A) Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by making the reaction more exergonic.
B) Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy barrier.
C) Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by reducing the rate of reverse reactions.
D) Enzymes change the equilibrium point of the reactions they catalyze.
E) Enzymes make the rate of a reaction independent of substrate concentrations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When chemical, transport, or mechanical work is done by an organism, what happens to the heat generated?
A) It is used to power yet more cellular work.
B) It is used to store energy as more ATP.
C) It is used to generate ADP from nucleotide precursors.
D) It is lost to the environment.
E) It is transported to specific organs such as the brain.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Organisms can increase their order, seemingly defying the second law of thermodynamics. This can only be accomplished if they
A) are a closed system.
B) constantly take energy from their surroundings and thus increase disorder in the environment.
C) constantly take energy from their surroundings and thus decrease disorder in the environment.
D) generate heat and increase disorder in the universe.
E) have a negative Gibbs free energy value.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Protein kinases are enzymes that transfer the terminal phosphate from ATP to an amino acid residue on the target protein. Many are located on the plasma membrane as integral membrane proteins or peripheral membrane proteins. What purpose may be served by their plasma membrane localization?
A) ATP is more abundant near the plasma membrane.
B) They can more readily encounter and phosphorylate other membrane proteins.
C) Membrane localization lowers the activation energy of the phosphorylation reaction.
D) They flip back and forth across the membrane to access target proteins on either side.
E) They require phospholipids as a cofactor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Living organisms increase in complexity as they grow, resulting in a decrease in the entropy of an organism. How does this relate to the second law of thermodynamics?
A) Living organisms do not obey the second law of thermodynamics, which states that entropy must increase with time.
B) Life obeys the second law of thermodynamics because the decrease in entropy as the organism grows is exactly balanced by an increase in the entropy of the universe.
C) Living organisms do not follow the laws of thermodynamics.
D) As a consequence of growing, organisms cause a greater increase in entropy in their environment than the decrease in entropy associated with their growth.
E) Living organisms are able to transform energy into entropy.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence: Catabolism is to anabolism as ________ is to ________.
A) exergonic; spontaneous
B) exergonic; endergonic
C) free energy; entropy
D) work; energy
E) entropy; enthalpy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + 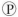 ᵢ, the free energy change is -7.3 kcal/mol under standard conditions (1 M concentration of both reactants and products) . In the cellular environment, however, the free energy change is about -13 kcal/mol. What can we conclude about the free energy change for the formation of ATP from ADP and
ᵢ, the free energy change is -7.3 kcal/mol under standard conditions (1 M concentration of both reactants and products) . In the cellular environment, however, the free energy change is about -13 kcal/mol. What can we conclude about the free energy change for the formation of ATP from ADP and 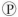 ᵢ under cellular conditions?
ᵢ under cellular conditions?
A) It is +7.3 kcal/mol.
B) It is less than +7.3 kcal/mol.
C) It is about +13 kcal/mol.
D) It is greater than +13 kcal/mol.
E) The information given is insufficient to deduce the free energy change.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Protein kinases are enzymes that catalyze phosphorylation of target proteins at specific sites, whereas protein phosphatases catalyze removal of phosphate(s) from phosphorylated proteins. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation can function as an on-off switch for a protein's activity, most likely through
A) the change in a protein's charge leading to a conformational change.
B) the change in a protein's charge leading to cleavage.
C) a change in the optimal pH at which a reaction will occur.
D) a change in the optimal temperature at which a reaction will occur.
E) the excision of one or more peptides.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an enzyme in solution is saturated with substrate, the most effective way to obtain a faster yield of products is to
A) add more of the enzyme.
B) heat the solution to 90°C.
C) add more substrate.
D) add an allosteric inhibitor.
E) add a noncompetitive inhibitor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an enzyme is added to a solution where its substrate and product are in equilibrium, what will occur?
A) Additional product will be formed.
B) Additional substrate will be formed.
C) The reaction will change from endergonic to exergonic.
D) The free energy of the system will change.
E) Nothing; the reaction will stay at equilibrium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the difference (if any) between the structure of ATP and the structure of the precursor of the A nucleotide in RNA?
