A) Glycolysis is widespread and is found in the domains Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
B) Glycolysis neither uses nor needs O₂.
C) Glycolysis is found in all eukaryotic cells.
D) The enzymes of glycolysis are found in the cytosol rather than in a membrane-enclosed organelle.
E) Ancient prokaryotic cells, the most primitive of cells, made extensive use of glycolysis long before oxygen was present in Earth's atmosphere.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Starting with one molecule of glucose, the energy-containing products of glycolysis are
A) 2 NAD⁺, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP.
B) 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP.
C) 2 FADH₂, 2 pyruvate, and 4 ATP.
D) 6 CO₂, 2 ATP, and 2 pyruvate.
E) 6 CO₂, 30 ATP, and 2 pyruvate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During aerobic respiration, which of the following directly donates electrons to the electron transport chain at the lowest energy level?
A) NAD⁺
B) NADH
C) ATP
D) ADP + ![]() ᵢ
ᵢ
E) FADH₂
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
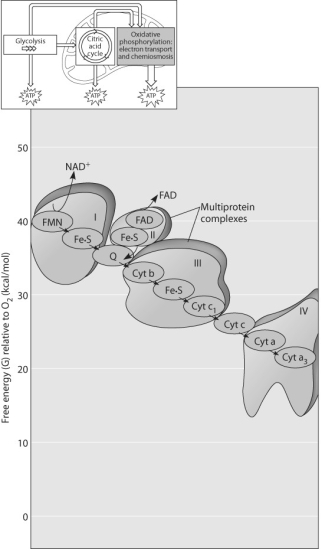 Figure 9.3
-Which of the protein complexes labeled with Roman numerals in Figure 9.3 will transfer electrons to O₂?
Figure 9.3
-Which of the protein complexes labeled with Roman numerals in Figure 9.3 will transfer electrons to O₂?
A) complex I
B) complex II
C) complex III
D) complex IV
E) All of the complexes can transfer electrons to O₂.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is proton-motive force?
A) the force required to remove an electron from hydrogen
B) the force exerted on a proton by a transmembrane proton concentration gradient
C) the force that moves hydrogen into the intermembrane space
D) the force that moves hydrogen into the mitochondrion
E) the force that moves hydrogen to NAD⁺
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where is ATP synthase located in the mitochondrion?
A) cytosol
B) electron transport chain
C) outer membrane
D) inner membrane
E) mitochondrial matrix
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Even though plants carry on photosynthesis, plant cells still use their mitochondria for oxidation of pyruvate. When and where will this occur?
A) in photosynthetic cells in the light, while photosynthesis occurs concurrently
B) in nonphotosynthesizing cells only
C) in cells that are storing glucose only
D) in all cells all the time
E) in photosynthesizing cells in the light and in other tissues in the dark
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9.1 illustrates some of the steps (reactions) of glycolysis in their proper sequence. Each step is lettered. Use these letters to answer the questions.
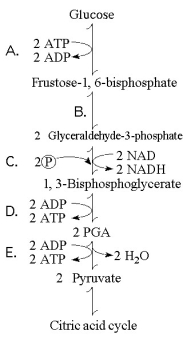 Figure 9.1
-Which portion of the pathway in Figure 9.1 involves an endergonic reaction?
Figure 9.1
-Which portion of the pathway in Figure 9.1 involves an endergonic reaction?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The immediate energy source that drives ATP synthesis by ATP synthase during oxidative phosphorylation is the
A) oxidation of glucose and other organic compounds.
B) flow of electrons down the electron transport chain.
C) affinity of oxygen for electrons.
D) H⁺ concentration across the membrane holding ATP synthase.
E) transfer of phosphate to ADP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the presence of oxygen, the three-carbon compound pyruvate can be catabolized in the citric acid cycle. First, however, the pyruvate (1) loses a carbon, which is given off as a molecule of CO₂, (2) is oxidized to form a two-carbon compound called acetate, and (3) is bonded to coenzyme A. -Why is coenzyme A, a sulfur-containing molecule derived from a B vitamin, added?
A) because sulfur is needed for the molecule to enter the mitochondrion
B) in order to utilize this portion of a B vitamin which would otherwise be a waste product from another pathway
C) to provide a relatively unstable molecule whose acetyl portion can be readily transferred to a compound in the citric acid cycle
D) because it drives the reaction that regenerates NAD⁺
E) in order to remove one molecule of CO₂
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Phosphofructokinase is an important control enzyme in the regulation of cellular respiration. Which of the following statements correctly describes phosphofructokinase activity?
