A) positively charged.
B) negatively charged.
C) without charge.
D) hydrophobic.
E) nonpolar.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is completely correct?
A) H₂CO₃ is a weak acid, and NaOH is a weak base (alkali) .
B) H₂CO₃ is a strong acid, and NaOH is a strong base (alkali) .
C) NH₃ is a weak base (alkali) , and H₂CO₃ is a strong acid.
D) NH₃ is a weak base (alkali) , and HCl is a strong acid.
E) NH₃ is a strong base (alkali) , and HCl is a weak acid.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The molecular mass of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) is 180 g. Which of the following procedures should you carry out to make a 0.5 M solution of glucose?
A) Dissolve 0.5 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of solution is 1 L.
B) Dissolve 90 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
C) Dissolve 180 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
D) Dissolve 0.5 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
E) Dissolve 180 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The bonds that are broken when water vaporizes are
A) ionic bonds.
B) hydrogen bonds between water molecules.
C) covalent bonds between atoms within water molecules.
D) polar covalent bonds.
E) nonpolar covalent bonds
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A given solution contains 0.0001(10⁻⁴) moles of hydrogen ions [H⁺] per liter. Which of the following best describes this solution?
A) acidic: H⁺ acceptor
B) basic: H⁺ acceptor
C) acidic: H⁺ donor
D) basic: H⁺ donor
E) neutral
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
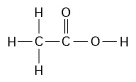 -How many grams of the molecule in Figure 3.2 would be required to make 1 L of a 0.5 M solution of the molecule?
(Carbon = 12, Oxygen = 16, Hydrogen = 1)
-How many grams of the molecule in Figure 3.2 would be required to make 1 L of a 0.5 M solution of the molecule?
(Carbon = 12, Oxygen = 16, Hydrogen = 1)
A) 29
B) 30
C) 60
D) 150
E) 342
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Measurements show that the pH of a particular lake is 4.0. What is the hydrogen ion concentration of the lake?
A) 4.0 M
B) 10⁻¹⁰ M
C) 10⁻⁴ M
D) 10⁴ M
E) 4%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A small birthday candle is weighed, then lighted and placed beneath a metal can containing 100 mL of water. Careful records are kept as the temperature of the water rises. Data from this experiment are shown on the graph. What amount of heat energy is released in the burning of candle wax?
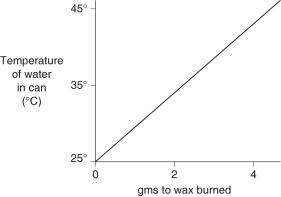
A) 0.5 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
B) 5 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
C) 10 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
D) 20 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
E) 50 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following takes place as an ice cube cools a drink?
A) Molecular collisions in the drink increase.
B) Kinetic energy in the drink decreases.
C) A calorie of heat energy is transferred from the ice to the water of the drink.
D) The specific heat of the water in the drink decreases.
E) Evaporation of the water in the drink increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Water is able to form hydrogen bonds because
A) oxygen has a valence of 2.
B) the water molecule is shaped like a tetrahedron.
C) the bonds that hold together the atoms in a water molecule are polar covalent bonds.
D) the oxygen atom in a water molecule has a weak positive charge.
E) each of the hydrogen atoms in a water molecule is weakly negative in charge.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following ionizes completely in solution and is considered to be a strong acid?
A) NaOH
B) HCl
C) NH₃
D) H₂CO₃
E) CH₃COOH
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pure, freshly-distilled water has a pH of 7. This means that
A) there are no H⁺ ions in the water.
B) there are no OH⁻ ions in the water.
C) the concentration of H⁺ ions in the water equals the concentration of OH⁻ ions in the water.
D) the concentration of H⁺ ions in the water is 7 times the concentration of OH⁻ ions in the water.
E) The concentration of OH⁻ ions in the water is 7 times the concentration of H⁺ ions in the water.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following solutions has the greatest concentration of hydroxyl ions [OH⁻]?
A) lemon juice at pH 2
B) vinegar at pH 3
C) tomato juice at pH 4
D) urine at pH 6
E) seawater at pH 8
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have a freshly-prepared 1M solution of glucose in water. You carefully pour out a 100 mL sample of that solution. How many glucose molecules are included in that 100 mL sample?
A) 6.02 × 10²³
B) 3.01 × 10²³
C) 6.02 × 10²⁴
D) 12.04 × 10²³
E) 6.02 × 10²²
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the pH of a solution is decreased from 9 to 8, it means that the
A) concentration of H⁺ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what it was at pH 9.
B) concentration of H⁺ has increased 10-fold (10X) compared to what it was at pH 9.
C) concentration of OH⁻ has increased 10-fold (10X) compared to what it was at pH 9.
D) concentration of OH⁻ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what it was at pH 9.
E) Both B and D are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following effects is produced by the high surface tension of water?
A) Lakes don't freeze solid in winter, despite low temperatures.
B) A water strider can walk across the surface of a small pond.
C) Organisms resist temperature changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reactions.
D) Water can act as a solvent.
E) The pH of water remains exactly neutral.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One liter of a solution pH 9 has how many more hydroxyl ions (OH⁻) than 1 L of a solution of pH 4?
A) 5 times more
B) 100 times more
C) 1,000 times more
D) 10,000 times more
E) 100,000 times more
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Research indicates that acid precipitation can damage living organisms by
A) buffering aquatic systems such as lakes and streams.
B) decreasing the H⁺ concentration of lakes and streams.
C) increasing the OH⁻ concentration of lakes and streams.
D) washing away certain mineral ions that help buffer soil solution and are essential nutrients for plant growth.
E) both B and C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have a freshly-prepared 0.1M solution of glucose in water. Each liter of this solution contains how many glucose molecules?
A) 6.02 × 10²³
B) 3.01 × 10²³
C) 6.02 × 10²⁴
D) 12.04 × 10²³
E) 6.02 × 10²²
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the pH of a solution with a hydrogen ion [H⁺] concentration of 10⁻⁸ M?
A) pH 2
B) pH 4
C) pH 6
D) pH 8
E) pH 10
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 66
Related Exams