A) 1.0 m/s, 30° below the x axis
B) 2.3 m/s, 50° below the x axis
C) 2.8 m/s, 60° below the x axis
D) 3.0 m/s, 45° below the x axis
E) not enough information
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 640-N acrobat falls 5.0 m from rest into a net.The net tosses him back up with the same speed he had just before he hit the net.The average upward force exerted on him by the net during this collision is:
A) 32 N
B) 64 N
C) 320 N
D) 640 N
E) impossible to determine from given data
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The law of conservation of momentum applies to a system of colliding objects only if:
A) there is no change in kinetic energy of the system
B) the coefficient of restitution is one
C) the coefficient of restitution is zero
D) the net external impulse is zero
E) the collisions are all elastic
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 64-kg woman stands on frictionless level ice with a 0.10-kg stone at her feet.She kicks the stone with her foot so that she acquires a velocity of 0.0017 m/s in the forward direction.The velocity acquired by the stone is:
A) 1.1 m/s forward
B) 1.1 m/s backward
C) 0.0017 m/s forward
D) 0.0017 m/s backward
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A block moves at 5 m/s in the positive x direction and hits an identical block, initially at rest.A small amount of gunpowder had been placed on one of the blocks.The explosion does not harm the blocks but it doubles their total kinetic energy.After the explosion the blocks move along the x axis and the incident block has a speed of:
A) 1.8 m/s
B) 3.2 m/s
C) 5.0 m/s
D) 6.8 m/s
E) 7.1 m/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rocket exhausts fuel with a velocity of 1500 m/s, relative to the rocket.It starts from rest in outer space with fuel comprising 80 per cent of the total mass.When all the fuel has been exhausted its speed is:
A) 3600 m/s
B) 2400 m/s
C) 1200 m/s
D) 880 m/s
E) 400 m/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2.0-kg block is attached to one end of a spring with a spring constant of 100 N/m and a 4.0-kg block is attached to the other end.The blocks are placed on a horizontal frictionless surface and set into motion.At one instant the 2.0-kg block is observed to be traveling to the right with a speed of 0.50 m/s and the 4.0-kg block is observed to be traveling to the left with a speed of 0.30 m/s.Since the only forces on the blocks are the force of gravity, the normal force of the surface, and the force of the spring, we conclude that:
A) the spring is compressed at the time of the observation
B) the spring is not compressed at the time of observation
C) the motion was started with the masses at rest
D) the motion was started with at least one of masses moving
E) the motion was started by compressing the spring
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 1000-kg space probe is motionless in space.To start moving, its main engine is fired for 5 s during which time it ejects exhaust gases at 5000 m/s.At the end of this process it is moving at 20 m/s.The approximate mass of the ejected gas is: 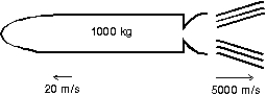
A) 0.8 kg
B) 4 kg
C) 5 kg
D) 20 kg
E) 25 kg
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two bodies of unequal mass, placed at rest on a frictionless surface, are acted on by equal horizontal forces for equal times.Just after these forces are removed, the body of greater mass will have:
A) greater speed than the other body
B) greater acceleration than the other body
C) smaller momentum than the other body
D) greater momentum than the other body
E) the same momentum as the other body
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The acceleration of the center of mass of a system of particles:
A) depends on all the forces on all the particles
B) depends on all the velocities of all the particles
C) depends only on the forces external to the system of particles
D) depends only on the forces internal to the system of particles
E) depends only on the force of gravity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The velocity of the center of mass of a system of particles changes as v = 4.5 t + 2.4 t2 + 1.1 t3, where v is in meters per second.If the system starts from rest at t = 0, what is its acceleration at t = 3.0 s?
A) 7.1 m/s2
B) 14 m/s2
C) 20 m/s2
D) 49 m/s2
E) 65 m/s2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The center of mass of Earth's atmosphere is:
A) a little less than halfway between the Earth's surface and the outer boundary of the atmosphere
B) near the surface of the Earth
C) near the outer boundary of the atmosphere
D) near the center of the Earth
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2-kg cart, traveling on a horizontal air track with a speed of 3 m/s, collides with a stationary 4-kg cart.The carts stick together.The impulse exerted by one cart on the other has a magnitude of:
A) 0 N∙s
B) 4 N∙s
C) 6 N∙s
D) 9 N∙s
E) 12 N∙s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whenever an object strikes a stationary object of equal mass:
A) the two objects cannot stick together
B) the collision must be elastic
C) the first object must stop
D) momentum is not necessarily conserved
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Object A strikes the stationary object B head-on in an elastic collision.The mass of A is fixed, you may choose the mass of B appropriately.Then:
A) for B to have the greatest recoil speed, choose mB = mA
B) for B to have the greatest recoil momentum, choose mB << mA
C) for B to have the greatest recoil kinetic energy, choose mB >> mA
D) for B to have the least recoil speed, choose mB = mA
E) for B to have the greatest recoil kinetic energy, choose mB = mA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When you step on the accelerator to increase the speed of your car, the force that accelerates the car is:
A) the force of your foot on the accelerator
B) the force of friction of the road on the tires
C) the force of the engine on the drive shaft
D) the normal force of the road on the tires
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 1.0 kg-ball moving at 2.0 m/s perpendicular to a wall rebounds from the wall at 1.5 m/s.The change in the momentum of the ball is:
A) zero
B) 0.5 N∙s away from wall
C) 0.5 N∙s toward wall
D) 3.5 N∙s away from wall
E) 3.5 N∙s toward wall
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements is true?
A) the center of mass of an object must lie within the object
B) all the mass of an object is actually concentrated at its center of mass
C) the center of mass of an object cannot move if there is zero net force on the object
D) the center of mass of a cylinder must lie on its axis
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The position of the center of mass of a system of particles moves as x = 4.5 t + 2.4 t2 + 1.1 t3, where x is in meters.If the system starts from rest at t = 0, what is its velocity at t = 3.0 s?
A) 8.0 m/s
B) 21 m/s
C) 49 m/s
D) 64 m/s
E) 65 m/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 10-kg block of ice is at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface.A 1.0-N force is applied in an easterly direction for 1.0 s.During this time interval, the block:
A) acquires a speed of 1 m/s
B) moves 10 cm
C) acquires a momentum of 1.0 kg. m/s
D) acquires a kinetic energy of 0.1 J
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 98
Related Exams