A) 0%
B) 2%
C) 38%
D) 100%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In glycolysis, for each molecule of glucose oxidized to pyruvate, ________.
A) two molecules of ATP are used, and two molecules of ATP are produced
B) two molecules of ATP are used, and four molecules of ATP are produced
C) four molecules of ATP are used, and two molecules of ATP are produced
D) two molecules of ATP are used, and six molecules of ATP are produced
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the summary statements below describes the results of the following reaction? C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂ → 6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O + Energy
A) C₆H₁₂O₆ is oxidized and O₂ is reduced.
B) O₂ is oxidized and H₂O is reduced.
C) CO₂ is reduced and O₂ is oxidized.
D) O₂ is reduced and CO₂ is oxidized.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Approximately how many molecules of ATP are produced from the complete oxidation of one molecule of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) in aerobic cellular respiration?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 18-24
D) 30-32
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a molecule of NAD⁺ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) gains a hydrogen atom (not a proton) , the molecule becomes ________.
A) dehydrogenated
B) oxidized
C) reduced
D) redoxed
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes is driven by chemiosmosis?
A) substrate-level phosphorylation
B) oxidative phosphorylation
C) ATP hydrolysis
D) reduction of NAD⁺ to NADH
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is directly involved in which of the following processes or events?
A) glycolysis
B) accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
C) the citric acid cycle
D) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the absence of oxygen, yeast cells can obtain energy by fermentation, which results in the production of which of the following sets of molecules?
A) ATP, CO₂, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol)
B) ATP, CO₂, and lactate
C) ATP, NADH, and ethanol
D) ATP, CO₂, and acetyl CoA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In mitochondria, exergonic redox reactions
A) are the source of energy driving prokaryotic ATP synthesis.
B) provide the energy that establishes the proton gradient.
C) reduce carbon atoms to carbon dioxide.
D) are coupled via phosphorylated intermediates to endergonic processes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Starting with one molecule of glucose, glycolysis results in the net production of which of the following sets of energy-containing products?
A) 2 NAD⁺, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
B) 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
C) 4 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 4 ATP
D) 6 CO₂, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person on a strict diet and exercise regimen lost 7 kg (about 15 pounds) of body fat in just two weeks. What is the most likely way that the lost fat left the body?
A) It was released as CO₂ and H₂O.
B) It was converted to heat and then released.
C) It was converted to ATP, which weighs much less than fat.
D) It was eliminated from the body as feces.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below.
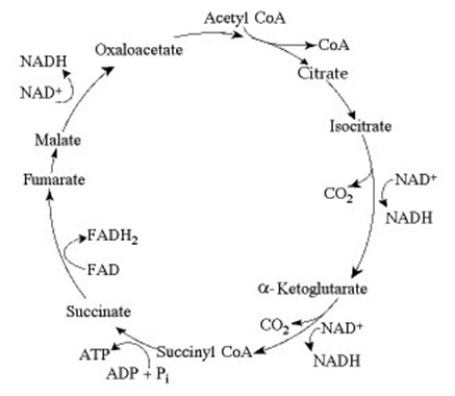 The citric acid cycle.
If pyruvate oxidation is blocked, what will happen to the levels of oxaloacetate and citric acid in the citric acid cycle shown in the accompanying figure?
The citric acid cycle.
If pyruvate oxidation is blocked, what will happen to the levels of oxaloacetate and citric acid in the citric acid cycle shown in the accompanying figure?
A) Oxaloacetate will decrease and citric acid will accumulate.
B) Oxaloacetate will accumulate and citric acid will decrease.
C) Both oxaloacetate and citric acid will decrease.
D) Both oxaloacetate and citric acid will accumulate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most CO₂ from catabolism is released during
A) glycolysis.
B) the citric acid cycle.
C) lactate fermentation.
D) electron transport.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which electron carrier(s) function in the citric acid cycle?
A) NAD⁺ only
B) NADH and FADH₂
C) the electron transport chain
D) ADP and ATP
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the presence of oxygen, the three-carbon compound pyruvate can be catabolized in the citric acid cycle. First, however, the pyruvate (1) loses a carbon, which is given off as a molecule of CO₂, (2) is oxidized to form a two-carbon compound called acetate, and (3) is bonded to coenzyme A. Which of the following sets of products result from these reactions?
A) acetyl CoA, O₂, and ATP
B) acetyl CoA, FADH₂, and CO₂
C) acetyl CoA, NADH, and CO₂
D) acetyl CoA, NAD⁺, ATP, and CO₂
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If glucose is the sole energy source, what fraction of the carbon dioxide exhaled by animals is generated only by the reactions involved in oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA?
A) 1/6
B) 1/3
C) 2/3
D) all of it
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes the primary role played by oxygen in cellular respiration?
A) It yields energy in the form of ATP as it is passed down the electron transport chain.
B) It oxidizes glucose to form two molecules of pyruvate.
C) It serves as an acceptor for carbon, forming CO₂ in the citric acid cycle.
D) It serves as the final acceptor for electrons from the electron transport chain.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction? Pyruvate + NADH + H⁻ Lactate + NAD⁻
A) oxygen
B) NADH
C) lactate
D) pyruvate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes generates a proton-motive force in mitochondria?
A) the flow of protons through ATP synthase down their concentration gradient
B) the reduction of NAD⁺ by the first electron carrier in the electron transport chain
C) lowering of pH in the mitochondrial matrix
D) pumping of hydrogen ions from the mitochondrial matrix across the inner membrane and into the intermembrane space
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that functions in aerobic oxidative phosphorylation is
A) oxygen.
B) water.
C) NAD⁺.
D) pyruvate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 68
Related Exams