A) arrector pili
B) hypodermis
C) sebaceous gland
D) epidermis and dermis
E) hair follicle
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of burn involves damage to the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue?
A) Full thickness
B) Partial thickness
C) Second degree
D) Total dermal thickness
E) First degree
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following skin changes is usually associated with aging?
A) There is an increase in the number of elastic fibers in the skin.
B) Skin becomes thicker.
C) The amount of collagen in the dermis increases.
D) Loss of subcutaneous tissue contributes to sagging of the skin.
E) Localized increase in sebaceous glands leads to dry skin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Intact skin provides protection because
A) the skin enhances water loss from the body.
B) macrophages roam in the epidermis.
C) its secretions keep the skin slightly alkaline.
D) the skin contains components of the excretory system.
E) it forms a physical barrier against the entry of microbes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The central axis of the hair is the
A) shaft.
B) cuticle.
C) root.
D) medulla.
E) hair bulb.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Vitamin C is essential for normal collagen synthesis. If a child suffered from a vitamin C deficiency, which layer of the skin would be most affected?
A) epidermis
B) stratum basale
C) stratum corneum
D) stratum granulosum
E) reticular layer of dermis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fingernails are comprised of:
A) collagen deposited by the lunula and the matrix
B) proteins secreted by the nail groove from the matrix
C) epithelial and collagen fibers produced in the dermis
D) thin, dead scaly cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
That portion of the hair that extends above the surface of the skin is the
A) cuticle.
B) hair bulb.
C) root.
D) medulla.
E) shaft.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Keratinocytes
A) produce skin pigments in cell organelles called melanosomes.
B) are responsible for the reduction of water loss from the skin.
C) determine thickness of the skin.
D) are special cells of the immune system.
E) are found in both the dermal and the epidermal layers of the skin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Skin glands do not include
A) sweat glands.
B) sebaceous glands.
C) mammary glands.
D) salivary glands.
E) ceruminous glands.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The proximal portion of the nail is the
A) nail root.
B) hyponychium.
C) nail body.
D) nail fold.
E) eponychium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The layer of the epidermis in which there is the greatest amount of mitotic activity.
A) stratum granulosum
B) stratum corneum
C) stratum lucidum
D) stratum spinosum
E) stratum basale
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An expanded knob at the base of the hair root is the
A) medulla.
B) cuticle.
C) hair bulb.
D) root.
E) shaft.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which layer of the epidermis are granules of keratohyalin formed?
A) stratum basale
B) stratum granulosum
C) stratum spinosum
D) stratum corneum
E) stratum lucidum
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Thin skin has only four epithelial strata. It lacks which of the following?
A) stratum basale
B) stratum granulosum
C) stratum spinosum
D) stratum lucidum
E) stratum corneum
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The length of hair is determined by the
A) size of the hair bulb.
B) age of the person.
C) length of the resting stage.
D) angle of the hair root.
E) rate of hair growth.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the arrector pili muscles contract
A) the body is able to lose heat.
B) no change is noted on the skin surface.
C) the hair on your arms and legs begins to curl.
D) the sweat glands empty their contents onto the surface of the skin.
E) "goose bumps" form on the skin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Light-skinned races such as Caucasians have
A) approximately the same number of melanocytes as races with darker skins.
B) more melanocytes than races with darker skins.
C) fewer melanocytes than races with darker skins.
D) more melanin in their skin.
E) a different kind of melanin in their skin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some drugs for treating acne include peroxides that increases 'peeling' or shedding of skin. This drugs' side effects include drying of the skin, redness, rashes, bleaching and possible loss of hair in areas in contact. Do peroxides have an effect on the sebum-production?
A) Yes, the effect is on the dermis and the sebaceous glands are located there.
B) No, the effect is on the dermis and the sebaceous glands are located there.
C) No, the effect is on the epidermis and the sebaceous glands are located there.
D) Yes, the effect is on the epidermis and the sebaceous glands are located there.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
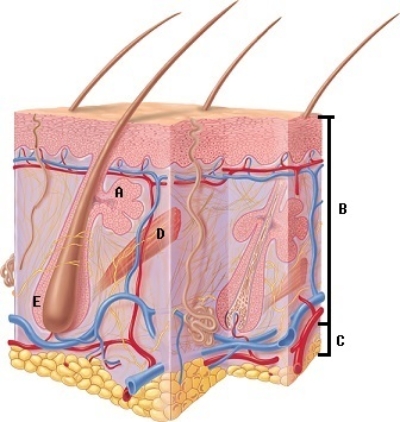 -What does structure "B" represent on the diagram?
-What does structure "B" represent on the diagram? 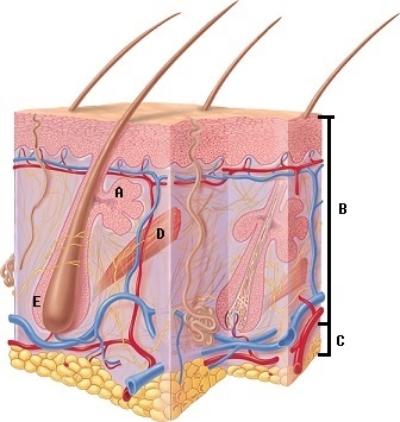
A) hair follicle
B) sebaceous gland
C) epidermis and dermis
D) hypodermis
E) arrector pili
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 152
Related Exams