A) unipolar.
B) bipolar.
C) anaxonic.
D) multipolar.
E) tripolar.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 12-2 The Nerve Action Potential
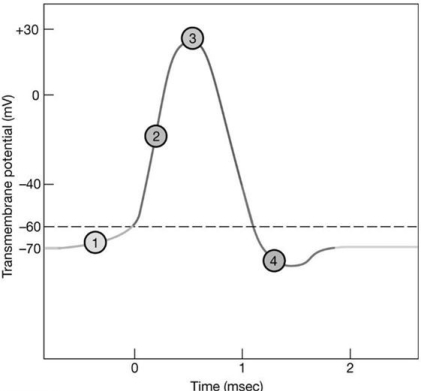 Use Figure 12-2 to answer the following questions:
-Which area of the graph shows when membrane potential approaches the potassium equilibrium potential?
Use Figure 12-2 to answer the following questions:
-Which area of the graph shows when membrane potential approaches the potassium equilibrium potential?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ________ division of the nervous system carries motor commands to muscles and glands.
A) spinal
B) peripheral
C) autonomic
D) afferent
E) efferent
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ line the brain ventricles and spinal canal.
A) Astrocytes
B) Satellite cells
C) Oligodendrocytes
D) Microglia
E) Ependymal cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Small, wandering cells that engulf cell debris and pathogens in the CNS are called
A) astrocytes.
B) satellite cells.
C) oligodendrocytes.
D) microglia.
E) ependymal cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The presence of ________ dramatically increases the speed at which an action potential moves along an axon.
A) a capsule
B) plasma protein
C) neurilemma
D) glial cells
E) myelin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ions can move across the plasma membrane in which of the following ways?
A) through voltage-gated channels as in the action potential
B) through passive or leak channels
C) by ATP-dependent ion pumps like the sodium-potassium exchange pump
D) through chemically gated channels as in neuromuscular transmission
E) All of the answers are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When pressure is applied to neural tissue, all of the following effects are possible except
A) a decrease in blood flow.
B) a decrease in available oxygen.
C) a change in neuron excitability.
D) glial cells degenerate.
E) neurons are triggered to divide.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not involved in creating the resting membrane potential of a neuron?
A) diffusion of potassium ions out of the cell
B) diffusion of sodium ions into the cell
C) membrane permeability for sodium ions greater than potassium ions
D) membrane permeability for potassium ions greater than sodium ions
E) The interior of the plasma membrane has an excess of negative charges.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During repolarization of a neuron
A) sodium ions move out of the cell.
B) potassium ions move out of the cell.
C) potassium ions move into the cell.
D) both sodium and potassium ions move into the cell.
E) sodium ions move into the cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 12-1 The Neuron
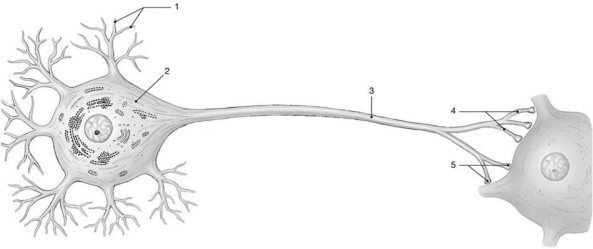 Use Figure 12-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structure labeled "4."
Use Figure 12-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structure labeled "4."
A) synaptic terminals
B) telodendria
C) dendritic spines
D) collateral branches
E) axons
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a function of astrocytes?
A) They create a three dimensional framework for the CNS.
B) They maintain the blood-brain barrier.
C) They guide neuron development.
D) They rebuild injured neurons.
E) They adjust the composition of the interstitial tissue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ________ principle states that the size and speed of the action potential are independent of the stimulus strength.
A) threshold
B) all-or-none
C) summation
D) polarization
E) potential
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of synapse is most common in the nervous system?
A) chemical
B) electrical
C) mechanical
D) processing
E) radiative
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In-Text Figure Based Questions -The axon hillock is a region between what two general regions of a neuron? (Figure 12-2)
A) dendrites and cell body
B) nucleolus and nucleus
C) axon and axon terminals
D) cell body and axon
E) dendrites and telodendria
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sensory information from skeletal muscles travels over ________ fibers.
A) type A
B) type B
C) type C
D) type D
E) type E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ are the most numerous type of neuron in the CNS.
A) Sensory neurons
B) Motor neurons
C) Unipolar neurons
D) Bipolar neurons
E) Interneurons
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Type ________ fibers have the largest diameter axons.
A) S
B) F
C) A
D) B
E) C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about threshold for an action potential?
A) It is more positive than the resting membrane potential.
B) Voltage-gated potassium channels begin to close.
C) Voltage-gated potassium channels begin to open.
D) The membrane begins to hyperpolarize.
E) Threshold for a typical neuron is approximately -30 mV.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neurons that have one axon and one dendrite, with the soma in between, are called
A) anaxonic.
B) unipolar.
C) bipolar.
D) tripolar.
E) multipolar.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 158
Related Exams