A) alter both equilibrium price and quantity.
B) alter equilibrium quantity but not equilibrium price.
C) alter equilibrium price but not equilibrium quantity.
D) have no effect on equilibrium price or quantity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When an economist says that the demand for a product has increased, this means that
A) consumers are now willing to purchase more of this product at each possible price.
B) the product has become particularly scarce for some reason.
C) product price has fallen and, as a consequence, consumers are buying a larger quantity of the product.
D) the demand curve has shifted to the left.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
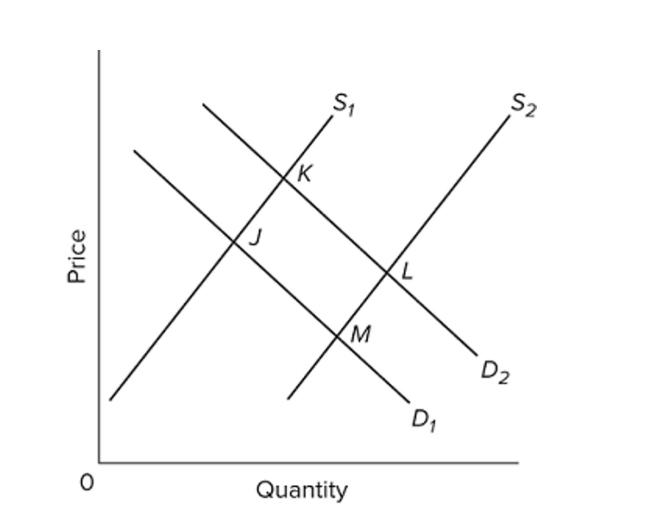 Refer to the diagram, in which S1 and D1 represent the original supply and demand curves and S2 and D2 the new curves. In this market the indicated shift in demand may have been caused by
Refer to the diagram, in which S1 and D1 represent the original supply and demand curves and S2 and D2 the new curves. In this market the indicated shift in demand may have been caused by
A) a decline in the number of buyers in the market.
B) a decline in the price of a substitute good.
C) an increase in incomes if the product is a normal good.
D) an increase in incomes if the product is an inferior good.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that in each of four successive years, producers sell more of their product and at lower prices. This could be explained
A) by small annual increases in supply accompanied by large annual increases in demand.
B) in terms of a stable supply curve and increasing demand.
C) in terms of a stable demand curve and increasing supply.
D) as an exception to the law of supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A market that achieves productive efficiency is necessarily producing the quantity of goods most desired by society.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Because of unseasonably cold weather, the supply of oranges has substantially decreased. This statement indicates the
A) demand for oranges will necessarily rise.
B) equilibrium quantity of oranges will rise.
C) amount of oranges that will be available at various prices has declined.
D) price of oranges will fall.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
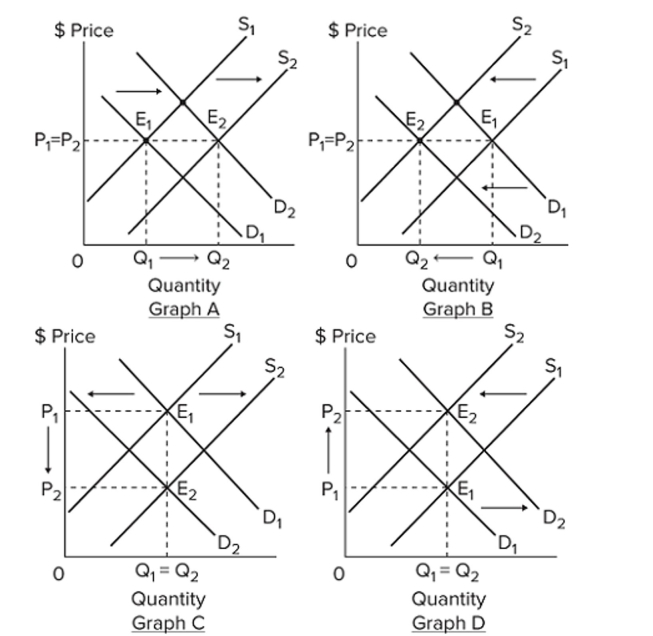 Refer to the four graphs above. Select the graph that best shows the changes in demand and supply in the market specified in the following situation: the market for corn, if gasoline producers
Use more ethanol from corn and good weather during the growing season yields a bumper harvest.
