A) Decreased density of subchondral bone
B) Osteophytes
C) Reduction in joint space
D) Narrowing of the neuroforamen
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pedicle sign refers to which of the following?
A) An increase in the visibility of a pedicle due to blastic disease
B) A decrease in the visibility of a pedicle due to lytic disease
C) The loss of contrast between a pedicle and the spinal canal due to an infection
D) The increase in contrast between a pedicle and the spinal canal due to hyperthyroidism
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
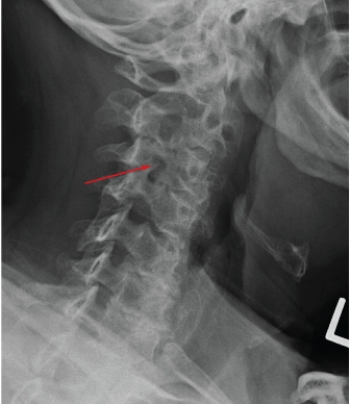 The arrow in the above image indicates:
The arrow in the above image indicates:
A) a pars interarticularis defect.
B) a Chance fracture.
C) an arthritic facet joint marginal osteophyte.
D) a calcified herniated disk.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which radiographic view is BEST for evaluating suspected rotational subluxation at C1/C2?
A) Open-mouth odontoid
B) Lateral C-spine with flexion and extension
C) AP view with cephalad angulation
D) Posterior oblique views
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
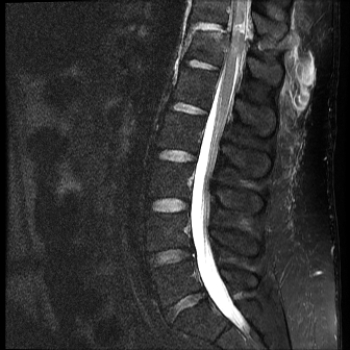 This image shows that the patient has which of the following?
This image shows that the patient has which of the following?
A) Severe dehydration of the vertebral disks
B) Transected spinal cord
C) Spinal cord tumor
D) Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) infection
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about disk herniations is INCORRECT?
A) Larger disk herniations always produce more severe radiculopathy than smaller disk herniations.
B) Midline disk herniations may produce less severe symptoms than foraminal herniations.
C) Chronic disk herniations are more likely to be associated with spondylosis than soft herniations.
D) They may contribute to the development of spinal stenosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
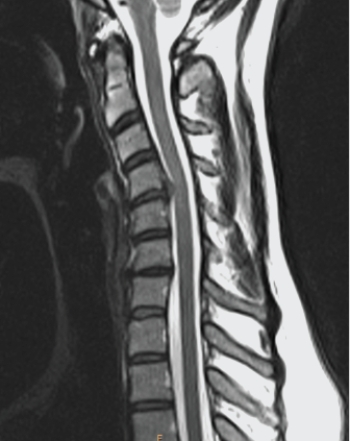 Your diagnosis based on the image shown is:
Your diagnosis based on the image shown is:
A) C4/C5 disk herniation.
B) dens fracture.
C) metastatic disease of the spine.
D) soft tissue neck injury.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
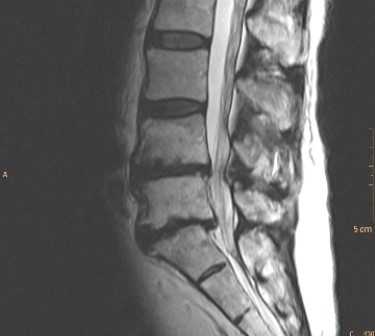 The image shows that this patient has:
The image shows that this patient has:
A) anterolisthesis of the sacrum.
B) retrolisthesis of L5 in relation to the sacrum.
C) bamboo spine.
D) sacral fracture.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
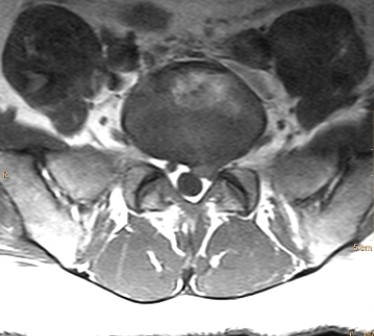 What would be your diagnosis based on the image of this patient?
What would be your diagnosis based on the image of this patient?
