A) Banks have invested heavily in credit card technology.
B) Japan has a low crime rate.
C) Interest rates in Japan have been below 1% since the 1990s.
D) Japan's retail sector is dominated by mom-and-pop stores that don't accept credit cards.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Economic Adjustments 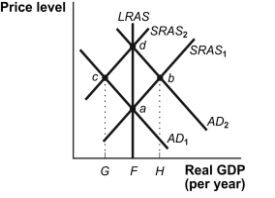 -(Figure: Economic Adjustments) Refer to Figure: Economic Adjustments. Assume that the economy is at point c. The effect of an increase in the money supply is represented by a shift of the _____ curve to _____.
-(Figure: Economic Adjustments) Refer to Figure: Economic Adjustments. Assume that the economy is at point c. The effect of an increase in the money supply is represented by a shift of the _____ curve to _____.
A) SRAS1; SRAS2
B) SRAS2; SRAS1
C) AD1; AD2
D) AD2; AD1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Quantitative easing occurs when instead of purchasing only short-term government debt, the Fed buys long-term government debt as well.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
One advantage of inflation targeting over the Taylor rule is that the central bank's policy can be evaluated by seeing how close to the target actual inflation rates are.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the Fed uses quantitative easing, it is:
A) buying three-month Treasury bills.
B) selling three-month Treasury bills.
C) buying longer-term government debt.
D) selling longer-term government debt.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When long-term rates are lower than short-term rates, the market is signaling that it expects short-term rates to fall.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the liquidity preference model:
A) an increase in the money supply lowers the equilibrium rate of interest.
B) a decrease in the money supply lowers the equilibrium rate of interest.
C) the money supply curve is a horizontal line.
D) the demand for money curve is a vertical line.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Short-Run Determination of the Interest Rate 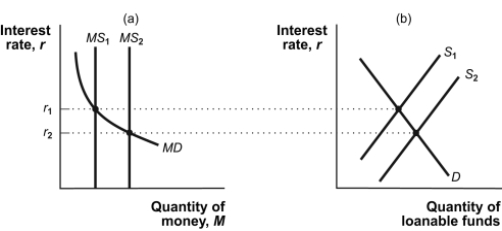 -(Figure: Short-Run Determination of the Interest Rate) Refer to Figure: Short-Run Determination of the Interest Rate. If the money supply is at MS2 and the central bank sells Treasury bills, then in the short run the interest rate will:
-(Figure: Short-Run Determination of the Interest Rate) Refer to Figure: Short-Run Determination of the Interest Rate. If the money supply is at MS2 and the central bank sells Treasury bills, then in the short run the interest rate will:
A) decrease below r2.
B) remain at r2.
C) increase to r1.
D) fluctuate randomly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the quantity of money demanded is $100 billion and the quantity of money supplied is $200 billion, then the interest rate will:
A) fall.
B) rise.
C) remain unchanged.
D) be in equilibrium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
U.S. banks did not offer interest on checking accounts until the beginning of the 1980s. Then banking regulations changed, allowing banks to pay interest on checking account funds. As a result, the _____ money _____ and shifted the money demand curve to the _____.
A) supply of; fell; left
B) demand for; fell; left
C) demand for; rose; right
D) supply of; rose; right
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Federal Reserve sets the federal funds rate on the basis of inflation and the output gap, then the Federal Reserve is following:
A) inflation targeting.
B) the Taylor rule.
C) money illusion.
D) the quantity theory.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The main objective of contractionary monetary policy is to:
A) decrease aggregate demand.
B) close a recessionary gap.
C) increase investment.
D) raise the level of potential output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Changes in the Money Supply 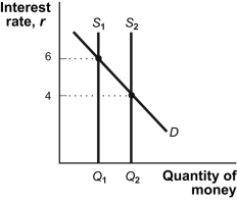 -(Figure: Changes in the Money Supply) Refer to Figure: Changes in the Money Supply. If the supply of money shifts from S1 to S2, the Federal Reserve must have _____ Treasury bills in the open market.
-(Figure: Changes in the Money Supply) Refer to Figure: Changes in the Money Supply. If the supply of money shifts from S1 to S2, the Federal Reserve must have _____ Treasury bills in the open market.
A) sold
B) bought
C) issued new
D) borrowed
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the economy is at potential output and the Fed increases the money supply, in the long run the price level will likely:
A) fluctuate randomly.
B) remain the same.
C) decrease.
D) increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetary policy that lowers the interest rate is called _____ because it _____.
A) contractionary; aims to head off inflation
B) expansionary; increases short-run aggregate supply
C) contractionary; reduces saving and increases consumption
D) expansionary; increases aggregate demand
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the Federal Reserve buys Treasury bills, this leads to a(n) :
A) decrease in the money supply.
B) increase in the money supply.
C) increase in short-term interest rates.
D) increase in the Federal Reserve funds rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the money supply causes _____ in output in the short run and _____ in output in the long run.
A) an increase; no change
B) an increase; an increase
C) no change; an increase
D) no change; no change
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is FALSE?
A) The Taylor rule sets the federal funds rate on the basis of both inflation rate and output gap, whereas inflation targeting is based on a desired inflation rate.
B) The Taylor rule sets the federal funds rate on the basis of past inflation rates, whereas inflation targeting is based on a forecast of the inflation rate.
C) The Taylor rule can be more flexible, whereas inflation targeting provides more transparency and accountability.
D) The Taylor rule sets the federal funds rate on the basis of only past inflation rates, whereas inflation targeting is based on a target interest rate and business cycles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Economic Adjustments  -(Figure: Economic Adjustments) Refer to Figure: Economic Adjustments. Assume that the economy is at point b. The effect of a decrease in the money supply is represented by a shift of the _____ curve to _____.
-(Figure: Economic Adjustments) Refer to Figure: Economic Adjustments. Assume that the economy is at point b. The effect of a decrease in the money supply is represented by a shift of the _____ curve to _____.
A) SRAS1; SRAS2
B) SRAS2; SRAS1
C) AD1; AD2
D) AD2; AD1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If during 2016 the interest rate on one-month Treasury bills was 2.5% and during 2017 it was 2%, the opportunity cost of holding money, assuming the inflation rate remained constant,:
A) decreased.
B) became negative.
C) increased.
D) did not change.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 316
Related Exams