A) Obtain creatinine level
B) Obtain fingerstick glucose
C) Order renal ultrasound
D) Perform urinalysis
E) Send urine culture
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 44-year-old man with a medical history of food allergy to peanuts is brought to the emergency department for an allergic reaction. The patient developed the acute onset of dyspnea and wheezing shortly after ingesting a cookie. His symptoms progressed to difficulty swallowing and swelling of the face and tongue. On arrival, temperature is 36.9 C (98.4 F) , pulse is 115/min, blood pressure is 85/74 mm Hg, and respirations are 28/min. Oxygen saturation is 93% on a nonrebreather face mask. He is anxious and pale with swollen lips, swollen tongue, and inspiratory stridor. On lung auscultation, bilateral wheezing is present. Intramuscular epinephrine, intravenous fluids, and racemic epinephrine via nebulizer are administered without improvement. The patient's distress is increasing, and he is becoming more agitated. The decision to intubate using awake fiberoptic nasotracheal intubation is made. Severe swelling of the upper airway is seen on laryngoscopy, and 3 attempts to pass the endotracheal tube are unsuccessful. The patient's blood pressure is 70/40 mm Hg, pulse is 75/min, and respirations are 40/min. Oxygen saturation is 72% on a nonrebreather face mask. What is the best next step in management of this patient?
A) Bag valve mask ventilation and reattempt
B) Cricothyrotomy
C) Noninvasive positive pressure ventilation
D) Supraglottic device
E) Tracheostomy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 40-year-old woman comes to the office to discuss nutrition. She says, "I have been overweight since the birth of my third child 10 years ago, and none of the diets I have tried ever seem to help." The patient reduced her food intake by 100-200 kcal/day on a restricted-fat diet 4 weeks ago, but her weight has not changed. She says, "I want to make sure I am doing the right thing. I tried to read about diets on the internet but I don't know what to believe." Medical history is notable for hypothyroidism, treated with a stable dose of levothyroxine. She does not smoke and drinks alcohol on social occasions only. Family history is significant for breast cancer and coronary artery disease in her mother and colon cancer in her father. Vital signs are normal. BMI is 32 kg/m2. The thyroid is normal to palpation. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. The abdomen is soft and nontender with no hepatomegaly. Deep tendon reflexes are normal and symmetric. Serum TSH is 2.1 µU/mL. Which of the following is the most appropriate nutritional recommendation for this patient?
A) Adding a fiber supplement will reduce your risk of breast and colon cancer.
B) Adding a vitamin D supplement can reduce your risk of fractures associated with weight loss.
C) Changing to a low-carbohydrate diet will give you greater long-term weight loss.
D) Increasing your caloric deficit to 500 kcal/day will produce weight loss of 0.45 kg (1 lb) per week.
E) Modifying your diet to include more whole grains, lean meat, and low-fat dairy can reduce your weight and the risk of heart disease.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 52-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department due to a day of fever, lethargy, and skin lesions. She is currently undergoing combination chemotherapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and her last treatment was 10 days ago. Yesterday, the patient developed a red rash on her right thigh. Within a few hours, a pustule formed in the center of the lesion, rapidly evolved into a dark bulla, and then ruptured and formed an ulcer. A second, similar skin lesion arose shortly thereafter. The patient has also had fever and chills and progressive weakness and lethargy. Temperature is 38.9 C (102 F) , blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg, and pulse is 106/min. She has an implanted central venous catheter with a subcutaneous port; the overlying skin is not erythematous or tender. Cardiopulmonary auscultation reveals clear lung fields and no cardiac murmurs. The abdomen is soft and nontender. Skin examination shows a nontender, necrotic ulcer with an erythematous rim and yellow-green, purulent exudate on the right thigh. There is another lesion with a hemorrhagic dark-bluish bulla and surrounding erythematous, indurated skin. Leukocyte count is 800/mm3 with 10% neutrophils. Which of the following statements regarding this patient's current condition is most accurate?
