A) Factors are expected to correlate.
B) Factors are non-orthogonal.
C) Factors are independent.
D) Kaiser's criterion is met.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In SPSS what criterion is used to extract factors?
A) Varimax
B) Kaiser's
C) Promax
D) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Based on the following output, which item on this questionnaire would most improve the reliability of the questionnaire if it were removed?
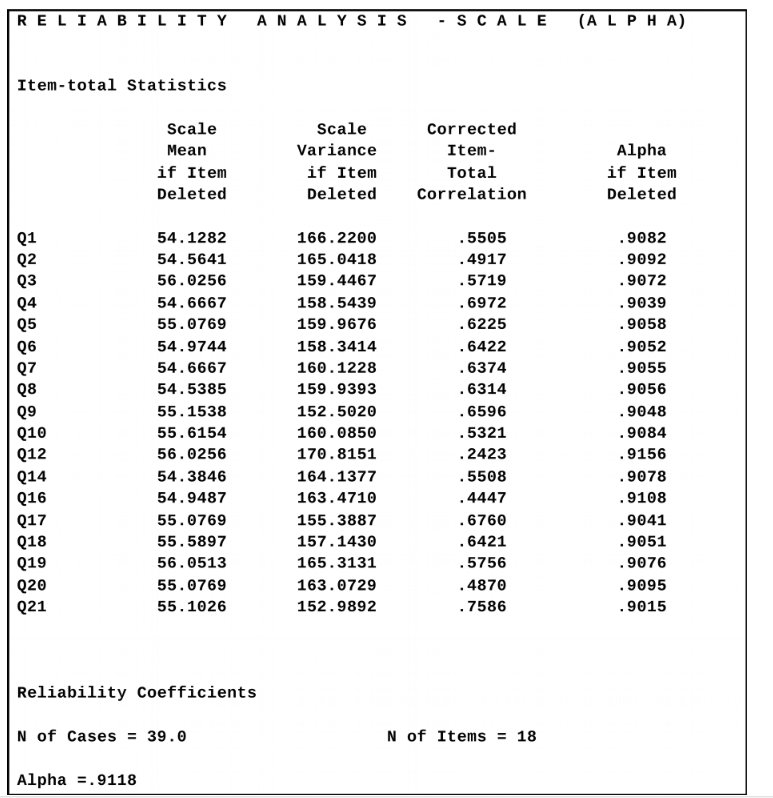
A) Q12.
B) Q16.
C) Q21.
D) Q4.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oblique rotation should be used when
A) Factors are expected to correlate.
B) Factors are orthogonal.
C) Factors are independent.
D) Kaiser's criterion is met.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an example of factor analysis methods?
A) Confirmatory factor analysis
B) Principal axis factoring
C) Hypothesis factoring
D) Image factoring
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does the following output from a factor analysis tell us? 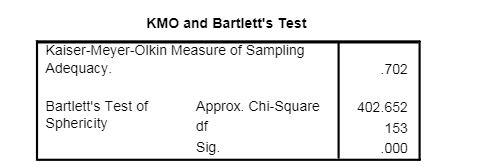
A) The sample size is sufficient, but there is multicollinearity in the data.
B) The sample size is inadequate, and there is multicollinearity in the data.
C) The sample size is adequate, and the correlations in the correlation matrix are significantly bigger than zero.
D) The sample size is adequate, but the correlations in the correlation matrix are not big enough.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an example of factor analysis methods?
A) Confirmatory factor analysis
B) Principal axis factoring
C) Hypothesis factoring
D) Image factoring
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Factor loadings are
A) The weights of each factor.
B) The weights of each variable.
C) Correlations between each variable and each factor.
D) Correlations between all the variables.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cronbach's alpha identified the following values for each of the three factors Factor 1 0.943 Factor 2 0.876 Factor 3 0.877 What process in SPSS provided this information?
A) Extraction
B) Rotation
C) Communalities
D) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an assumption of factor analysis?
A) Large sample size (> 150)
B) Small sample size (< 50)
C) Linearity
D) Factorability of correlation matrix
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Liu and Shen (2008) conducted a study to investigate and confirm the dimensional structure of the Care Giver Strain Questionnaire measured from subjects used in clinical research. A factor analysis generated a range of data and included the following scree plot. On this plot, where does the point of inflexion occur? 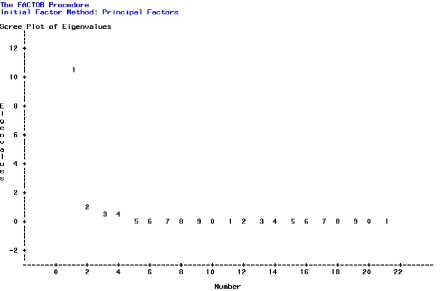 Source: http:/ / www2.sas.com/ proceedings/ forum2008/ 383-2008.pdf
Source: http:/ / www2.sas.com/ proceedings/ forum2008/ 383-2008.pdf
A) At eigenvalue 2 on the Y-axis and 2 on the X-axis
B) Between eigenvalues 2 and 3 on the Y-axis and at 2 on the Y-axis
C) Between eigenvalues 3 and 4 on the Y-axis
D) Between eigenvalues 1 and 2 on the Y-axis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Kaiser's criterion for retaining factors is
A) Retain any factor with an eigenvalue greater than 0.7.
B) Retain any factor with an eigenvalue greater than 1.
C) Retain factors before the point of inflexion on a scree plot.
D) Retain factors with communalities greater than 0.7.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Principal component analysis is
A) Used to summarize data whilst retaining maximum variance.
B) Used to summarize data whilst retaining minimum variance.
C) Derive as few factors as possible.
D) Derive as many solutions as possible.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which procedure would you not use to determine the number of factors to be included in your interpolation of an EFA?
A) Select the number of factors with eigenvalues of 1.00 or higher.
B) Examine a scree plot of eigenvalues plotted against the factor numbers.
C) Disregard any communalities.
D) Analyse increasing numbers of factors; stop when all non-trivial variance is accounted for.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does Cronbach's alpha test for?
A) Significance of factors
B) Functionality
C) Reliability
D) Significance of variables
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these is a form of oblique rotation?
A) Varimax
B) Quartimax
C) Equamax
D) Promax
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rotation means
A) Turning the matrix on one side.
B) Simplifying the loadings.
C) Interpretation of the factors.
D) Interpretation of the graph.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most researchers use exploratory factor analysis to
A) Confirm the data are real.
B) Determine the number of factors/ constructs underlying a set of variables.
C) Reduce the data to a smaller number of variables.
D) Confirm the number of factors.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In SPSS what criterion is used to extract factors?
A) Varimax
B) Kaiser's
C) Promax
D) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rotation means
A) Turning the matrix on one side.
B) Simplifying the loadings.
C) Interpretation of the factors.
D) Interpretation of the graph.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 44
Related Exams