A) are very close to the Milky Way and appear to be gravitationally bound to it.
B) have very bright, very hot starlike central cores with variable energy output.
C) are completely devoid of structure, appearing to be amorphous spheres of gas and dust.
D) are in the constellation of Seyfert in Earth's southern hemisphere sky.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The strongest direct evidence for supermassive black holes at the centers of normal galaxies comes from
A) gravitational lensing.
B) the Doppler shifts of stars.
C) gamma-ray emissions.
D) the motions of galaxies during mergers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fact that quasars can be detected from distances from which even the biggest and most luminous galaxies cannot be seen means that
A) they must be in directions where gravitational focusing by the masses of nearer galaxies makes them visible from Earth.
B) they must be far more luminous than the brightest galaxies.
C) they must be in directions where intergalactic absorption by dark matter is minimum, allowing observers to see them.
D) their spectra have not been as redshifted by their motion as those of galaxies and hence they can still be seen.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the unified model of active galaxies, the main difference among quasars, BL Lacertae objects, and radio galaxies appears to be that
A) astronomers see the accretion disk around the central black hole from a different angle in each case-face-on for BL Lacertae, edge-on for radio galaxies, and in between for quasars.
B) the rate at which matter is falling into the central black hole is different in each case-largest in quasars, less in BL Lacertae objects, and least in radio galaxies.
C) the mass of the central black hole is different in each case-largest in quasars, less in BL Lacertae, and least in radio galaxies.
D) the galaxy type with which they are associated is different in each case-spiral for BL Lacertae, elliptical for quasars, and irregular for radio galaxies.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What do astronomers expect to be the relationship between the number of active galaxies they detect and the number of active galaxies that actually exist?
A) The energy output from active galaxies is so large that it is easy to detect them. Thus, astronomers believe that they have detected all that exist.
B) The nuclei of many active galaxies are hidden by dust in the accretion disk. Thus, astronomers expect the actual number to be much greater than the observed number.
C) Astronomers cannot detect active galaxies unless the jets are pointed more or less toward Earth. The jets point toward Earth in only a few cases, so they expect the actual number to be greater than the observed number.
D) Active galaxies are created in galaxy collisions. But galaxy collisions occurred only in the early universe and are no longer occurring. The active galaxies all died off while their light was traveling to Earth.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What appears to be the central energy-generating system or "engine" that is producing prodigious amounts of energy in the centers of galaxies, active galaxies, and quasars?
A) steady series of supernova explosions, the late evolutionary stages of massive stars
B) rapidly rotating core of matter, where friction between it and the surrounding matter causes tremendous heat and energy output
C) supermassive black hole, where matter is compressed on falling into the hole and heated to extremely high temperatures
D) There is no central "engine" in these sources. Their high gravity has focused radiation from many sources beyond them by gravitational lensing and they thus appear to be very bright.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An active galaxy is measured to be 100 Mpc away. How many million years ago did the light observers see now leave this galaxy?
A) 30.7
B) 100
C) 326
D) 652
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A moving electron in a magnetic field in space follows a spiral pattern, emitting what type of radiation as it does so?
A) synchrotron radiation
B) no radiation at all, since it is moving smoothly without acceleration
C) Cherenkov radiation
D) Lyman radiation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The distance to the bright quasar 3C 273 is estimated to be
A) 2 billion ly.
B) 20,000 ly.
C) just beyond the Milky Way.
D) 3 million ly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Astronomers initially had difficulty identifying the emission lines in quasar spectra at optical wavelengths because
A) the emission lines were smeared out by the extremely high speed of the quasars, making them hard to measure.
B) the emission lines were from ionized atoms that had not been seen before.
C) the emission lines were found to be created from elements that do not exist on Earth.
D) no one expected to see the pattern of spectral lines characteristic of the ultraviolet hydrogen spectra in the visible region.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of these objects typically has the greatest luminosity?