A) An associated auto-inflammatory systemic disorder is most likely present.
B) Evaluation by an ophthalmologist is essential to look for endophthalmitis.
C) Extensive and repeated surgical debridements are most likely required.
D) Intravenous antibiotics are most likely to improve this condition.
E) Skin-directed antineoplastic therapy is the treatment of choice.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 29-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 0, at 26 weeks gestation comes to the office for a routine prenatal visit. She reports no contractions, vaginal bleeding, or leakage of fluid. There is good fetal movement. The patient has a history of polycystic ovarian syndrome. This pregnancy was conceived through ovulation induction but has otherwise been uncomplicated. She has no other chronic medical conditions or previous surgeries. The patient walks for 30-45 minutes 5 days a week. She takes prenatal vitamins and folate supplementation daily. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg and pulse is 89/min. BMI is 27 kg/m2. Fetal heart tones are 150/min. Fundal height is 28 cm. Third-trimester laboratory results are as follows: 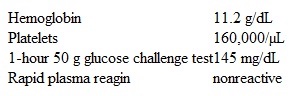 Testing of which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
Testing of which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A) Fasting blood glucose level
B) Glucose tolerance
C) Hemoglobin A1c level
D) No further testing is indicated
E) Serial fasting and postprandial glucose levels
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 42-year-old man comes to the hospital with a 4-day history of periodic fever, chills, headache, and myalgias. For the past day, he also had mild abdominal discomfort, nausea, and vomiting. The patient has no chest pain, cough, dyspnea, or diarrhea. He returned from an African safari 2.5 weeks ago, and family members who traveled with him have no symptoms. The patient has no past known medical problems. His temperature is 39.4 C (103 F) , blood pressure is 122/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 114/min and regular. On examination, he is diaphoretic and uncomfortable. There is mild pharyngeal erythema without exudates or lymphadenopathy. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. There is no neck stiffness. The abdomen is soft with mild generalized tenderness and splenomegaly. He has no skin rash. Neurologic examination is normal. Laboratory results are as follows:
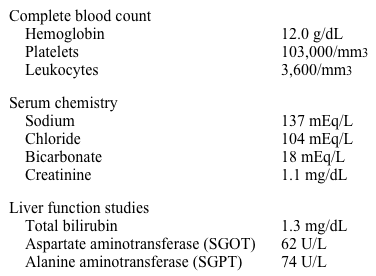 Chest x-ray reveals no abnormalities. Which of the following interventions could have prevented his current condition?
Chest x-ray reveals no abnormalities. Which of the following interventions could have prevented his current condition?
A) Avoidance of contact with sick persons
B) Consumption of bottled water and cooked food only
C) Prophylactic antimicrobials
D) Use of barrier contraceptives
E) Vaccinations prior to travel
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 59-year-old man comes to the office due to cough and mild dyspnea. His symptoms began 10 days ago with nasal congestion and a sore throat, which improved spontaneously after a few days. However, the cough, productive of white sputum, has persisted. He has also had an episode of blood-streaked sputum. The patient has a history of hypertension and stable coronary artery disease. He is a current smoker with a 20-pack-year history. The patient is a car salesman and has not traveled recently. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F) , blood pressure is 110/72 mm Hg, and respirations are 18/min. Lung examination shows scattered wheezes bilaterally. Chest x-ray demonstrates no parenchymal infiltrate or consolidation, but a 2-cm peripherally located nodule is present in the left lower lobe. No prior chest imaging is available. CT scan of the chest confirms a 2.2-cm, peripherally located nodule in the left lower lobe surrounded by lung parenchyma. The nodule has spiculated borders and eccentric calcification on the periphery, and no lymphadenopathy is present. CT scan of the abdomen reveals no abnormalities of the liver or adrenal glands. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient's lung lesion?
