A) accept lower real wages today in exchange for higher real wages in the future.
B) work longer hours.
C) increase their demand for goods and services.
D) sacrifice some present consumption.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run, economic growth can be expected to lead to I.increases in consumption. II.increases in the capital stock. III.increases in the savings rate. IV.outward shifts in the production possibilities curve.
A) I, II, III, and IV
B) I, II, and III only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) I and IV only
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
According to the rule of 72, a 12% annual increase in real GDP would lead to a doubling of real GDP in 8 years.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the rate of growth of output is 8% and the rate of growth of population is 2%, what is the rate of growth of output per capita?
A) 2%
B) 4%
C) 6%
D) 8%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A change in the availability of natural resources will shift the aggregate production function.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Holding all else constant, a country's standard of living will rise if its
A) nominal GDP grows at a faster rate than real GDP.
B) nominal GDP grows at a slower rate than real GDP.
C) rate of population growth exceeds the rate of growth of real GDP.
D) rate of population growth is less than the rate of growth of real GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
All other things unchanged, higher saving rates contribute to higher rates of capital formation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: Production Possibilities Curves 1 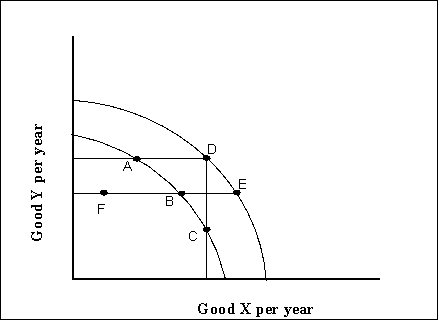 -(Exhibit: Production Possibilities Curves 1)
A movement from F to B
-(Exhibit: Production Possibilities Curves 1)
A movement from F to B
A) will increase real GDP and represents economic growth.
B) will increase real GDP but does not represent economic growth.
C) implies that the country's productive ability has increased.
D) will not increase real GDP or potential output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true? I.Small differences in rates of economic growth can lead to large differences in levels of potential output over time. II.From the perspective of the rule of 72, small differences in rates of economic growth between two countries will not significantly affect their respective standards of living. III.Countries that have higher population growth rates are likely to see higher economic growth rates because increases in population lead to increases in the size of the labor force.
A) I and III
B) II and III
C) I only
D) II only
E) III only
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Over the past century, the average household income in the United States
A) has increased in nominal terms but has decreased in real terms.
B) has increased in nominal terms but has remained constant in real terms.
C) has increased in real terms.
D) has increased only marginally both in real and nominal terms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Holding everything else unchanged, if a nation's output grows at approximately 2.4% per year and its population doubles in 45 years, calculate the approximate rate of change in per capita real GDP.
A) 0.8% per year
B) 1.6% per year
C) 2.4% per year
D) 4% per year
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Diminishing marginal returns occurs when
A) each additional unit of a variable factor adds less to total output than the previous unit, given constant quantities of other factors.
B) each additional unit of a variable factor adds more to total output than the previous unit, given constant quantities of other factors.
C) each additional unit of a variable factor diminishes total output, given constant quantities of other factors.
D) each additional unit of a variable factor adds a constant amount to total output than the previous unit, given diminishing quantities of other factors.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If output per capita doubles in 24 years and the population doubles in 18 years, what is the growth rate of output?
A) 4% per year
B) 5% per year
C) 6% per year
D) 7% per year
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To assess changes in average standards of living,
A) we examine the difference between the percentage rate of growth of output per capita and the percentage rate of growth of population.
B) we subtract the percentage rate of growth of population from the percentage rate of growth of output per capita to get the percentage rate of growth of output.
C) we subtract the percentage rate of growth of population from the percentage rate of growth of output to get the percentage rate of growth of output per capita.
D) we divide the percentage rate of growth of output by the percentage rate of growth of population to get the percentage rate of growth of output per capita.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A curve that relates an economy's total output to the total amount of labor employed, holding all other determinants of output constant, is called
A) an input-output matrix.
B) an average output function.
C) a marginal product function.
D) an aggregate production function.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose real GDPs in Hauck and Meran are identical at $10 trillion in 2010.Suppose Hauck's economic growth rate is 2% and Meran's is 4% and the rates remain constant over time.Calculate the percentage difference in their levels of potential output in 2046.
A) There will be no difference in their levels of potential output.
B) Meran's potential output will be 50% higher than that of Hauck's.
C) Hauck's potential output will be 100% higher than that of Meran's.
D) Meran's potential output will be 100% higher than that of Hauck's.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: Economic Growth, AD and AS Analysis 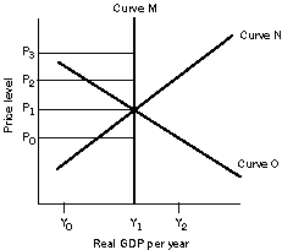 -(Exhibit: Economic Growth, AD and AS Analysis)
Assume that the economy is initially in long-run equilibrium.If oil prices in the economy increased dramatically and remained high for so long that most of the industries in the economy had to significantly form new capital and retool much of its existing capital, the economy would suffer.In this event,
-(Exhibit: Economic Growth, AD and AS Analysis)
Assume that the economy is initially in long-run equilibrium.If oil prices in the economy increased dramatically and remained high for so long that most of the industries in the economy had to significantly form new capital and retool much of its existing capital, the economy would suffer.In this event,
A) the long-run aggregate supply and the short-run aggregate supply curves would shift left, reducing the future industrial capacity and prospects for economic growth.
B) the aggregate demand curve would shift left, reducing the future industrial capacity and prospects for economic growth.
C) only the short-run aggregate supply curve would shift left, permanently reducing the economy's potential output.
D) the long-run aggregate supply, the short-run aggregate supply, and the aggregate demand curves would shift left, sending the economy into a long recession.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: Aggregate Production Function, Labor Market, and LRAS 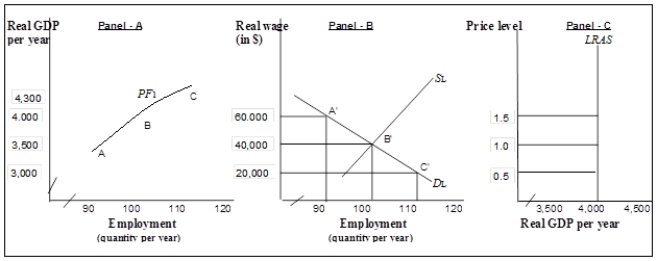 -(Exhibit: Aggregate Production Function, Labor Market, and LRAS)
In Panel (c)
, the position of the long-run aggregate supply curve is determined by
-(Exhibit: Aggregate Production Function, Labor Market, and LRAS)
In Panel (c)
, the position of the long-run aggregate supply curve is determined by
A) the economy's potential output and its aggregate production function.
B) the economy's potential output and the demand and supply curves for labor.
C) the price level and potential output.
D) the price level and the demand and supply curves for labor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are sources of economic growth except
A) increases in human capital.
B) an increase in the savings rate.
C) an increase in consumption spending to stimulate production.
D) increases in physical capital.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a firm that produces output using labor and capital.The firm's stock of capital is fixed and in order to increase output, it must employ more workers.Which of the following occurs as the number of workers increases?
A) Output per worker rises.
B) Capital per worker falls.
C) Wage per worker falls.
D) Total output increases exponentially.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 131
Related Exams