A) in the mitochondrial inner membrane.
B) in the mitochondrial outer membrane.
C) in the plasma membrane.
D) in the cytoplasm.
E) in the bacterial outer membrane.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a mitochondrion,if the matrix ATP concentration is high,and the intermembrane space proton concentration is too low to generate sufficient proton-motive force,then
A) ATP synthase will increase the rate of ATP synthesis.
B) ATP synthase will stop working.
C) ATP synthase will hydrolyze ATP and pump protons into the intermembrane space.
D) ATP synthase will hydrolyze ATP and pump protons into the matrix.
E) ATP synthase will continue to function at a typical rate for that cell type.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. Exposing inner mitochondrial membranes to ultrasonic vibrations will disrupt the membranes.However,the fragments will reseal "inside out." These little vesicles that result can still transfer electrons from NADH to oxygen and synthesize ATP.If the membranes are agitated further,however,the ability to synthesize ATP is lost. -These inside-out membrane vesicles
A) will become acidic inside the vesicles when NADH is added.
B) will become alkaline inside the vesicles when NADH is added.
C) will make ATP from ADP and ℗ᵢ if transferred to a pH 4 buffered solution after incubation in a pH 7 buffered solution.
D) will hydrolyze ATP to pump protons out of the interior of the vesicle to the exterior.
E) will reverse electron flow to generate NADH from NAD⁺ in the absence of oxygen.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
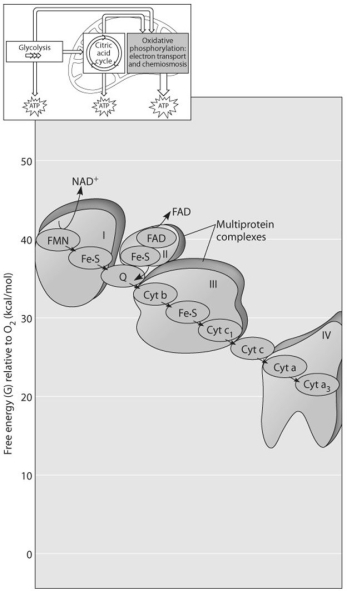 -The figure above shows the electron transport chain.Which of the following is the combination of substances that is initially added to the chain?
-The figure above shows the electron transport chain.Which of the following is the combination of substances that is initially added to the chain?
A) oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water
B) NAD⁺, FAD, and electrons
C) NADH, FADH₂, and protons
D) NADH, FADH₂, and O₂
E) oxygen and protons
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether oxygen (O) is present or absent?
A) electron transport
B) glycolysis
C) the citric acid cycle
D) oxidative phosphorylation
E) chemiosmosis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction? Pyruvate + NADH + H⁺ → Lactate + NAD⁺
A) oxygen
B) NADH
C) NAD⁺
D) lactate
E) pyruvate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events takes place in the electron transport chain?
A) the breakdown of glucose into two pyruvate molecules
B) the breakdown of an acetyl group to carbon dioxide
C) the extraction of energy from high-energy electrons remaining from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
D) substrate-level phosphorylation
E) reduction ADP to ATP
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You have collected samples from mud at the bottom of a nearby pond and have isolated different bacteria and protists from that community.You put the cultures in appropriate media in test tubes with loose-fitting lids and leave for the night,confident that your cultures will be growing well when you return. -The immediate energy source that drives ATP synthesis by ATP synthase during oxidative phosphorylation is the
A) oxidation of glucose and other organic compounds.
B) flow of electrons down the electron transport chain.
C) affinity of oxygen for electrons.
D) H⁺ concentration across the membrane holding ATP synthase.
E) transfer of phosphate to ADP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following occurs in the cytosol of a eukaryotic cell?
A) glycolysis and fermentation
B) fermentation and chemiosmosis
C) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
D) citric acid cycle
E) oxidative phosphorylation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why does the oxidation of organic compounds by molecular oxygen to produce CO₂ and water release free energy?
A) The covalent bonds in organic molecules and molecular oxygen have more kinetic energy than the covalent bonds in water and carbon dioxide.
