A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
E) all three
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following characteristics, structures, or processes is common to both bacteria and viruses?
A) metabolism
B) ribosomes
C) genetic material composed of nucleic acid
D) cell division
E) independent existence
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the treatments listed below to answer the following questions. You isolate an infectious substance that is capable of causing disease in plants, but you do not know whether the infectious agent is a bacterium, virus, viroid, or prion. You have four methods at your disposal that you can use to analyze the substance in order to determine the nature of the infectious agent. I. treating the substance with nucleases that destroy all nucleic acids and then determining whether it is still infectious II. filtering the substance to remove all elements smaller than what can be easily seen under a light microscope III. culturing the substance by itself on nutritive medium, away from any plant cells IV. treating the sample with proteases that digest all proteins and then determining whether it is still infectious -Which treatment could definitively determine whether or not the component is a viroid?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) first II and then III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the following questions.
In 1971, David Baltimore described a scheme for classifying viruses based on how the virus produces mRNA.
The table below shows the results of testing five viruses for nuclease specificity, the ability of the virus to act as an mRNA, and presence (+) or absence (-) of its own viral polymerase.
 -Based on the above table, which virus meets the Baltimore requirements for a retrovirus?
-Based on the above table, which virus meets the Baltimore requirements for a retrovirus?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following series best reflects what we know about how the flu virus moves between species?
A) An avian flu virus undergoes several mutations and rearrangements such that it is able to be transmitted to other birds and then to humans.
B) The flu virus in a pig is mutated and replicated in alternate arrangements so that humans who eat the pig products can be infected.
C) A flu virus from a human epidemic or pandemic infects birds; the birds replicate the virus differently and then pass it back to humans.
D) An influenza virus gains new sequences of DNA from another virus, such as a herpesvirus; this enables it to be transmitted to a human host.
E) An animal such as a pig is infected with more than one virus, genetic recombination occurs, the new virus mutates and is passed to a new species such as a bird, the virus mutates and can be transmitted to humans.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following accounts for someone who has had a herpesvirus-mediated cold sore or genital sore getting flare-ups for the rest of his or her life?
A) re-infection by a closely related herpesvirus of a different strain
B) re-infection by the same herpesvirus strain
C) co-infection with an unrelated virus that causes the same symptoms
D) copies of the herpesvirus genome permanently maintained in host nuclei
E) copies of the herpesvirus genome permanently maintained in host cell cytoplasm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -A linear piece of viral DNA of 8 kb can be cut with either of two restriction enzymes (X or Y) . These are subjected to electrophoresis and produce the following bands:
-A linear piece of viral DNA of 8 kb can be cut with either of two restriction enzymes (X or Y) . These are subjected to electrophoresis and produce the following bands:
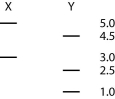 Cutting the same 8 kb piece with both enzymes together results in bands at 4.0, 2.5, 1.0, and 0.5.
Of the possible arrangements of the sites given below, which one is most likely?
Cutting the same 8 kb piece with both enzymes together results in bands at 4.0, 2.5, 1.0, and 0.5.
Of the possible arrangements of the sites given below, which one is most likely?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. Some viruses can be crystallized and their structures analyzed. One such virus is Desmodium, or yellow mottle virus, which infects beans. This is a member of the tymovirus group and has a single-stranded RNA genome of ~6,300 nucleotides. Its virion is 25-30 nm in diameter, and is made up of 180 copies of a single capsid protein that self-associate to form each capsomere, which has icosahedral symmetry with 20 facets. -If this virus has capsomeres with 20 facets, how many proteins form each one?
A) 1
B) 5
C) ~6
D) ~20
E) ~180
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most human-infecting viruses are maintained in the human population only. However, a zoonosis is a disease that is transmitted from other vertebrates to humans, at least sporadically, without requiring viral mutation. Which of the following is the best example of a zoonosis?
A) rabies
B) herpesvirus
C) smallpox
D) HIV
E) hepatitis virus
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In many ways, the regulation of the genes of a particular group of viruses will be similar to the regulation of the host genes. Therefore, which of the following would you expect of the genes of the bacteriophage?