A) Fiberoptic bronchoscopy
B) Induced sputum cytology
C) No additional intervention
D) Referral for surgical excision
E) Repeat CT scan in 6 months
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2-week-old girl is admitted to the hospital for dehydration and vomiting. She had an uncomplicated vaginal delivery at home and did not undergo newborn screening. Breastfeeding has been difficult due to the newborn's lethargy and frequent vomiting. The mother has no medical problems, took no medications during the pregnancy, and had normal prenatal laboratory results. Family history is significant for a brother who died at age 1 month from severe dehydration several years ago. The newborn has a 2-year-old sister who is healthy. Vital signs show hypotension and tachycardia. Examination shows a sunken fontanelle and ambiguous genitalia. The rest of the examination is unremarkable. Abdominal x-ray, abdominal ultrasound, and upper gastrointestinal studies are normal. Karyotype analysis is pending. Serum chemistry results are as follows:  Which of the following is the best next step in the treatment of this patient's condition?
Which of the following is the best next step in the treatment of this patient's condition?
A) Clitoroplasty and vaginoplasty
B) Estrogen
C) Hydrocortisone
D) Progesterone
E) Soy formula
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 6-year-old girl is brought to the clinic for evaluation of acne. Her parents first noticed mild acne on her forehead and nose 3 weeks ago as well as adult-type body odor that requires her to bathe more frequently. The patient was born at 35 weeks gestation but has no ongoing medical conditions. Blood pressure is normal. Weight is at or above the 97th percentile and height is at the 97th percentile. BMI is at or above the 97th percentile. Comedonal acne is present on the forehead, cheeks, and nose but not on the back or chest. Fundoscopic examination and pupillary reaction are normal bilaterally. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. The areolae are enlarged, and breast tissue is palpable bilaterally. The abdomen is soft and nontender with no palpable masses. Coarse, dark pubic hair is noted. Bone age is 9 years. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A) Central precocious puberty
B) Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
C) McCune-Albright syndrome
D) Polycystic ovary syndrome
E) Premature adrenarche
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 22-year-old woman comes to the physician with her husband for intermittent dizziness, weakness, and unsteady gait for the last several weeks. She has also had visual loss and pain in the right eye that worsens with eye movement for the past 2 days. A year ago, the patient had tingling and numbness of her right hand accompanied by unsteadiness, which improved spontaneously after 3-4 days. She has no other medical problems and does not take any medications. The patient has no significant social or family history. Her temperature is 37.2 C (99 F) , blood pressure is 122/80 mm Hg, pulse is 82/min, and respirations are 16/min. On neurologic examination, her right eye has diminished visual acuity and an afferent pupillary defect. She also has a right arm intention tremor. Both lower extremities have spastic paresis, hyperreflexia, and positive Babinski sign. The patient has marked symptomatic improvement within a few days of initial treatment and is scheduled for physical therapy. Which of the following is the most appropriate long-term pharmacotherapy for this patient?
A) Beta-interferon
B) Low-dose prednisone
C) Pramipexole
D) Rivastigmine
E) Topiramate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 29-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine preventive examination. He is currently feeling well but states that he has always had "some dark spots" on his back. The patient has no family history of heart disease or cancer. He does not spend much time outdoors and had no prior sunburn. He does not smoke. Physical examination shows many pigmented lesions on his back as shown below. 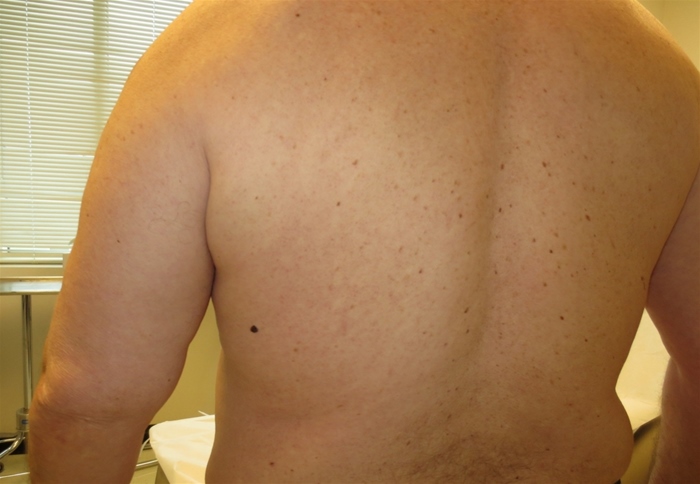 Which of the following is the best factor to assess risk of malignancy in a suspicious skin lesion in this patient?
