A) binomial distribution.
B) normal distribution.
C) Poisson distribution.
D) Bernoulli distribution.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The maximum likelihood estimates for Tobit models can be more easily obtained than the OLS estimates of a linear model.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) A probit or logit model should be used for corner solution outcomes, and a Poisson regression model should be used for a binary response.
B) A Poisson regression model should be used for corner solution outcomes, and a probit or logit model should be used for a binary response.
C) A probit or logit model should be used for count variables, and a Poisson regression model should be used for a binary response.
D) A Poisson regression model should be used for count variables, and a probit or logit model should be used for a binary response.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the Poisson regression model, the probability distribution is given by P(y = h|x) = exp[-exp(xâ)][exp(xâ)]h/h!, h = 0, 1, …..
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) A truncated regression is a special case of a random sample selection.
B) Nonrandom sample selection can arise in cases of cross-sectional and time series data, but not in the case of panel data.
C) The Tobit regression model is based on endogenous sample selection.
D) The censored regression model is based on nonrandom sample selection.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In case of endogenous sample selection, OLS is unbiased but consistent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The likelihood ratio statistic is given by:
A) LR = (log-likelihoodunrestricted + log-likelihoodrestricted)
B) LR = 2 × (log-likelihoodunrestricted + log-likelihoodrestricted)
C) LR = (log-likelihoodunrestricted - log-likelihoodrestricted)
D) LR = 2 × (log-likelihoodunrestricted - log-likelihoodrestricted)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A count variable refers to a dependent variable that can take on:
A) nonnegative integer values.
B) nonnegative fractional values.
C) negative fractional values.
D) negative integer values.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A common form of sample selection that does not observe the dependent variable because of the outcome of another variable is called _____.
A) nonrandom sample selection
B) exogenous sample selection
C) incidental truncation
D) endogenous sample selection
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The _____ model is designed to model corner solution dependent variables.
A) linear probability
B) logit
C) probit
D) Tobit
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The model: G(z) = [exp(z) ]/[1 + exp(z) ], where G is between zero and one for all real numbers 'z', represents a:
A) logit model.
B) probit model.
C) Tobit model.
D) linear probability model.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The model: y* = 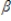 0 + x
0 + x 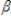 + u, given u|x ˜ Normal(0,
+ u, given u|x ˜ Normal(0,  2) and y = max(0, y*) represents a:
2) and y = max(0, y*) represents a:
A) ARCH model.
B) GARCH model
C) Tobit model
D) logit model
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When a variable is top coded, its value is known only up to a certain threshold.
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The model: G(z) = 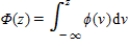 , where
, where  (z) = (2
(z) = (2 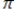 ) -1/2exp(-z2/2) represents a:
) -1/2exp(-z2/2) represents a:
A) Tobit model.
B) logit model.
C) probit model.
D) linear probability model.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) OLS estimates in censored regression models are consistent estimators of the population coefficients.
B) In a truncated regression model, the samples are not included randomly from an underlying population but are based on a given rule.
C) In a censored regression model, units in the sample are taken from a particular subset of the population.
D) Maximum likelihood estimators are consistent in truncated regression models even if there is nonnormality or heteroskedasticity in the error terms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Taking logarithmic of a count variable is a suitable way to model it.
B) All standard count data distributions exhibit heteroskedasticity.
C) The nonlinear least squares estimation aims at maximizing R2.
D) Count variables cannot take on the value zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following tests can be used to test hypotheses with multiple restrictions under a Tobit model?
A) White test
B) Wald test
C) Dickey Fuller test
D) Durbin Watson test
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between the LPM model and the logit and probit models is that:
A) the LPM assumes constant marginal effects for all the independent variables, while the logit and probit models imply diminishing magnitudes of the partial effects.
B) the LPM assumes constant marginal effects for some of the independent variables, while the logit and probit models imply diminishing magnitudes of the partial effects.
C) the LPM assumes constant marginal effects for the dependent variable, while the logit and probit models imply diminishing magnitudes of the partial effects.
D) the LPM assumes different marginal effects for all independent variables, while the logit and probit models imply diminishing magnitudes of the marginal effects.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the probit model, G is the:
A) standard normal cumulative distribution function.
B) cumulative distribution of normal distribution function.
C) standard normal probability distribution function.
D) normal probability distribution function.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a binary response model?
A) MA model
B) ARCH model
C) GARCH model
D) Logit model
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 25
Related Exams