A) 4.69 mol, 6.18 atm
B) 4.69 mol, 27.2 atm
C) 2.34 mol, 13.6 atm
D) 2.34 mol, 3.09 atm
E) 9.38 mol, 27.2 atm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given a fixed amount of gas held at constant pressure, calculate the temperature to which the gas would have to be changed if a 3.50 L sample at 23.0°C were to have a final volume of 1.50 L.
A) 2.0°C
B) 127°C
C) −146°C
D) 9.8°C
E) 43.2°C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the number of moles in 55 g of N2, and the volume that it would occupy at STP.
A) 2.0 mol, 45 L
B) 2.0 mol, 0.089 L
C) 1.5 x 103 mol, 67 L
D) 1.5 x 103 mol, 3.4 x 104 L
E) 3.9 mol, 88 L
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the volume of a sample of gas is held constant, while the temperature is decreased, the pressure will
A) become higher because of fewer collisions with the container.
B) become lower because of fewer collisions with the container.
C) become lower because of more collisions with the container.
D) become higher because of more collisions with the container.
E) stay the same because temperature has no effect on pressure.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Convert 1.28 atm to mm Hg.
A) 1.28 x 103 mm Hg
B) 1.30 x 105 mm Hg
C) 1.68 x 10-3 mm Hg
D) 972.8 mm Hg
E) 1.03 x 10-3 mm Hg
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sample of gas initially occupies 2.50 L at a pressure of 905 torr at 22.0°C. What will the temperature be if the pressure is changed to 2.00 atm, and the volume is changed to 1.50 L?
A) 22.2°C
B) 554°C
C) 1.09°C
D) 271°C
E) 24.5°C
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which characteristic does not describe an ideal gas?
A) negligible volume occupied by ideal gas molecules
B) no attractive forces between ideal gas molecules
C) obeys the equation PV = nRT
D) PV/RT = a constant
E) strong repulsions between molecules
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sample of gas initially occupies 2.50 L at a pressure of 0.900 atm at 22.0°C. What will the pressure be if the temperature is changed to 56.5°C, and the volume is changed to 1.50 L?
A) 0.584 atm
B) 3.85 atm
C) 1.68 atm
D) 1.34 atm
E) 3.77 atm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A liter container of CO2 and a liter container of H2 are both at 25°C and 1 atm pressure. Which of the following statements about these gas samples is true?
A) The CO2 and H2 molecules have the same average velocity.
B) There are more H2 molecules than CO2 molecules.
C) The average kinetic energy of the CO2 molecules is greater than that of the H2 molecules.
D) The CO2 molecules on average are moving more slowly than the H2 molecules.
E) The masses of the two gas samples are equal.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under which conditions would the density of helium be the smallest?
A) high pressure and high temperature
B) low pressure and high temperature
C) high pressure and low temperature
D) low pressure and low temperature
E) The density of helium is independent of pressure and temperature.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given a fixed amount of gas held at constant pressure, calculate the temperature to which the gas would have to be changed if a 1.75 L sample at 23.0°C were to have a final volume of 3.50 L.
A) 46.0°C
B) 89.5°C
C) 169°C
D) 319°C
E) 592°C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the density of NO2 in g/L at STP.
A) 22.41 g/L
B) 2.053 g/L
C) 1.031 x 103 g/L
D) 0.04462 g/L
E) 0.4871 g/L
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "Before" image in the figure shows the initial condition of a gas at a certain temperature in a container with a movable piston. Which of the images represents the condition of the gas when the temperature of the gas is increased, and the external pressure is held constant? 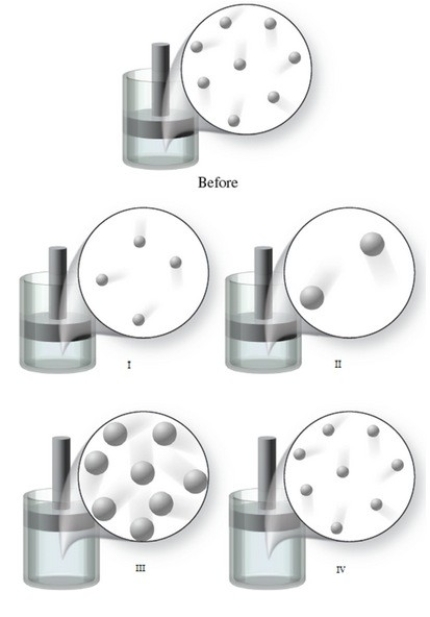
A) image I
B) image II
C) image III
D) image IV
E) None of the images
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A gas in a closed container with constant volume is heated from room temperature to 100°C. According to the kinetic molecular theory, the
A) average velocity of the molecules will increase.
B) gas will increase in weight.
C) individual molecules of the gas will increase their size.
D) average distance between molecules will increase.
E) pressure on the sides of the container will decrease.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sample of gas initially occupies 5.50 L at a pressure of 0.750 atm at 13.0°C. What will the pressure be if the temperature is changed to 22.5°C, and the volume is changed to 1.50 L?
A) 6.39 atm
B) 11.4 atm
C) 0.211 atm
D) 2.84 atm
E) 1.59 atm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements related to kinetic-molecular theory of gases is correct for an ideal gas?
A) Gases are composed of small particles with a small amount of space between them.
B) Gas particles move in a zigzag pattern until they collide with something.
C) When gas particles collide, they lose some of their kinetic energy, and will slow down over time.
D) In a mixture of gases, attractive forces between particles cause the measured pressure to be lower than that expected for a pure gas.
E) The pressure of a gas arises from the sum of the collisions of the particles with the walls of the container.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to kinetic-molecular theory, molecules of different gases at the same temperature always have the same
A) molar mass.
B) pressure.
C) average kinetic energy.
D) volume.
E) number of moles.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A weather balloon filled with helium gas gets larger as it ascends to high altitudes. The expansion of the balloon is primarily due to
A) a decrease in the average kinetic energy of the helium atoms inside the balloon.
B) an increase in the average kinetic energy of the helium atoms inside the balloon.
C) a decrease in the average kinetic energy of the air molecules outside the balloon.
D) an increase in the rate of collision of the helium atoms against the inside walls of the balloon.
E) a decrease in the rate of collision of the air molecules on the outside walls of the balloon.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Propane burns in air according to the equation: C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) → 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) What volume of O2 would be required if 8.00 L of propane burns, assuming that all of the gases are under the same conditions?
A) 8.00 L
B) 40.0 L
C) 20.0 L
D) 15.0 L
E) 1.60 L
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
If a steel tank is filled with acetylene to a pressure of 7.50 atm in the morning, when the temperature is 18.0oC, what will the pressure (in atm)be in the afternoon, when the temperature rises to 33.5oC?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 121
Related Exams