A) savanna
B) temperate broadleaf forest
C) temperate grassland
D) tropical rain forest
E) coniferous forest
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which lake zone would be absent in a very shallow lake?
A) benthic zone
B) aphotic zone
C) pelagic zone
D) littoral zone
E) limnetic zone
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An area in which different terrestrial biomes grade into each other is known as a(n)
A) littoral zone.
B) vertically stratified canopy.
C) ecotone.
D) abyssal zone.
E) cline.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following diagram from the text showing the spread of the cattle egret, Bulbulcus ibis, since its arrival in the New World, to answer the following question.
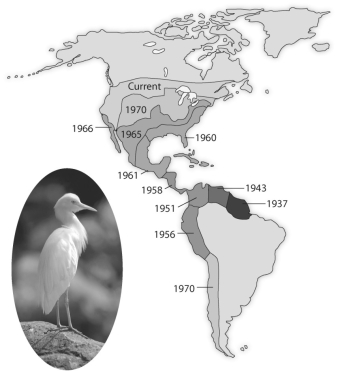 Figure 52.1
-Where would an ecologist find the most phytoplankton in a lake?
Figure 52.1
-Where would an ecologist find the most phytoplankton in a lake?
A) profundal zone
B) benthic zone
C) photic zone
D) oligotrophic zone
E) aphotic zone
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When climbing a mountain, we can observe transitions in biological communities that are analogous to the changes
A) in biomes at different latitudes.
B) at different depths in the ocean.
C) in a community through different seasons.
D) in an ecosystem as it evolves over time.
E) across the United States from east to west.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two plant species live in the same biome but on different continents. Although the two species are not at all closely related, they may appear quite similar as a result of
A) parallel evolution.
B) convergent evolution.
C) allopatric speciation.
D) introgression.
E) gene flow.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes the effect of climate on biome distribution?
A) Knowledge of annual temperature and precipitation is sufficient to predict which biome will be found in an area.
B) Fluctuation of environmental variables is not important if areas have the same annual temperature and precipitation means.
C) It is not only the average climate that is important in determining biome distribution, but also the pattern of climatic variation.
D) Temperate forests, coniferous forests, and grasslands all have the same mean annual temperatures and precipitation.
E) Correlation of climate with biome distribution is sufficient to determine the cause of biome patterns.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following diagram from the text showing the spread of the cattle egret, Bulbulcus ibis, since its arrival in the New World, to answer the following question.
 Figure 52.1
-Phytoplankton is most frequently found in which of the following zones?
Figure 52.1
-Phytoplankton is most frequently found in which of the following zones?
A) oligotrophic
B) photic
C) benthic
D) abyssal
E) aphotic
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ecology as a discipline directly deals with all of the following levels of biological organization except
A) population.
B) cellular.
C) organismal.
D) ecosystem.
E) community.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As climate changes because of global warming, species' ranges in the northern hemisphere may move northward. The trees that are most likely to avoid extinction in such an environment are those that
A) have seeds that are easily dispersed by wind or animals.
B) have thin seed coats.
C) produce well-provisioned seeds.
D) have seeds that become viable only after a forest fire.
E) disperse many seeds in close proximity to the parent tree.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Trees are not usually found in the tundra biome because of
A) insufficient annual precipitation.
B) acidic soils.
C) extreme winter temperatures.
D) overbrowsing by musk ox and caribou.
E) permafrost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following diagram from the text showing the spread of the cattle egret, Bulbulcus ibis, since its arrival in the New World, to answer the following question.
 Figure 52.1
-Species introduced to new geographic locations
Figure 52.1
-Species introduced to new geographic locations
A) are usually successful in colonizing the area.
B) always spread because they encounter no natural predators.
C) increase the diversity and therefore the stability of the ecosystem.
D) can out-compete and displace native species for biotic and abiotic resources.
E) are always considered pests by ecologists.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following levels of organization is arranged in the correct sequence from most to least inclusive?
A) community, ecosystem, individual, population
B) ecosystem, community, population, individual
C) population, ecosystem, individual, community
D) individual, population, community, ecosystem
E) individual, community, population, ecosystem
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fire suppression by humans
A) will always result in an increase in the species diversity in a given biome.
B) can change the species composition within biological communities.
C) will result ultimately in sustainable production of increased amounts of wood for human use.
D) is necessary for the protection of threatened and endangered forest species.
E) is a management goal of conservation biologists to maintain the healthy condition of biomes.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Deserts typically occur in a band at 30 degrees north and south latitude because
A) descending air masses tend to be cool and dry.
B) trade winds have a little moisture.
C) water is heavier than air and is not carried far over land.
D) ascending air tends to be moist.
E) these locations get the most intense solar radiation of any location on Earth
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
"How does the foraging of animals on tree seeds affect the distribution and abundance of the trees? " This question
A) would require an elaborate experimental design to answer.
B) is difficult to answer because a large experimental area would be required.
C) is difficult to answer because a long-term experiment would be required.
D) is a question that a present-day ecologist would be likely to ask.
E) A, B, C and D are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the examples below provides appropriate abiotic and biotic factors that might determine the distribution of the species in question?
A) The amount of nitrate and phosphate in the soil and wild flower abundance and diversity
B) The number of frost-free days and competition between species of introduced grasses and native alpine grasses
C) Increased predation and decreased food availability and a prairie dog population after a prairie fire
D) Available sunlight and increased salinity in the top few meters of the ocean and the abundance and diversity of phytoplankton communities
E) The pH and dissolved oxygen concentration and the streams in which brook trout can live
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Imagine some cosmic catastrophe jolts Earth so that its axis is perpendicular to the orbital plane between Earth and the sun. The most obvious effect of this change would be
A) the elimination of tides.
B) an increase in the length of night.
C) an increase in the length of a year.
D) a decrease in temperature at the equator.
E) the elimination of seasonal variation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following areas of study focuses on the exchange of energy, organisms, and materials between ecosystems?
A) population ecology
B) organismal ecology
C) landscape ecology
D) ecosystem ecology
E) community ecology
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Turnover of water in temperate lakes during the spring and fall is made possible by which of the following?
A) warm, less dense water layered at the top
B) cold, more dense water layered at the bottom
C) a distinct thermocline between less dense warm water and cold, dense water.
D) the density of water changes as seasonal temperatures change.
E) currents generated by nektonic animals
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 71
Related Exams