B) Electrons are being moved from atoms that have a lower affinity for electrons (such as C) To atoms with a higher affinity for electrons (such as O) .
C) The oxidation of organic compounds can be used to make ATP.
D) The electrons have a higher potential energy when associated with water and CO₂ than they do in organic compounds.
E) The covalent bond in O₂ is unstable and easily broken by electrons from organic molecules.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron loses potential energy when it
A) shifts to a less electronegative atom.
B) shifts to a more electronegative atom.
C) increases its kinetic energy.
D) increases its activity as an oxidizing agent.
E) ᵐᵒᵛᵉˢ ᶠᵃʳᵗʰᵉʳ ᵃʷᵃʸ ᶠʳᵒᵐ ᵗʰᵉ ⁿᵘᶜˡᵉᵘˢ ᵒᶠ ᵗʰᵉ ᵃᵗᵒᵐ.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement best supports the hypothesis that glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway that originated before the last universal common ancestor of life on Earth?
A) Glycolysis is widespread and is found in the domains Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
B) Glycolysis neither uses nor needs O₂.
C) Glycolysis is found in all eukaryotic cells.
D) The enzymes of glycolysis are found in the cytosol rather than in a membrane-enclosed organelle.
E) Ancient prokaryotic cells, the most primitive of cells, made extensive use of glycolysis long before oxygen was present in Earth's atmosphere.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Phosphofructokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate,an early step of glycolysis.In the presence of oxygen,an increase in the amount of ATP in a cell would be expected to
A) inhibit the enzyme and thus slow the rates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
B) activate the enzyme and thus slow the rates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
C) inhibit the enzyme and thus increase the rates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
D) activate the enzyme and increase the rates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
E) inhibit the enzyme and thus increase the rate of glycolysis and the concentration of citrate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When electrons flow along the electron transport chains of mitochondria,which of the following changes occurs?
A) The pH of the matrix increases.
B) ATP synthase pumps protons by active transport.
C) The electrons gain free energy.
D) The cytochromes phosphorylate ADP to form ATP.
E) NAD⁺ is oxidized.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you were to add one of the eight citric acid cycle intermediates to the culture medium of yeast growing in the laboratory,what do you think would happen to the rates of ATP and carbon dioxide production?
A) There would be no change in ATP production, but we would observe an increased rate of carbon dioxide production.
B) The rates of ATP production and carbon dioxide production would both increase.
C) The rate of ATP production would decrease, but the rate of carbon dioxide production would increase.
D) Rates of ATP and carbon dioxide production would probably both decrease.
E) There would be not change to either ATP or carbon dioxide production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chemiosmotic ATP synthesis (oxidative phosphorylation) occurs in
A) all cells, but only in the presence of oxygen.
B) only eukaryotic cells, in the presence of oxygen.
C) only in mitochondria, using either oxygen or other electron acceptors.
D) all respiring cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, using either oxygen or other electron acceptors.
E) all cells, in the absence of respiration.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many oxygen molecules (O) are required each time a molecule of glucose (C₆H₁₂O) Is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water via aerobic respiration?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 6
D) 12
E) 30
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which co-enzyme is the most versatile electron acceptor in the cell?
A) Acetyl Co-A
B) FAD
C) NAD⁺
D) ATP
E) CytC
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Brown fat cells produce a protein called thermogenin in their mitochondrial inner membrane.Thermogenin is a channel for facilitated transport of protons across the membrane.What will occur in the brown fat cells when they produce thermogenin?
A) ATP synthesis and heat generation will both increase.
B) ATP synthesis will increase, and heat generation will decrease.
C) ATP synthesis will decrease, and heat generation will increase.
D) ATP synthesis and heat generation will both decrease.
E) ATP synthesis and heat generation will stay the same.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where does substrate-level phosphorylation occur?
A) in glycolysis
B) in the citric acid cycle
C) in both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
D) during oxidative phosphorylation
E) in glycolysis, the citric acid cycle and during oxidative phosphorylation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 128
Related Exams