Refer to the four graphs above. Select the graph that best shows the changes in demand and supply in the market specified in the following situation: the market for corn, if gasoline producers
Use more ethanol from corn and good weather during the growing season yields a bumper harvest.
A) Graph A
B) Graph B
C) Graph C
D) Graph D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economists use the term "demand" to refer to
A) a particular price-quantity combination on a stable demand curve.
B) the total amount spent on a particular commodity over a fixed time period.
C) an upsloping line on a graph that relates consumer purchases and product price.
D) a schedule of various combinations of market prices and quantities demanded.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
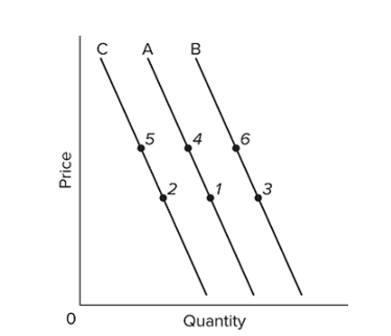 Refer to the above graph with three demand curves. A "decrease in demand" would be illustrated as a change from
Refer to the above graph with three demand curves. A "decrease in demand" would be illustrated as a change from
A) point 1 to point 4.
B) point 1 to point 3.
C) line C to B.
D) line A to C.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the supply of a product decreases and the demand for that product simultaneously increases, then equilibrium
A) price must rise, but equilibrium quantity may rise, fall, or remain unchanged.
B) price must rise and equilibrium quantity must fall.
C) price and equilibrium quantity must both increase.
D) price and equilibrium quantity must both decline.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the diagrams below, the subscript "1" refers to the initial position of the curve, while the subscript "2" refers to the final position after the curve shifts.
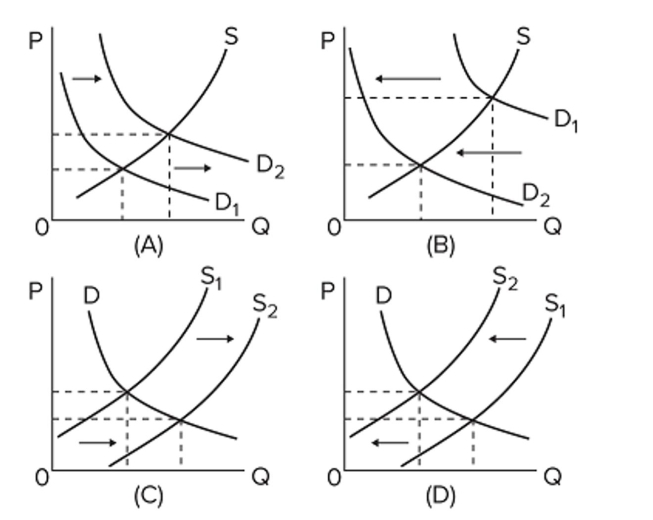 Which diagram illustrates the effect on the natural-gas market of the widespread use of "fracking,"
Or hydraulic fracturing, by gas-drilling companies?
Which diagram illustrates the effect on the natural-gas market of the widespread use of "fracking,"
Or hydraulic fracturing, by gas-drilling companies?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "dynamic pricing" model used by the ride-sharing firm Uber, along with a few other firms, illustrates which of the following?
A) When there is shortage in a market, the equilibrium price will rise.
B) Once the equilibrium price is reached, it will remain there for at least several days.
C) Since actual quantity bought always equals actual quantity sold, the market is always at equilibrium.
