquidity trap refers to a situation in which:
A) taking away liquidity from the banks has a major positive effect on lending.
B) adding liquidity to banks has major positive effects on lending.
C) adding liquidity to banks has little or no positive effects on lending.
D) taking away liquidity to banks has a major negative effect on lending.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 239 of 239
Related Exams