A) nonrivalrous in consumption.
B) rivalrous in consumption.
C) nonexcludable.
D) excludable.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a positive externality exists,
A) external benefits are necessarily greater than private benefits.
B) social benefits are greater than private benefits.
C) social benefits are less than private benefits.
D) social benefits equal private benefits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A good is a nonexcludable if
A) its consumption by one person does not reduce its consumption by others.
B) it is impossible to prevent people from obtaining the benefits of the good once it has been produced.
C) no negative externalities are associated with its production and consumption.
D) it is free in the first place; that is, it is so abundant that people can get all they want at zero price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is false ?
A) A positive externality is internalized if the person that generated the externality incorporates into his or her own private cost-benefit calculations the external benefits that third parties receive.
B) Internalizing externalities is not the same as adjusting for externalities.
C) An externality has been completely internalized if the socially optimal output emerges.
D) Assigning property rights is one way to internalize externalities.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a negative externality exists, __________ in order for the socially optimal output to be reached.
A) supply needs to increase
B) supply needs to decrease
C) demand needs to increase
D) supply and demand both need to increase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 30-3 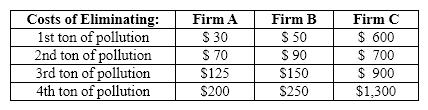 Refer to Exhibit 30-3. What is the cost to Firm C of eliminating 2 tons of pollution?
Refer to Exhibit 30-3. What is the cost to Firm C of eliminating 2 tons of pollution?
A) $1,300
B) $300
C) $1,500
D) $2,200
E) $3,500
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Externalities can be internalized through voluntary agreements as long as
A) transaction costs are low relative to expected benefits.
B) transaction costs are high relative to expected benefits.
C) the agreement is a short-run agreement.
D) the agreement is a long-run agreement.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If private property rights were established in the air, there would probably be
A) more air pollution.
B) less air pollution.
C) the same amount of air pollution that exists without private property rights in the air.
D) better weather.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
From an economist's point of view, zero pollution is always preferable to some pollution.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Ronald Coase stressed the necessity of using taxes to internalize negative externalities.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 30-5
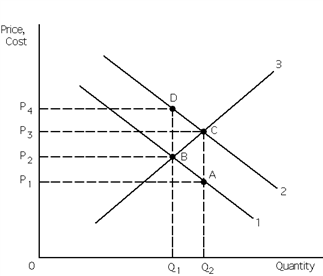 Refer to Exhibit 30-5. If a positive externality exists, then the external benefits associated with the positive externality equal the distance between points ____________ and the socially optimal output is
Refer to Exhibit 30-5. If a positive externality exists, then the external benefits associated with the positive externality equal the distance between points ____________ and the socially optimal output is
A) C and A; Q1.
B) D and B; Q1.
C) D and B; Q2.
D) A and B; Q2.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The free rider problem is the main source of market failure in the provision of nonexcludable public goods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 30-2
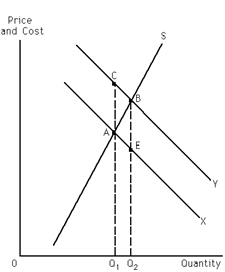 Refer to Exhibit 30-2. If the exhibit represents a positive externality situation, the private benefit of expanding output from Q1 to Q2 is the area of
Refer to Exhibit 30-2. If the exhibit represents a positive externality situation, the private benefit of expanding output from Q1 to Q2 is the area of
A) Q1ABQ2.
B) Q1AEQ2.
C) Q1CBQ2.
D) ABE.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It seems quite possible that cigarette companies concealed information about the effects of smoking on health, causing cigarette prices to be __________ and cigarette sales to be __________ than would have been the case under symmetric information.
A) higher; higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; higher
D) lower; lower
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a positive externality exists, __________ in order for the socially optimal output to be reached.
A) supply needs to decrease
B) demand needs to increase
C) demand needs to decrease
D) supply and demand both need to increase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The open lands in the early West were overgrazed largely because no one owned the land being used for grazing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 30-2
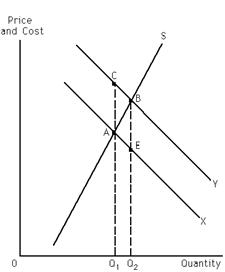 Refer to Exhibit 30-2. This graph represents a positive externality situation. Given this, which of the two curves, X or Y, represents marginal social benefits and why?
Refer to Exhibit 30-2. This graph represents a positive externality situation. Given this, which of the two curves, X or Y, represents marginal social benefits and why?
A) Curve X, because if there is a positive externality, negative external benefits are associated with it: social costs external benefits - private benefits, therefore the marginal social benefit curve must lie below the marginal private benefit curve.
B) Curve X, because if there is a positive externality, external benefits are associated with it: social benefits = external benefits + private benefits, therefore the marginal social benefit curve must lie below the marginal private benefit curve.
C) Curve Y, because if there is a positive externality, external costs are associated with it: social benefits = external costs + private benefits, therefore the marginal social benefit curve must lie above the marginal private benefit cost curve.
D) Curve Y, because if there is a positive externality, external benefits are associated with it: social benefits = external benefits + private benefits, therefore the marginal social benefit curve must lie above the marginal private benefit curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 30-3 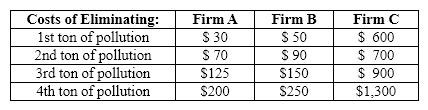 Refer to Exhibit 30-3. Suppose that Firms A, B, and C are the only polluters in the state and that each emits 4 tons of pollution into the atmosphere. To cut the level of pollution in half, the government mandates system whereby each firm must reduce its pollution level by one-half. The total cost of complying with the mandate is
Refer to Exhibit 30-3. Suppose that Firms A, B, and C are the only polluters in the state and that each emits 4 tons of pollution into the atmosphere. To cut the level of pollution in half, the government mandates system whereby each firm must reduce its pollution level by one-half. The total cost of complying with the mandate is
A) $433.
B) $1,540.
C) $2,750.
D) $8,570.
E) $11,650.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If society is experiencing a net social cost from the production of a good, this implies that
A) the socially optimal level of output is being produced and society is willing to accept the costs that result.
B) producers would rather produce the output at which marginal social cost equals the demand for the good.
C) negative externalities are involved in the production of this good.
D) positive externalities must be involved in the production of this good.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) A tax applied to an activity that generates a negative externality always brings about the socially optimal level of output.
B) A subsidy applied to an activity that generates a positive externality always brings about the socially optimal level of output.
C) A tax applied to an activity that generates a positive externality may bring about the socially optimal level of output.
D) A tax applied to an activity that generates a negative externality may bring about the socially optimal level of output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 183
Related Exams