A) Unmyelinated axons rest in invaginations of Schwann cells or oligodendrocytes.
B) Myelination will not influence the speed of conduction of action potentials.
C) The myelin sheath inhibits the flow of electrical charges at nodes.
D) The myelin sheath is a protein wrapping.
E) The myelin sheath does not electrically insulate the axons from one another.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The peripheral nervous system includes the ________.
A) brain
B) spinal cord
C) cranial nerves
D) blood-brain barrier
E) cerebellum
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose both excitatory and inhibitory neurons synapse with a single postsynaptic neuron. What determines if an action potential is initiated in the postsynaptic neuron?
A) The kind of neuron involved
B) The size of the neuron involved
C) Whether the neuron is myelinated or non-myelinated
D) The number of EPSPs in relation to the number of IPSPs
E) This situation is not possible in humans.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
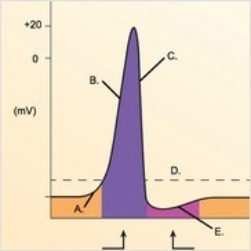 -The figure illustrates changes in the membrane potential during an action potential. What does "D" represent?
A) Repolarization
B) Depolarization
C) Local potential
D) Threshold
E) Afterpotential
-The figure illustrates changes in the membrane potential during an action potential. What does "D" represent?
A) Repolarization
B) Depolarization
C) Local potential
D) Threshold
E) Afterpotential
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
 -The figure is a process figure of the chemical synapse. What does "D" represent?
A) Postsynaptic membrane
B) Synaptic cleft
C) Synaptic vesicle
D) Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel
E) Presynaptic terminal
-The figure is a process figure of the chemical synapse. What does "D" represent?
A) Postsynaptic membrane
B) Synaptic cleft
C) Synaptic vesicle
D) Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel
E) Presynaptic terminal
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
 -The figure illustrates changes in the membrane potential during an action potential. What does "A" represent?
A) Repolarization
B) Depolarization
C) Local potential
D) Threshold
E) Afterpotential
-The figure illustrates changes in the membrane potential during an action potential. What does "A" represent?
A) Repolarization
B) Depolarization
C) Local potential
D) Threshold
E) Afterpotential
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neurotransmitters are released from the ________.
A) epineurium
B) synaptic cleft
C) presynaptic terminal
D) postsynaptic membrane
E) Ca2+ channels
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Cerebrospinal fluid is produced by ________ cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is responsible for problem-solving skills?
A) Central nervous system
B) Peripheral nervous system
C) Somatic nervous system
D) Autonomic nervous system
E) None of the choices are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Any two EPSPs will override one IPSP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A series of local potentials causes the membrane potential to move to -80 mV. Predict the result.
A) Threshold is reached.
B) Depolarization occurs.
C) The neuron is hyperpolarized.
D) Information of frequency is needed to predict the result.
E) The neuron releases neurotransmitter in response.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dendrites
A) are the input part of the neuron.
B) conduct action potentials away from the cell body.
C) are generally long and unbranched.
D) form synapses with the microglia.
E) contain the trigger zone.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A neuron within the central nervous system that carries action potentials from one neuron to another is called a/an ________.
A) motor neuron
B) sensory neuron
C) afferent neuron
D) efferent neuron
E) interneuron
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A local potential
A) does not occur until threshold.
B) transmits information from one cell to another.
C) might be a depolarization event but cannot be a hyperpolarization event.
D) increases or decreases in direct proportion to the stimulus strength.
E) does not alter resting membrane potential.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Continuous conduction of action potentials means that
A) once an action potential is created, it moves in both directions along the axon.
B) the whole axon depolarizes at the same time.
C) an action potential in one site generates local currents causing depolarization to threshold at the adjacent site.
D) an action potential is conducted from one node of Ranvier to the next node.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange the events of synaptic transmission in correct sequence. (1) Na+ diffuses into the cell and cause a local potential (2) Neurotransmitter binds with receptor on postsynaptic cell (3) Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft (4) Membrane permeability to Na+ on postsynaptic cell increases (5) Action potential causes release of neurotransmitter
A) 5, 2, 3, 4, 1
B) 5, 2, 3, 1, 4
C) 5, 3, 4, 1, 2
D) 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
E) 5, 3, 2, 4, 1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the resting membrane potential, increasing the Na+ concentration in the ECF results in
A) hyperpolarization.
B) depolarization.
C) hypopolarization.
D) little change in membrane potential.
E) There is not enough information to determine the results.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During depolarization of the plasma membrane,
A) Na+ moves rapidly into the cell.
B) K+ moves rapidly out of the cell.
C) membrane permeability to Na+ decreases.
D) the outside of the cell becomes positively charged relative to the inside.
E) Na+ moves rapidly out of the cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Gray matter consists of bundles of myelinated axons.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements accurately describe events that occur as a result of a local potential reaching threshold?
A) Activation gates of Na+ channels begin to close.
B) Inactivation gates of Na+ channels begin to open.
C) A positive feedback cycle develops in which depolarization causes activation gates of Na+ channels to open.
D) K+ channels begin to close.
E) Both "Inactivation gates of Na+ channels begin to open" and "A positive feedback cycle develops in which depolarization causes activation gates of Na+ channels to open" are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 192
Related Exams