A) 3p
B) 2p
C) 4d
D) 3d
E) 2d
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Pauli exclusion principle is obeyed by:
A) all particles
B) all charged particles
C) all particles with spin quantum numbers of 1/2
D) all particles with spin quantum numbers of 1
E) all particles with mass
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron in a K shell of an atom has the principal quantum number:
A) n = 0
B) n = 1
C) n = 2
D) n = 3
E) n =
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the energy required to ionize a neon atom is i, the energy to excite it is e, and its energy due to thermal agitation at room temperature is t.In increasing order, these three energies are:
A) i, e, t
B) t, i, e
C) e, t, i
D) i, t, e
E) t, e, i
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a lithium atom is made from a helium atom by adding a proton (and neutron) to the nucleus and an electron outside, the electron goes into an n = 2, ℓ=0 state rather than an n = 1, ℓ=0 state.This is an indication that electrons:
A) obey the Pauli exclusion principle
B) obey the minimum energy principle
C) undergo the Zeeman effect
D) are diffracted
E) and protons are interchangeable
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Five electrons are in a two-dimensional square potential energy well with sides of length L.The potential energy is infinite at the sides and zero inside.The single-particle energies are given by where nx and ny are integers.The energy of the ground state of the system is
A) 0
B) 10 (h2/8mL2)
C) 19 (h2/8mL2)
D) 24 (h2/8mL2)
E) 48 (h2/8mL2)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is essential for the laser action to occur between two energy levels of an atom?
A) the lower level is metastable
B) there are more atoms in the upper level than in the lower level
C) there are more atoms in the lower level than in the upper level
D) the lower level is the ground state
E) the lasing material is a gas
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A magnetic dipole is placed between the poles of a magnet as shown.The direction of the associated force exerted on the dipole is: 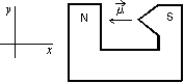
A) positive x
B) positive y
C) negative x
D) negative y
E) into or out of the page
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron in an atom is in a state with ℓ=5.The minimum angle between and the z axis is:
A) 0
B) 18.0
C) 24.1
D) 33.6
E) 36.7
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following (n, ℓ, mℓ, ms) combinations is impossible for an electron in an atom?
A) 3, 1, 1, -1/2
B) 6, 2, 0, 1/2
C) 3, 2, -2, -1/2
D) 3, 1, -2, 1/2
E) 1, 0, 0, -1/2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The number of values of the orbital quantum number ℓ associated with the principal quantum number n = 3 is:
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 7
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Photons in a laser beam are produced by:
A) transitions from a metastable state
B) transitions from a state that decays rapidly
C) splitting of other photons
D) pumping
E) reflection from mirrors
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a Moseley graph:
A) the x-ray frequency is plotted as a function of atomic number
B) the square of the x-ray frequency is plotted as a function of atomic number
C) the square root of the x-ray frequency is plotted as a function of atomic number
D) the x-ray frequency is plotted as a function of the square root of atomic number
E) the square root of the x-ray frequency is plotted as a function of atomic mass
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ionization energy of an atom in its ground state is:
A) the energy required to remove the least energetic electron
B) the energy required to remove the most energetic electron
C) the energy difference between the most energetic electron and the least energetic electron
D) the same as the energy of a K photon
E) the same as the excitation energy of the most energetic electron
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The purpose of the mirrors at the ends of a helium-neon laser is:
A) to assure that no laser light leaks out
B) to increase the number of stimulated emissions
C) to absorb some of the photons
D) to keep the light used for pumping inside the laser
E) to double the effective length of the laser
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a laser:
A) excited atoms are stimulated to emit photons by radiation external to the laser
B) the transitions for laser emission are directly to the ground state
C) the states which give rise to laser emission are usually very unstable states that decay rapidly
D) the state in which an atom is initially excited is never between two states that are involved in the stimulated emission
E) a minimum of two energy levels are required.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The group of atoms at the ends of periods of the periodic table is called:
A) alkali metal atoms
B) rare earth atoms
C) transition metal atoms
D) alkaline atoms
E) noble gas atoms
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The magnetic quantum number mℓ is most closely associated with what property of the electron in an atom?
A) Magnitude of the orbital angular momentum
B) Energy
C) z component of the spin angular momentum
D) z component of the orbital angular momentum
E) Radius of the orbit
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is essential for laser action to occur between two energy levels of an atom?
A) the lower level is metastable
B) the upper level is metastable
C) the lower level is the ground state
D) the are more atoms in the lower level than in the upper level
E) the lasing material is a gas
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The magnitude of the orbital magnetic dipole moment of an atom is ( B is the Bohr magneton, and ℓ is a positive integer) :
A) " B"
B) " B ℓ"
C) "![]() "
"
D) " B (2ℓ+1) "
E) " B ℓ2"
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 76
Related Exams