A) The bone matrix is very dense and contains deposits of calcium salts.
B) The matrix of the bone contains osteoclasts and chondroblasts.
C) Narrow channels pass through the matrix to allow for muscle attachment.
D) The matrix of bone is mostly collagen with very little calcium.
E) For strength, compact bone is organized into a meshwork of matrix called trabeculae.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How do sex hormones affect bone growth?
A) Testosterone stimulates osteoclast activity.
B) They cause ossification to be faster than cartilage replacement.
C) They stimulate the cleavage of hydroxyapetite.
D) They cause osteoporosis.
E) Estrogen causes slower epiphyseal closure.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Connective tissue fibers incorporated into bone tissue from ligaments are called
A) elastic fibers.
B) reticular fibers.
C) perforating fibers.
D) superficial fibers.
E) calcified fibers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While on a school skiing trip in Colorado, Heidi falls and breaks her tibia and fibula in a Pott's fracture. What would you expect as a prominent part of her clinical assessment several hours after the fall?
A) hypertension
B) tachycardia
C) erythema
D) hematoma
E) cyanosis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bone plays a central role in the regulation of blood levels of
A) potassium.
B) iron.
C) sulfate.
D) calcium.
E) sodium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most abundant mineral in the human body is
A) sodium.
B) potassium.
C) phosphorus.
D) calcium.
E) hydrogen.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The central canal of an osteon contains
A) bone marrow.
B) osteocytes.
C) concentric lamellae.
D) blood vessels.
E) lacunae.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The shaft of long bones is called the
A) epiphysis.
B) metaphysis.
C) diaphysis.
D) paraphysis.
E) endophysis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The carpal bones are examples of ________ bones.
A) long
B) short
C) flat
D) irregular
E) sesamoid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most abundant cell type in bone is
A) osteoclasts.
B) osteoblasts.
C) osteolytes.
D) osteoprogenitor cells.
E) osteocytes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Small bones that fill gaps between bones of the skull are called ________ bones.
A) irregular
B) sesamoid
C) sutural
D) sagittal
E) tendon
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 6-1 The Structure of Compact Bone
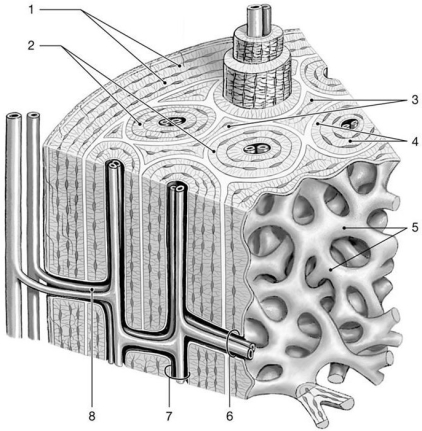 Use Figure 6-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structures labeled "4."
Use Figure 6-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structures labeled "4."
A) concentric lamellae
B) circumferential lamellae
C) interstitial lamellae
D) trabeculae
E) periosteum
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following chemicals is not present in bone?
A) calcium phosphate
B) collagen fibers
C) calcium carbonate
D) chondroitin sulfate
E) hydroxyapatite
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Intramembranous ossification
A) produces flat bones, as in the bones of the roof of the skull.
B) explains how a juvenile's bone can grow in length.
C) occurs in the diaphysis of a long bone.
D) occurs inside a bag of cartilage.
E) occurs in all bones before birth.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 6-1 The Structure of Compact Bone
 Use Figure 6-1 to answer the following questions:
-The structure labeled "3" is the result of which process?
Use Figure 6-1 to answer the following questions:
-The structure labeled "3" is the result of which process?
A) bone cells adding matrix between existing osteons
B) surface growth of bone
C) remodeling of compact bone
D) remodeling of spongy bone
E) osteoporosis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If osteoclasts are more active than osteoblasts, bones will become
A) denser.
B) thicker.
C) osteopenic.
D) stronger.
E) calcified.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If blood calcium levels drop below 8.5 mg/dL which hormone is likely to be activated?
A) parathyroid hormone
B) estrogen
C) calcitonin
D) calcitriol
E) both calcitriol and parathyroid hormone
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When production of sex hormones increases at puberty, epiphyseal plates
A) widen.
B) become narrower.
C) increase slowly.
D) accelerate rapidly, but mostly in thickness.
E) are hardly affected.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aging has what effect on the skeletal system?
A) progressive loss of processes and tuberosities
B) fusion of joints, especially in the vertebral column
C) loss of calcium and collagen fibers from matrix
D) increase in the number of cranial foramina
E) increase in adipose tissue in epiphyses
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Damage to a bone because of extreme load, sudden impact, or stresses applied from an unusual directioniscalled a
A) dislocation.
B) contortion.
C) rupture.
D) fragmentation.
E) fracture.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 165
Related Exams