Which of the following is the best factor to assess risk of malignancy in a suspicious skin lesion in this patient?
A) Café-au-lait lesion
B) Herald patch
C) Similarity to other skin lesions
D) "Stuck-on" appearance
E) Variability in color
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 65-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife due to severe upper-abdominal pain. The pain began suddenly 4 hours ago while he was watching television; it radiates to the back and is exacerbated by any movement. The patient has had gastroesophageal reflux disease for many years and has been taking over-the-counter antacids for symptom control. He also has hypertension, which is controlled with a thiazide diuretic. He walks 5 miles daily. The patient has been consuming large amounts of milk and other dairy products to relieve "burning" symptoms in his stomach. His temperature is 37.8 C (100 F) , blood pressure is 110/62 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 22/min. He lies flat and motionless on the bed. His mucous membranes are dry. Abdominal examination shows marked tenderness on superficial palpation. The patient does not allow any further palpation of the abdomen. Electrocardiogram shows sinus tachycardia. Which of the following is the best initial test for this patient?
A) Abdominal ultrasound
B) Chest and abdominal x-rays
C) Non-contrast CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis
D) Peritoneal lavage
E) Serum lipase and lactic acid levels
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 65-year-old woman comes to the physician with a 5-day history of rash and generalized itching. She initially developed a rash on her hand that spread to her feet, abdomen, and groin area. The patient also has intense pruritus that is worse at night. Her husband started having similar symptoms approximately 3 days ago. She works as a patient aide in a nursing home and has no other medical conditions. The patient had chickenpox when she was 7 years old. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Skin examination (image below) shows multiple small erythematous papules on her palms, sides of the fingers, wrists, lateral aspect of the feet, and periumbilical area. Her husband has similar lesions on the same body parts and also over the shaft of his penis. The remainder of her examination is within normal limits. 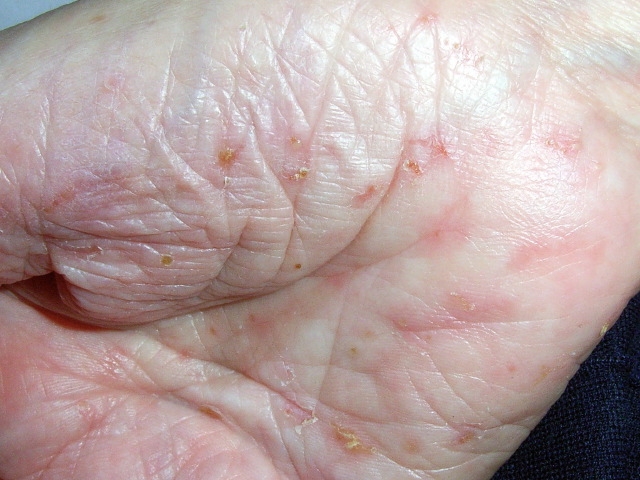 The patient's test results confirm the suspected diagnosis. Which of the following is the treatment of choice for this condition?
The patient's test results confirm the suspected diagnosis. Which of the following is the treatment of choice for this condition?
