A) polysynaptic reflexes involving contraction of the right hamstring and left quadriceps.
B) polysynaptic reflexes involving contraction of the right quadriceps and left hamstrings.
C) a monosynaptic reflex causing contraction of the right hamstring and a polysynaptic reflex causing contraction of the left hamstring.
D) a monosynaptic reflex causing contraction of the right quadriceps and a polysynaptic reflex causing contraction of the the left hamstring.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In general, nerves from the posterior division of the brachial plexus tend to innervate muscles that extend the parts of the upper limb.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The innermost of the meninges is the pia mater.
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A specific segment of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve is a ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Anatomy of the spinal cord & spinal nerves. 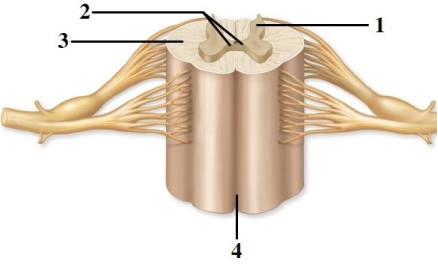 -This figure shows a cross section of the spinal cord. What structure does number 1 indicate?
-This figure shows a cross section of the spinal cord. What structure does number 1 indicate?
A) Lateral horn
B) Anterior horn
C) Gray commissure
D) Posterior horn
E) Posterior funiculus
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In adults, the spinal cord is not the same length as the vertebral canal, and most of the lumbar part of the spinal cord is within
A) the coccyx.
B) the sacrum.
C) the cervical vertebrae.
D) the thoracic vertebrae.
E) the cauda equina.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Anatomy of the spinal cord & spinal nerves. 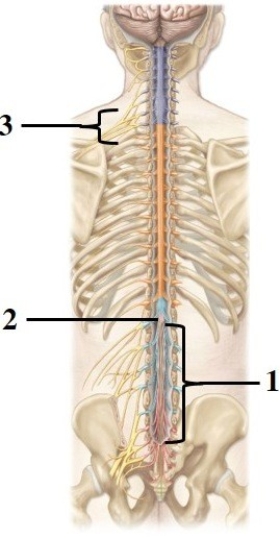 -This figure shows the spinal cord and spinal nerves. What structure does number 1 indicate?
-This figure shows the spinal cord and spinal nerves. What structure does number 1 indicate?
A) Dura mater
B) Filum terminale
C) Cauda equina
D) Conus medullaris
E) Posterior rootlets
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The spinal cord part with the largest diameter is the ________ part.
A) thoracic
B) cervical
C) lumbar
D) sacral
E) coccygeal
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This figure shows a cross section of a vertebra and the spinal cord. What structure does number 1 indicate? 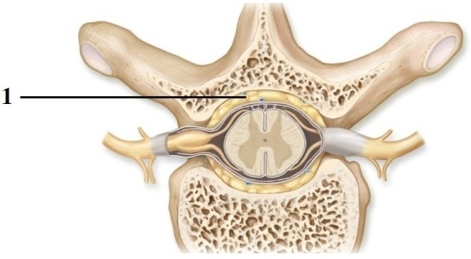
A) Epidural space
B) Pia mater
C) Subarachnoid space
D) Central canal
E) Dura mater
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Anatomy of the spinal cord & spinal nerves.  -This figure shows the spinal cord and spinal nerves. What structure does number 2 indicate?
-This figure shows the spinal cord and spinal nerves. What structure does number 2 indicate?
A) Dura mater
B) Filum terminale
C) Cauda equina
D) Conus medullaris
E) Posterior rootlets
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Golgi tendon reflex
A) helps to overcome pain.
B) aids in sending sensory information to the muscles.
C) prevents skeletal muscles from tensing excessively.
D) prevents muscles from contracting.
E) helps to gain balance through a complex series of muscular contractions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nerve responsible for innervation (movement) of the quadriceps femoris muscle is the ________ nerve.
A) femoral
B) sciatic
C) obturator
D) genitofemoral
E) tibial
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Axons of the corticobulbar tracts
A) descend in the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord and synapse with anterior horn motor neurons.
B) descend in the anterior funiculus of the spinal cord and synapse with lateral horn motor neurons.
C) do not pass through the spinal cord, as they synapse with lower motor neurons in brainstem cranial nuclei.
D) do not pass through the spinal cord, as they synapse with cerebellar Purkinje cells.
E) connect the supplementary motor cortex with the primary motor cortex.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Following an injury to his arm, a patient complains that he has no sensations from his "pinky." You suspect that he has damaged the
A) median nerve.
B) radial nerve.
C) musculocutaneous nerve.
D) ulnar nerve.
E) axillary nerve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The simple knee-jerk reflex is an example of a(n) ________ reflex.
A) ipsilateral
B) contralateral
C) monosynaptic
D) crossed-extensor
E) multisynaptic
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A reflex arc in which both the receptor and the effector organs of the reflex are on the same side of the spinal cord is
A) monosynaptic.
B) polysynaptic.
C) ipsilateral.
D) contralateral.
E) None of the choices is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The posterior ramus of a typical spinal nerve innervates the
A) deep muscles of the back and the skin of the back.
B) major thoracic and abdominal organs.
C) abdominal wall.
D) anterior and lateral trunk and the limbs.
E) special senses.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Anatomy of the spinal cord & spinal nerves.  -This figure shows a cross section of the spinal cord. What structure does number 4 indicate?
-This figure shows a cross section of the spinal cord. What structure does number 4 indicate?
A) Posterior median sulcus
B) White commissure
C) Anterior funiculus
D) Lateral funiculus
E) Anterior median fissure
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For many reflexes, including the stretch reflex, the excitation of a muscle leads to
A) excitation of all motorneurons that are contralateral.
B) inhibition of motor neurons of its antagonist.
C) inhibition of motor neurons of its synergist.
D) excitation of motor neurons of the antagonist.
E) inhibition of sensory neurons that initiate the reflex.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The spinal cord relays both sensory and motor information between the CNS and rest of the body.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 143
Related Exams