A) regulation via acetylation of histones
B) positive control mechanisms rather than negative
C) control of more than one gene in an operon
D) reliance on transcription activators
E) utilization of eukaryotic polymerases
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. Some viruses can be crystallized and their structures analyzed. One such virus is Desmodium, or yellow mottle virus, which infects beans. This is a member of the tymovirus group and has a single-stranded RNA genome of ~6,300 nucleotides. Its virion is 25-30 nm in diameter, and is made up of 180 copies of a single capsid protein that self-associate to form each capsomere, which has icosahedral symmetry with 20 facets. -In a cell-free system, what other components would you have to provide for this virus to express its genes?
A) ribosomes, tRNAs and amino acids
B) ribosomes, tRNAs, amino acids, and GTP
C) RNA nucleotides and GTP
D) RNA nucleotides, RNA polymerase, and GTP
E) bean cell enzymes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A researcher lyses a cell that contains nucleic acid molecules and capsomeres of tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) . The cell contents are left in a covered test tube overnight. The next day this mixture is sprayed on tobacco plants. Which of the following would be expected to occur?
A) The plants would develop some but not all of the symptoms of the TMV infection.
B) The plants would develop symptoms typically produced by viroids.
C) The plants would develop the typical symptoms of TMV infection.
D) The plants would not show any disease symptoms.
E) The plants would become infected, but the sap from these plants would be unable to infect other plants.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Viral envelopes can best be analyzed with which of the following techniques?
A) transmission electron microscopy
B) antibodies against specific proteins not found in the host membranes
C) staining and visualization with the light microscope
D) use of plaque assays for quantitative measurement of viral titer
E) immunofluorescent tagging of capsid proteins
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bacterium is infected with an experimentally constructed bacteriophage composed of the T2 phage protein coat and T4 phage DNA. The new phages produced would have
A) T2 protein and T4 DNA.
B) T2 protein and T2 DNA.
C) a mixture of the DNA and proteins of both phages.
D) T4 protein and T4 DNA.
E) T4 protein and T2 DNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which viruses have single-stranded RNA that acts as a template for DNA synthesis?
A) lytic phages
B) proviruses
C) viroids
D) bacteriophages
E) retroviruses
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes plant virus infections?
A) They can be controlled by the use of antibiotics.
B) They are spread via the plasmodesmata.
C) They have little effect on plant growth.
D) They are seldom spread by insects.
E) They can never be passed vertically.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the most probable fate of a newly emerging virus that causes high mortality in its host?
A) It is able to spread to a large number of new hosts quickly because the new hosts have no immunological memory of them.
B) The new virus replicates quickly and undergoes rapid adaptation to a series of divergent hosts.
C) A change in environmental conditions such as weather patterns quickly forces the new virus to invade new areas.
D) Sporadic outbreaks will be followed almost immediately by a widespread pandemic.
E) The newly emerging virus will die out rather quickly or will mutate to be far less lethal.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the following questions.
In 1971, David Baltimore described a scheme for classifying viruses based on how the virus produces mRNA.
The table below shows the results of testing five viruses for nuclease specificity, the ability of the virus to act as an mRNA, and presence (+) or absence (-) of its own viral polymerase.
 -Given Baltimore's scheme, a positive sense single-stranded RNA virus such as the polio virus would be most closely related to which of the following?
-Given Baltimore's scheme, a positive sense single-stranded RNA virus such as the polio virus would be most closely related to which of the following?
A) T-series bacteriophages
B) retroviruses that require a DNA intermediate
C) single-stranded DNA viruses such as herpes viruses
D) nonenveloped double-stranded RNA viruses
E) linear double-stranded DNA viruses such as adenoviruses
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the following questions.
In 1971, David Baltimore described a scheme for classifying viruses based on how the virus produces mRNA.
The table below shows the results of testing five viruses for nuclease specificity, the ability of the virus to act as an mRNA, and presence (+) or absence (-) of its own viral polymerase.
 -Based on the above table, which virus meets the requirements for a bacteriophage?
-Based on the above table, which virus meets the requirements for a bacteriophage?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To cause a human pandemic, the H5N1 avian flu virus would have to
A) spread to primates such as chimpanzees.
B) develop into a virus with a different host range.
C) become capable of human-to-human transmission.
D) arise independently in chickens in North and South America.
E) become much more pathogenic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 47
Related Exams