A) Oral valacyclovir for 7-10 days
B) Topical application of 1% hydrocortisone cream
C) Topical application of 1% terbinafine cream
D) Topical application of 5% permethrin cream
E) Topical application of acyclovir cream
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 57-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to difficulty speaking. Two hours ago, the patient was on the phone, at work, arguing with her daughter when she suddenly could not find her words. She had to end the call and then could not explain to co-workers what was wrong. The patient also noticed some weakness in her right arm. Her symptoms resolved on the way to the emergency department. She has not had similar symptoms before. Medical history includes hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F) , blood pressure is 155/90 mm Hg, pulse is 89/min, and respirations are 14/min. Complete neurologic examination shows no abnormalities. Blood glucose is normal. Noncontrast head CT scan is normal. The patient feels "back to normal" and requests to be discharged home. Which of the following is the most appropriate response by the physician?
A) "Because your examination and imaging are normal, you can be safely discharged. You should follow up with a neurologist within the month."
B) "Because your examination and imaging are normal, your symptoms were likely due to stress. No further workup is required."
C) "Despite a normal examination and imaging, a repeat CT scan in 6 hours is required to confirm that your symptoms were not due to a stroke."
D) "Despite a normal examination and imaging, you are having a stroke and your symptoms will likely return without thrombolysis."
E) "Despite a normal examination and imaging, you have an increased risk of stroke in the next few days and should have further testing."
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 24-year-old female is brought to the emergency department (ED) after an episode of witnessed seizure activity in her home. Her mother says that she has a history of generalized tonic-clonic seizures. She has been seizure-free for the past six years. She stopped taking all her medications two years ago. Her only current daily medication includes a multivitamin and an oral contraceptive pill. At the ED, she is given a loading dose of IV fosphenytoin and started on maintenance doses of oral phenytoin. Over the next three days, she does not have any further seizures. On the fourth day, she has developed a horizontal nystagmus. Her total phenytoin level on the same day is 20 mcg/mL (normal range is10-20 mcg/mL) . Repeat blood work returns with the same value. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
A) Stop phenytoin completely.
B) Stop phenytoin and repeat the drug levels in two days.
C) Continue treatment and repeat the drug levels in two days.
D) Discontinue the oral contraceptive pill.
E) Reduce the dose of phenytoin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 74-year-old Caucasian female is brought to the physician's office by her daughter because she has been coughing a lot for the past four weeks. Her cough is present throughout the day, and is most prominent at nighttime. She easily gets "out of breath" while walking around the house. She denies fevers, rigors, or sputum production. She has a past medical history of hypertension, atrial fibrillation, congestive heart failure with an ejection fraction of 35%, history of ventricular tachycardia, hypothyroidism, and vascular dementia. Her daily medications include aspirin, metoprolol, furosemide, levothyroxine, amiodarone, and multivitamins. She is allergic to ACE inhibitors and penicillin. On examination, her temperature is 37.2C (99F) , blood pressure is 110/82 mmHg, heart rate is 82/min, and respiratory rate is 20/min. Her mucous membranes are moist. There is no evidence of jugular venous distention. The lung examination reveals equal and normal air entry on both sides, with fine end inspiratory crackles heard at both the lung bases. Cardiovascular examination reveals a regular heart rhythm with no evidence of S3 gallop or murmurs. The rest of her physical examination is unremarkable. An initial chest x-ray reveals the presence of a normal cardiac silhouette. There is no evidence of pleural effusions. There are diffuse interstitial opacities seen bilaterally in the lower lung fields. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in her management?