A) giant elliptical galaxy
B) Seyfert galaxy
C) radio galaxy
D) quasar
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Quasars emit significant amounts of radiation from the Lyman-alpha transition. When the spectrum is observed on Earth, it is found that the Lyman-alpha line is accompanied by many absorption lines, called the Lyman-alpha forest. What is the origin of these lines? See Figure 18-5 in the text. 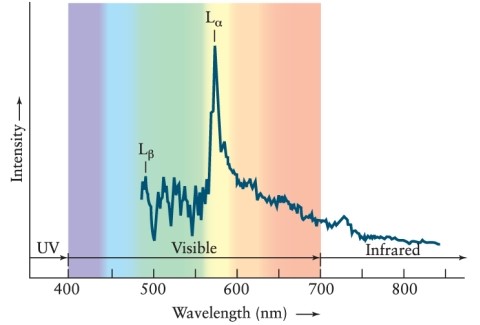
A) The absorption lines are caused by the rotation of the quasar. Different parts of the quasar thus give rise to Lyman-alpha lines with different Doppler shifts.
B) The absorption lines are the result of gravitational lensing by objects between the quasar and Earth.
C) The emitted Lyman-alpha radiation is absorbed by many gas clouds between the quasar and Earth. The lines are receding at various velocities and thus are absorbed at different Doppler-shifted wavelengths.
D) Because the quasar's jets are aimed at various directions, the jet plasma has Doppler shifts that are different from those of the quasar itself. The result is a variety of Lyman-alpha wavelengths in the spectrum received on Earth.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nearest quasar is
A) in the Milky Way Galaxy.
B) in the Local Group of galaxies.
C) about 600 million light-years from the Milky Way.
D) barely visible at the remote edge of the observable universe, 13 billion light-years away.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the jet of an active galaxy is aimed directly at Earth, astronomers might classify the object as a
A) radio galaxy.
B) BL Lacertae object.
C) pulsar.
D) Seyfert galaxy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The radio emission from the jets in a double-radio source is
A) recombination radiation from electrons combining with protons to form neutral hydrogen gas as the gas cools within the jets.
B) 21-cm emission from neutral hydrogen atoms.
C) thermal emission from very hot matter ejected from the accretion disk around the central black hole.
D) synchrotron radiation from relativistic electrons spiraling in magnetic fields.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cygnus A, a strong radio source, is also designated 3C 405. What does the "3C" stand for?
A) "3C" stands for the Third Cambridge Catalog, an important list of radio sources.
B) This radio source is a Type 3C radio source as opposed to a Type 1A or a Type 2B.
C) Cygnus A was discovered through a joint program run by Cambridge, Connecticut, and Calgary universities.
D) A chopper is a device needed to cut off and delineate a signal from a source, and three such choppers are required to isolate an intelligible signal from Cygnus A.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The emission lines in quasar spectra were difficult to identify initially because
A) no one expected violet and ultraviolet spectral lines to be shifted so far toward the red.
B) the observed emission lines were so broad because of internal motions in the quasar that they were difficult to identify.
C) they appeared to be created by elements that did not exist on Earth.
D) they were very faint and could not be measured accurately.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Observationally, the biggest difference between quasars and other active galaxies such as Seyfert and radio galaxies appears to be that
A) quasars appear to be located inside elliptical galaxies, whereas Seyfert and radio galaxies are spirals.
B) Seyfert and radio galaxies do not have the bright, starlike nuclei of quasars.
C) the brightness of Seyfert and radio galaxies does not vary with time.
D) Seyfert and radio galaxies are less powerful energy emitters than quasars.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is an Einstein ring?
A) arc of relativistic particles ejected from a galactic nucleus
B) example of the image formed by a gravitational lens
C) ring of material in some spiral galaxies created by a collision with a smaller galaxy
D) accretion disk around a black hole
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The puzzle about quasar spectra, which was finally solved by Maarten Schmidt, was
A) that the characteristic pattern of hydrogen spectral lines was seen but at much greater blueshifts than is usual from hydrogen in stellar sources.
B) that the brightnesses of hydrogen lines in the familiar spectral sequence were seen to fluctuate wildly over times of seconds from such a bright and therefore presumably large object.
C) that the characteristic pattern of hydrogen spectral lines was seen but at much greater redshifts than is usual from hydrogen in stellar sources.
D) that a familiar spectral line sequence of hydrogen lines was detected from these starlike objects, but they had intensity ratios between lines radically different from those seen in spectra from nearby stars.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 118
Related Exams