D) When there is surplus in a market, the equilibrium price will rise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
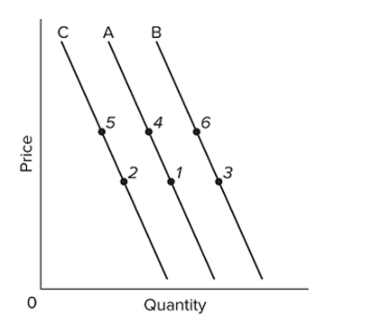 Refer to the above graph with three demand curves. An increase in price, other factors constant, would cause a change from
Refer to the above graph with three demand curves. An increase in price, other factors constant, would cause a change from
A) point 4 to point 5.
B) point 3 to point 6.
C) point 1 to point 5.
D) point 2 to point 4.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Last year the price of corn was $3 a bushel and the quantity of corn demanded was 10 million bushels. This year the price of corn was $4.00 a bushel and the quantity demanded was 12 million Bushels. Is this evidence that the law of demand does not apply to corn?
A) Yes, because there is a direct relationship between the price of corn and the quantity supplied.
B) Yes, because there is an inverse relationship between the price of corn and the quantity demanded.
C) No, because the other-things-equal assumption was violated over the two-year period.
D) No, because the evidence indicates that there is a shortage of corn.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in demand and an increase in supply will
A) affect price in an indeterminate way and decrease the equilibrium quantity.
B) increase price and affect the equilibrium quantity in an indeterminate way.
C) decrease price and affect the equilibrium quantity in an indeterminate way.
D) increase price and increase the equilibrium quantity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the equilibrium quantity of hybrid cars would be caused by which of the following?
A) an increase in the demand for hybrid cars
B) a decrease in the demand for hybrid cars
C) higher prices of car batteries
D) lower prices for gasoline
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Black markets are associated with
A) price floors and the resulting product surpluses.
B) price floors and the resulting product shortages.
C) ceiling prices and the resulting product shortages.
D) ceiling prices and the resulting product surpluses.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would best be classified as a complement for new houses/homes?
A) lumber or steel
B) construction equipment
C) mortgage loans
D) rental apartments
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
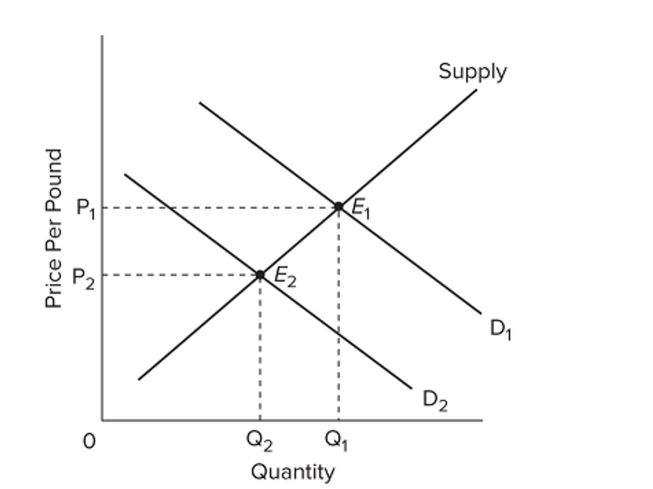 Refer to the above graph, which shows the market for beef where demand shifted from D1 to D2. The change in equilibrium from E1 to E2 cannot be a result of
Refer to the above graph, which shows the market for beef where demand shifted from D1 to D2. The change in equilibrium from E1 to E2 cannot be a result of
A) buyers' expectations of lower prices for beef in the very near future.
B) a health report warning of the dangers of beef consumption
C) a widespread concern about mad-cow disease.
D) a decrease in the productivity of cattle farms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that in the clothing market, production costs have fallen, but the equilibrium price and quantity purchased have both increased. Based on this information we can conclude that
A) the supply of clothing has grown faster than the demand for clothing.
B) demand for clothing has grown faster than the supply of clothing.
C) the supply of and demand for clothing have grown by the same proportion.
D) there is no way to determine what has happened to supply and demand with this information.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 357
Related Exams