A) 1/2
B) 1
C) 2
D) none
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which person might have a high basal metabolic rate?
A) a 70-year-old woman who knits for most of the day
B) a 30-year-old man who is a professional athlete
C) a 50-year-old woman who exercises twice a week
D) a 65-year-old man who walks three miles daily
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In cellular respiration, which molecule is released after the citric acid cycle?
A) oxygen
B) carbon dioxide
C) water
D) glucose
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why isn't the Body Mass Index (BMI) a perfectly reliable way to estimate your health?
A) It considers your height but not your weight.
B) It considers your weight but not your height.
C) It doesn't account for differences in muscle mass between individuals.
D) Body fat estimates are not correlated with the risk of illness and death.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of metabolic pathway requires oxygen?
A) aerobic
B) anaerobic
C) photosynthetic
D) fermentative
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement describes enzymes?
A) Enzymes are not very specific.
B) Enzymes are not affected by high heat, as proteins are.
C) Enzymes can be recycled and used over and over again.
D) Enzymes are "used up" during chemical reactions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would happen if activation energy barriers didn't exist?
A) Substrates would not bind properly to enzymes.
B) Chemical reactions in the body would never occur.
C) Coenzymes would not work, but enzyme function would not be affected.
D) All chemical reactions in the body would proceed whether they were needed or not.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
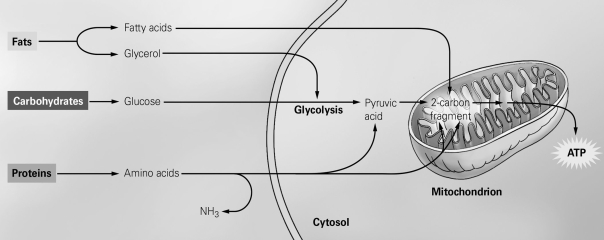 -The figure shows the different pathways taken by the subunits of macronutrients during cellular respiration. Which macronutrient subunit is never converted into pyruvic acid before entering the citric acid cycle?
-The figure shows the different pathways taken by the subunits of macronutrients during cellular respiration. Which macronutrient subunit is never converted into pyruvic acid before entering the citric acid cycle?
A) an amino acid
B) a fatty acid
C) glycerol
D) glucose
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lactose is a disaccharide found in milk. What makes some people "lactose intolerant" as adults?
A) Some people don't produce any enzymes, including the one needed to digest lactose.
B) Lactose can only be digested by people who produce enough lipase to digest it.
C) Lactose-intolerant people don't produce adequate amounts of lactase.
D) The active site of the lactose-digesting enzyme can vary from person to person.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which molecules are made during glycolysis?
A) NADH and ATP
B) ADP and NADPH
C) water and NAD⁺
D) oxygen and water
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a muscle cell contracts, what type of work is being powered by ATP?
A) chemical
B) transport
C) mechanical
D) potential
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the name of the protein channel where H⁺ ions escape into the matrix of the mitochondrion?
A) ATP synthase
B) OAA
C) grana
D) pyruvic acid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which process occurs inside the mitochondria?
A) glycolysis
B) fermentation
C) citric acid cycle and electron transport
D) glycolysis and electron transport
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are the proteins that catalyze chemical reactions in the body?
A) enzymes
B) coenzymes
C) antioxidants
D) high-density lipoproteins (HDLs)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Creatine phosphate (marketed as "creatine") is a popular supplement taken by weightlifters and other athletes. What might the phosphates in this supplement be expected to do?
A) They readily allow for the regeneration of ATP.
B) They break down glucose during the citric acid cycle.
C) They accept electrons at the end of the electron transport chain.
D) They ensure ATP is never broken down into ADP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which process provides the carbon dioxide you exhale?
A) aerobic respiration
B) anaerobic respiration
C) glycolysis
D) transpiration
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why does sour cream have a sharp, tart flavor
A) from the ADP produced by microbes during glycolysis
B) from the lactic acid, produced anaerobically by microbes
C) from the ethyl alcohol formed as the cream is broken down by microbes
D) from the citric acid released by microbes during the citric acid cycle
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If necessary, our muscles can rely upon an anaerobic (fermentative) pathway to metabolize glucose, but this can only last a short period of time. Why can't our cells survive very long under such anaerobic conditions?
A) Fermentation doesn't extract enough ATP from glucose to sustain our energy-craving cells.
B) Anaerobic conditions create a "carbon dioxide debt" that must be repaid before cells die.
C) The ethyl alcohol that builds up in muscles as a result of fermentation is a toxin.
D) Lactic acid causes the cell to die when it's exposed to even lower concentrations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does ATP provide energy to a cell?
A) It loses a phosphate group, releasing energy in the process.
B) It releases electrons, which are a source of energy.
C) It releases protons, which are used in the mitochondrion to create energy.
D) It shuttles electrons across the mitochondrial membrane to create potential energy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does recent research suggest about the relationships between weight and health risks?
A) People of normal weights have the lowest health risks.
B) People who are moderately obese have the highest health risks.
C) People who are slightly overweight have the lowest health risks.
D) People who are underweight have the highest health risks.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 63
Related Exams