A) Stop amiodarone
B) Increase the dose of furosemide (Lasix)
C) Discontinue metoprolol
D) Increase the dose of metoprolol
E) Start digoxin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 70-year-old man comes to the hospital due to fever, lethargy, productive cough, and shortness of breath. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, and peripheral vascular disease. His medications include warfarin, sotalol, insulin detemir, and lisinopril. Chest x-ray shows infiltrates in the left lung base. He is admitted and treated with azithromycin, ceftriaxone, and oxygen therapy. On examination, the patient is now awake and alert but oriented only to person. His blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, pulse is 65/min, and respirations are 14/min. Laboratory tests ordered 30 minutes before the first event are shown below. 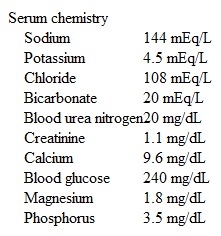 Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
A) Intravenous amiodarone
B) Intravenous lidocaine
C) Intravenous magnesium sulfate
D) Oral metoprolol
E) Temporary transvenous pacing
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 38-year-old woman, gravida 3 para 3, comes to the office for evaluation of vaginal discharge. She underwent a total laparoscopic hysterectomy 2 weeks ago for symptomatic uterine fibroids. The patient had an uncomplicated postoperative course. She was able to ambulate, void, and tolerate a regular diet within 12 hours of surgery and went home on postoperative day 1. However, over the past week, the patient has had persistent malodorous vaginal discharge, requiring her to change pads multiple times a day. She has also been voiding frequently in small volumes and is having increasing vulvar pruritus. She has had no fever, chills, hematuria, or dysuria. The patient has type 2 diabetes mellitus controlled with oral medications. Her other surgeries include 2 cesarean deliveries and laparoscopic cholecystectomy. The patient does not use alcohol or illicit drugs, but she smokes 1 or 2 cigarettes a day. Temperature is 37.1 C (98.8 F) , blood pressure is 130/86 mm Hg, and pulse is 80/min. BMI is 32 kg/m2. Abdominal incision sites are clean, dry, and intact. External genitalia are diffusely erythematous with superficial excoriations. Sterile speculum examination reveals a pool of clear, thin fluid in the vaginal vault. Nitrazine paper indicates a pH of 5. The vagina has a small, red area of granulation tissue over the anterior aspect; the cuff at the vaginal apex appears intact. On bimanual examination, there are no palpable masses in the vaginal vault. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A) Collect a sample for gonorrhea and chlamydia testing
B) Evaluate for a postsurgical vesicovaginal fistula
C) Order a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis
D) Perform urodynamic incontinence testing
E) Reassure the patient that the discharge is normal after a hysterectomy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 41-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to worsening shortness of breath. The patient had an uncomplicated spontaneous vaginal delivery 8 days ago and was discharged from the hospital 2 days after delivery. She says the dyspnea initially occurred only when walking, but now she "cannot catch her breath" even at rest. The patient has been breastfeeding her infant every 2-3 hours and says that due to this schedule she is fatigued throughout the day. She tries to sleep when her infant does but has worsening shortness of breath when lying down. The patient has had no fevers, chills, headaches, chest pain, or abdominal pain. She continues to have vaginal bleeding that partially saturates a sanitary napkin every 4-5 hours. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and has had no previous surgeries. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F) , blood pressure is 166/98 mm Hg, pulse is 70/min, and respirations are 24/min. Pulse oximetry is 92% on room air. Cardiac examination reveals a regular rhythm. Auscultation of the lungs reveals diffuse bilateral rales. There is 3+ pitting edema to the knees. Deep tendon reflexes have multiple beats of clonus. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A) Peripartum cardiomyopathy
B) Postpartum preeclampsia
C) Pulmonary embolism
D) Pulmonary hypertension
E) Sheehan syndrome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 46-year-old Caucasian female is hospitalized for upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage. She had two episodes of coffee ground colored vomiting during the past twelve hours. She has had intermittent episodes of passage of black stools over the last week. She visited a doctor two days ago and underwent an endoscopy that showed erosive gastritis and mild reflux esophagitis. Omeprazole therapy has been started. Her past medical history is significant for polycystic kidney disease and hypertension. Her most recent serum creatinine level is 4.1 mg/dL. Coagulation studies demonstrate the following results:  Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
A) Observation and supportive therapy
B) IV desmopressin
C) Platelet transfusion
D) Cryoprecipitate infusion
E) Immediate surgery
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 401 - 420 of 1121
Related Exams