A) The sugar molecule is different.
B) The nitrogen-containing base is different.
C) The number of phosphates is three instead of one.
D) The number of phosphates is three instead of two.
E) There is no difference.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reactants capable of interacting to form products in a chemical reaction must first overcome a thermodynamic barrier known as the reaction's
A) entropy.
B) activation energy.
C) endothermic level.
D) equilibrium point.
E) free-energy content.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions are based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in the figure below.
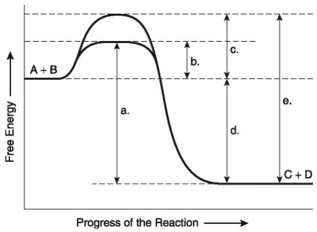 -Which of the following represents the activation energy required for a noncatalyzed reaction in the figure above?
-Which of the following represents the activation energy required for a noncatalyzed reaction in the figure above?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Besides turning enzymes on or off, what other means does a cell use to control enzymatic activity?
A) cessation of cellular protein synthesis
B) localization of enzymes into specific organelles or membranes
C) exporting enzymes out of the cell
D) connecting enzymes into large aggregates
E) hydrophobic interactions
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increasing the substrate concentration in an enzymatic reaction could overcome which of the following?
A) denaturization of the enzyme
B) allosteric inhibition
C) competitive inhibition
D) saturation of the enzyme activity
E) insufficient cofactors
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of potential rather than kinetic energy?
A) the muscle contractions of a person mowing grass
B) water rushing over Niagara Falls
C) light flashes emitted by a firefly
D) a molecule of glucose
E) the flight of an insect foraging for food
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. A patient comes into the emergency room having accidentally ingested methanol (a component in anti-freeze) . Methanol toxicity can lead to blindness, neurological issues, or death and must be treated quickly. Methanol is oxidized by the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) to produce formaldehyde which is then converted to formic acid. ADH has a higher affinity to ethanol, where it functions to oxidize ethanol into acetaldehyde with the end product of the pathway being acetic acid (vinegar) . -Knowing what you know about enzyme function, what would be your suggested course of treatment?
A) Give plenty of fluids and monitor the patient.
B) Give the patient acetic acid.
C) Give the patient high levels of ethanol and carefully monitor.
D) Keep the patient warm and rested and let it take its course.
E) Give the patient an enzyme inhibitor so no formaldehyde is produced.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For living organisms, which of the following is an important consequence of the first law of thermodynamics?
A) The energy content of an organism is constant.
B) The organism ultimately must obtain all of the necessary energy for life from its environment.
C) The entropy of an organism decreases with time as the organism grows in complexity.
D) Organisms grow by converting energy into organic matter.
E) Life does not obey the first law of thermodynamics.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A number of systems for pumping ions across membranes are powered by ATP. Such ATP-powered pumps are often called ATPases although they don't often hydrolyze ATP unless they are simultaneously transporting ions. Because small increases in calcium ions in the cytosol can trigger a number of different intracellular reactions, cells keep the cytosolic calcium concentration quite low under normal conditions, using ATP-powered calcium pumps. For example, muscle cells transport calcium from the cytosol into the membranous system called the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) . If a resting muscle cell's cytosol has a free calcium ion concentration of 10⁻⁷ while the concentration in the SR is 10⁻², then how is the ATPase acting?
A) ATPase activity must be powering an inflow of calcium from the outside of the cell into the SR.
B) ATPase activity must be transferring ![]() ᵢ to the SR to enable this to occur.
ᵢ to the SR to enable this to occur.
C) ATPase activity must be pumping calcium from the cytosol to the SR against the concentration gradient.
D) ATPase activity must be opening a channel for the calcium ions to diffuse back into the SR along the concentration gradient.
E) ATPase activity must be routing calcium ions from the SR to the cytosol, and then to the cell's environment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following metabolic processes can occur without a net influx of energy from some other process?
A) ADP + ![]() ᵢ → ATP + H₂O
ᵢ → ATP + H₂O
B) C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂ → 6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O
C) 6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂
D) amino acids → protein
E) glucose + fructose → sucrose
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 88
Related Exams