A) 200 milliseconds or 0.20 seconds duration.
B) 40 milliseconds or 0.04 seconds duration.
C) 3 seconds duration.
D) millivolts of amplitude.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When assessing the 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) or a rhythm strip,it is helpful to understand that the electrical activity is viewed in relation to the positive electrode of that particular lead.When an electrical signal is aimed directly at the positive electrode,the inflection will be:
A) negative.
B) upside down.
C) upright.
D) equally positive and negative.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse is reading the cardiac monitor and notes that the patient's heart rhythm is extremely irregular and there are no discernible P waves.The ventricular rate is 90 beats per minute,and the patient is hemodynamically stable.The nurse realizes that the patient's rhythm is:
A) atrial fibrillation.
B) atrial flutter.
C) atrial flutter with rapid ventricular response.
D) junctional escape rhythm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm: 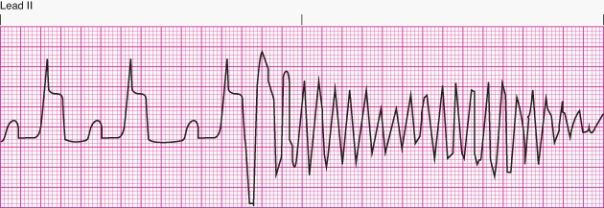
A) R-on-T phenomenon
B) Sinus rhythm with multifocal premature ventricular contractions
C) Nonsustained ventricular tachycardia
D) Sinus rhythm with bigeminal premature ventricular contractions
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The patient is asymptomatic but is diagnosed with second-degree heart block Mobitz I.The patient is on digitalis medication at home.The nurse should expect that:
A) the patient has had an anterior wall myocardial infarction.
B) the physician will order the digitalis to be continued in the hospital.
C) a digitalis level would be ordered upon admission.
D) the patient will require a transcutaneous pacemaker.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The patient's heart rhythm shows an inverted P wave with a PR interval of 0.06 seconds.The heart rate is 54 beats per minute.The nurse recognizes the rhythm as a junctional escape rhythm,and understands that the rhythm is due to the:
A) loss of sinus node activity.
B) increased rate of the AV node.
C) increased rate of the SA node.
D) decreased rate of the AV node.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse notes the following rhythm on the heart monitor.The patient is unresponsive and not breathing.The nurse should 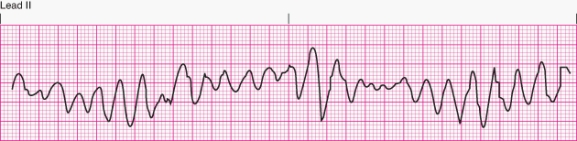
A) treat with intravenous amiodarone or lidocaine.
B) provide emergent basic and advanced life support.
C) provide electrical cardioversion.
D) ignore the rhythm because it is benign.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm: 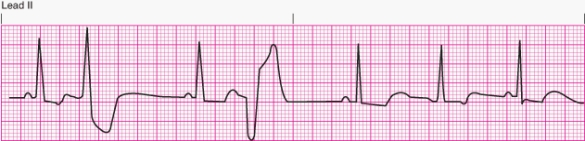
A) Sinus rhythm with multifocal premature ventricular contractions
B) Sinus rhythm with unifocal premature ventricular contractions
C) Sinus rhythm with bigeminal premature ventricular contractions
D) Sinus rhythm with paired premature ventricular contractions (couplets)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm: 
A) First-degree AV block
B) Second-degree AV block Mobitz I (Wenckebach phenomenon)
C) Second-degree AV block Mobitz II
D) Third-degree AV block (complete heart block)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm: 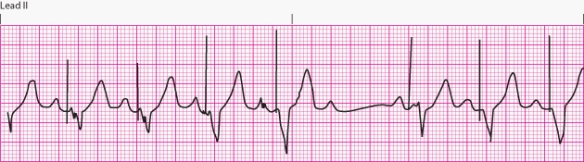
A) Normal pacemaker function
B) Failure to capture.
C) Failure to pace.
D) Failure to sense.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm: 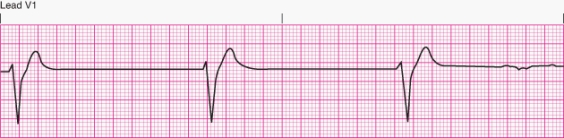
A) Idioventricular rhythm
B) Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
C) Ventricular tachycardia
D) Ventricular fibrillation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm: 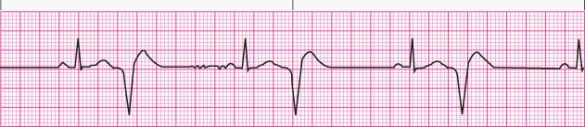
A) Sinus rhythm with multifocal premature ventricular contractions
B) Sinus rhythm with unifocal premature ventricular contractions
C) Sinus rhythm with bigeminal premature ventricular contractions
D) Sinus rhythm with paired premature ventricular contractions (couplets)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm: 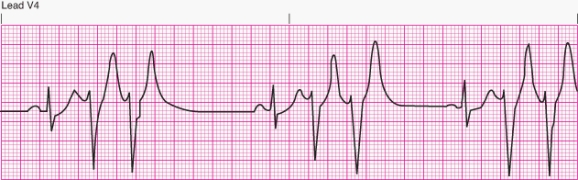
A) Sinus rhythm with multifocal premature ventricular contractions
B) Sinus rhythm with unifocal premature ventricular contractions
C) Sinus rhythm with bigeminal premature ventricular contractions
D) Sinus rhythm with paired premature ventricular contractions (couplets)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The patient has a permanent pacemaker inserted.The provider has set the pacemaker to the demand mode at a rate of 60 beats per minute.The nurse realizes that:
A) the pacemaker will pace only if the patient's intrinsic heart rate is less than 60 beats per minute.
B) the demand mode often competes with the patient's own rhythm.
C) the demand mode places the patient at risk for the R-on-T phenomenon.
D) the fixed rate mode is safer and is the mode of choice.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the functions of the atrioventricular (AV) node is to:
A) pace the heart if the ventricles fail.
B) slow the impulse arriving from the SA node.
C) send the impulse to the SA node.
D) allow for ventricular filling during systole.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The patient is in chronic junctional escape rhythm with no atrial activity noted.Studies have demonstrated normal AV node function.This patient may be a candidate for which type of pacing?
A) Atrial pacing
B) Ventricular pacing
C) Dual-chamber pacing
D) Transcutaneous pacing
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The patient has an irregular heart rhythm.To determine an accurate heart rate,the nurse first:
A) identifies the markers on the ECG paper that indicate a 6-second strip.
B) counts the number of large boxes between two consecutive P waves.
C) counts the number of small boxes between two consecutive QRS complexes.
D) divides the number of complexes in a 6-second strip by 10.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse understands that in a third-degree AV block:
A) every P wave is conducted to the ventricles.
B) some P waves are conducted to the ventricles.
C) none of the P waves are conducted to the ventricles.
D) the PR interval is prolonged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse is talking with the patient when the monitor alarms and shows a wavy baseline without a PQRST complex.The nurse should:
A) defibrillate the patient immediately.
B) initiate basic life support.
C) initiate advanced life support.
D) assess the patient and the electrical leads.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The patient is admitted with sinus pauses causing periods of loss of consciousness.The patient is asymptomatic,awake and alert,but fatigued.He answers questions appropriately.When admitting this patient,the nurse should first:
A) prepare the patient for temporary pacemaker insertion.
B) prepare the patient for permanent pacemaker insertion.
C) assess the patient's medication profile.
D) apply transcutaneous pacemaker paddles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 59
Related Exams