A) the level of household borrowing.
B) consumer expectations.
C) the stock of wealth.
D) the level of income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
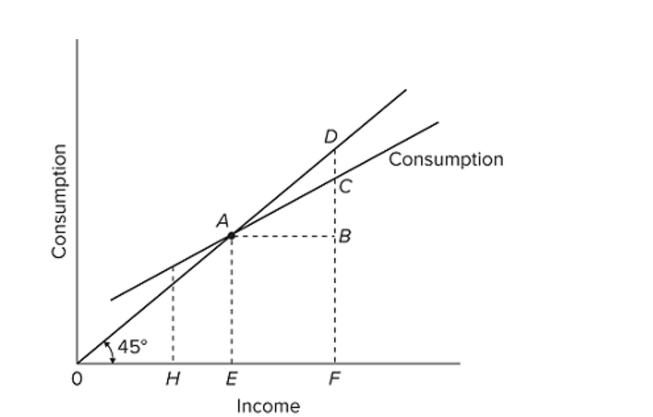 Refer to the given diagram. Consumption will be equal to income at
Refer to the given diagram. Consumption will be equal to income at
A) an income of E.
B) an income of F.
C) point C.
D) point D.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The multiplier is defined as
A) 1 − MPS.
B) change in GDP × initial change in spending.
C) change in GDP / initial change in spending.
D) change in GDP − initial change in spending.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
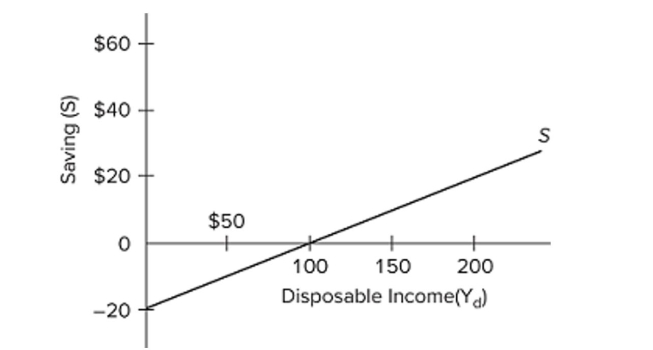 Refer to the diagram. The average propensity to consume
Refer to the diagram. The average propensity to consume
A) is greater than 1 at all levels of disposable income above $100.
B) is greater than 1 at all levels of disposable income below $100.
C) is equal to the average propensity to save.
D) cannot be determined from the information given.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A decline in the real interest rate will shift the investment demand curve to the right.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most important determinant of consumption and saving is the
A) level of bank credit.
B) level of income.
C) interest rate.
D) price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the slope of the consumption schedule is 0.75, then the slope of the saving schedule
A) is 0.25.
B) is 0.75.
C) is 1.25.
D) cannot be determined from the data.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Investment spending in the United States tends to be unstable because
A) expected profits are highly variable.
B) capital goods are durable.
C) innovation occurs at an irregular pace.
D) all of the factors mentioned in other answers contribute to the instability.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
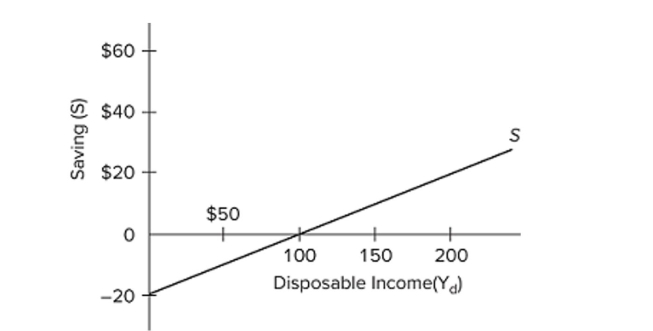 (Advanced analysis) The equation for the given saving schedule is
(Advanced analysis) The equation for the given saving schedule is
A) Yd = −20 + 0.8S.
B) Yd = 20 + 0.2S.
C) S = −20 + 0.2Yd.
D) S = 20 + 0.8Yd.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If 100 percent of any change in income is spent, the multiplier will be
A) equal to the MPC.
B) 1.
C) zero.
D) infinitely large.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Economists widely agree that the value of the real-world multiplier is 2.5.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the marginal propensity to save is 0.2 in an economy, a $20 billion rise in investment spending will increase
A) GDP by $120 billion.
B) GDP by $20 billion.
C) saving by $25 billion.
D) consumption by $80 billion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the inflation rate is 10 percent and the real interest rate is 12 percent, the nominal interest rate is
A) 2 percent.
B) zero percent.
C) 10 percent.
D) 22 percent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that for the entire business sector of a private closed economy, there are $0 worth of investment projects that will yield an expected rate of return of 25 percent or more. But there are $15 Worth of investments that will yield an expected rate of return of 20-25 percent, another $15 with an Expected rate of return of 15-20 percent, and an additional $15 of investment projects in each Successive rate of return range down to and including the 0-5 percent range. The expected rate of Return curve
A) shows a direct relationship between the interest rate and investment.
B) is also the investment demand curve.
C) is indeterminate.
D) implies a direct (positive) relationship between the interest rate and the level of GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
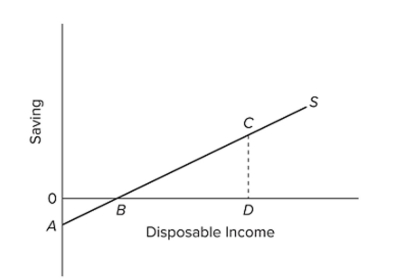 Refer to the diagram. At disposable income level D, the average propensity to save is equal to
Refer to the diagram. At disposable income level D, the average propensity to save is equal to
A) CD/BD.
B) CD/0D.
C) 0D/CD.
D) 0A/0B.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following will not cause the consumption schedule to shift?
A) a sharp increase in the amount of wealth held by households
B) a change in consumer incomes
C) the expectation of a recession
D) a growing expectation that consumer durables will be increasing in price soon
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The multiplier shows the relationship between changes in a component of spending, say, investment, and the consequent changes in real income and output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The relationship between the MPS and the MPC is such that
A) MPC − MPS = 1.
B) MPS/MPC = 1.
C) 1 − MPC = MPS.
D) MPC − 1 = MPS.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the Hennige family's marginal propensity to consume is 0.70, then it will necessarily consume seven- tenths of its total income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The wealth effect is shown graphically as a
A) shift of the consumption schedule.
B) movement along an existing consumption schedule.
C) shift of the investment schedule.
D) movement along an existing investment schedule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 233
Related Exams