A) It is inhibited by AMP.
B) It is activated by ATP.
C) It is activated by citrate, an intermediate of the citric acid cycle.
D) It catalyzes the conversion of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate, an early step of glycolysis.
E) It is an allosteric enzyme.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When hydrogen ions are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix across the inner membrane and into the intermembrane space, the result is the
A) formation of ATP.
B) reduction of NAD⁺.
C) restoration of the Na⁺/K⁺ balance across the membrane.
D) creation of a proton-motive force.
E) lowering of pH in the mitochondrial matrix.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
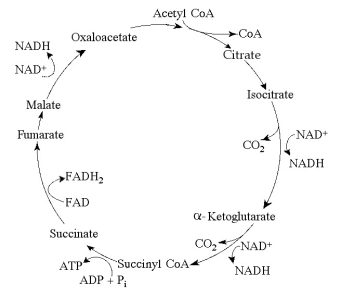 Figure 9.2 The citric acid cycle.
-Carbon skeletons for amino acid biosynthesis are supplied by intermediates of the citric acid cycle. Which intermediate would supply the carbon skeleton for synthesis of a five-carbon amino acid (see Figure 9.2) ?
Figure 9.2 The citric acid cycle.
-Carbon skeletons for amino acid biosynthesis are supplied by intermediates of the citric acid cycle. Which intermediate would supply the carbon skeleton for synthesis of a five-carbon amino acid (see Figure 9.2) ?
A) succinate
B) malate
C) citrate
D) α-ketoglutarate
E) isocitrate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During glycolysis, when each molecule of glucose is catabolized to two molecules of pyruvate, most of the potential energy contained in glucose is
A) transferred to ADP, forming ATP.
B) transferred directly to ATP.
C) retained in the two pyruvates.
D) stored in the NADH produced.
E) used to phosphorylate fructose to form fructose 6-phosphate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The free energy for the oxidation of glucose to CO₂ and water is -686 kcal/mol and the free energy for the reduction of NAD⁺ to NADH is +53 kcal/mol. Why are only two molecules of NADH formed during glycolysis when it appears that as many as a dozen could be formed?
A) Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose is used in the production of ATP in glycolysis.
B) Glycolysis is a very inefficient reaction, with much of the energy of glucose released as heat.
C) Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose remains in pyruvate, one of the products of glycolysis.
D) There is no CO₂ or water produced as products of glycolysis.
E) Glycolysis consists of many enzymatic reactions, each of which extracts some energy from the glucose molecule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9.1 illustrates some of the steps (reactions) of glycolysis in their proper sequence. Each step is lettered. Use these letters to answer the questions.
 Figure 9.1
-Which portion of the pathway in Figure 9.1 contains a phosphorylation reaction in which ATP is the phosphate source?
Figure 9.1
-Which portion of the pathway in Figure 9.1 contains a phosphorylation reaction in which ATP is the phosphate source?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why does the oxidation of organic compounds by molecular oxygen to produce CO₂ and water release free energy?
A) The covalent bonds in organic molecules and molecular oxygen have more kinetic energy than the covalent bonds in water and carbon dioxide.
B) Electrons are being moved from atoms that have a lower affinity for electrons (such as C) to atoms with a higher affinity for electrons (such as O) .
C) The oxidation of organic compounds can be used to make ATP.
D) The electrons have a higher potential energy when associated with water and CO₂ than they do in organic compounds.
E) The covalent bond in O2 is unstable and easily broken by electrons from organic molecules.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Energy released by the electron transport chain is used to pump H⁺ into which location in eukaryotic cells?
A) cytosol
B) mitochondrial outer membrane
C) mitochondrial inner membrane
D) mitochondrial intermembrane space
E) mitochondrial matrix
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When electrons move closer to a more electronegative atom, what happens?
A) The more electronegative atom is reduced, and energy is released.
B) The more electronegative atom is reduced, and energy is consumed.
C) The more electronegative atom is oxidized, and energy is consumed.
D) The more electronegative atom is oxidized, and energy is released.
E) The more electronegative atom is reduced, and entropy decreases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A molecule that is phosphorylated
A) has been reduced as a result of a redox reaction involving the loss of an inorganic phosphate.
B) has a decreased chemical reactivity; it is less likely to provide energy for cellular work.
C) has been oxidized as a result of a redox reaction involving the gain of an inorganic phosphate.
D) has an increased chemical potential energy; it is primed to do cellular work.
E) has less energy than before its phosphorylation and therefore less energy for cellular work.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 107
Related Exams