A) The patient has disk herniation with nerve compression.
B) The patient has left L5/S1 facet joint osteoarthritis.
C) The patient has bilateral L5 pedicle fractures.
D) The patient has cauda equina impingement syndrome.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
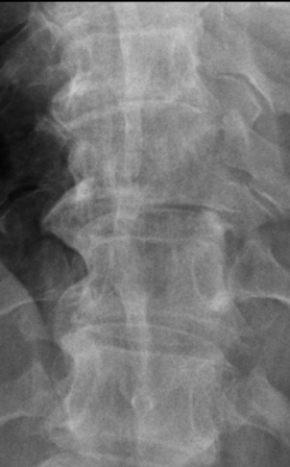 This image likely shows a patient with:
This image likely shows a patient with:
A) lytic bone disease.
B) scoliosis.
C) vertebral body compression fracture.
D) degenerative disk disease.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT associated with a bamboo spine?
A) Bridging syndesmophytes
B) Sacroilitis
C) Facet joint hypertrophy
D) HLA-B27 genotype
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
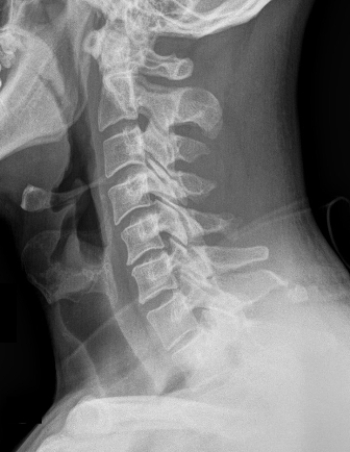 Which type of fracture(s) does the image indicate?
Which type of fracture(s) does the image indicate?
A) Chance fracture
B) Clay-shoveler's fracture
C) Hangman's fracture
D) Cervical facet fractures
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following radiographic views BEST displays a pars interarticularis fracture?
A) AP
B) PA
C) Lateral
D) Oblique
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
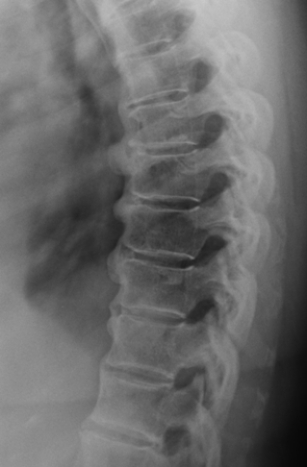 The above image depicts a patient with:
The above image depicts a patient with:
A) degenerative disk disease.
B) DISH.
C) lytic bone disease.
D) facet joint osteoarthritis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT true of degenerative disk disease?
A) It is typically associated with marginal osteophytes.
B) It is typically associated with disk dehydration.
C) It is always associated with back pain.
D) It does not require advanced imaging, such as MRI, for diagnosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following cervical fractures are typically stable?
A) Teardrop
B) Bilateral facet
C) Anterior wedge compression
D) Hangman's
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In patients who have severe spine trauma but do not show neurologic signs, the procedure of choice is:
A) CT.
B) MRI.
C) radiography.
D) ultrasound.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DISH is radiologically defined by the presence of:
A) overhanging osteophytes on four or more contiguous facet joints.
B) spondylolisthesis in four or more contiguous vertebrae.
C) bridging syndesmophytes on four or more contiguous vertebral bodies.
D) vacuum disks in four or more sequential disks.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Modic changes refer to:
A) facet joint osteoarthritis.
B) vacuum disks.
C) bone marrow changes associated with disk degeneration.
D) annular fibrosis tears.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
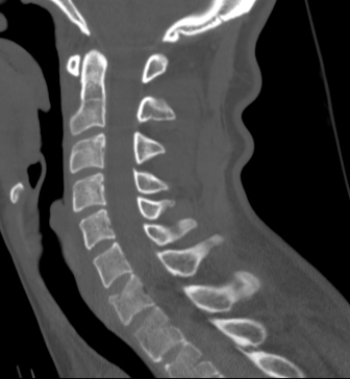 The patient in this image has which of the following?
The patient in this image has which of the following?
A) A fractured arch at C1
B) A fractured hyoid bone
C) A vertebral body compression fracture
D) A spinal metastatic disease
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 29
Related Exams