A) 10
B) 12
C) 14
D) 16
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In some cases, tradable pollution permits may be better than a corrective tax because
A) pollution permits allow for a market solution while a corrective tax does not.
B) pollution permits generate more revenue for the government than a corrective tax.
C) pollution permits are never preferred over a corrective tax.
D) the government can set a maximum level of pollution using permits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Emission controls on automobiles are an example of a
A) corrective tax.
B) command-and-control policy to increase social efficiency.
C) policy that reduces pollution by allocating resources through market mechanisms.
D) policy to reduce congestion on urban freeways.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that elementary education creates a positive externality. If the government subsidizes education by an amount equal to the per-unit externality it creates, then
A) the equilibrium quantity of education will equal the socially optimal quantity of education.
B) the equilibrium quantity of education will be greater than the socially optimal quantity of education.
C) the equilibrium quantity of education will be less than the socially optimal quantity of education.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Negative externalities lead markets to produce
A) greater than efficient output levels and positive externalities lead markets to produce smaller than efficient output levels.
B) smaller than efficient output levels and positive externalities lead markets to produce greater than efficient output levels.
C) greater than efficient output levels and positive externalities lead markets to produce efficient output levels.
D) efficient output levels and positive externalities lead markets to produce greater than efficient output levels.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a market experiences a positive externality,
A) the demand curve does not reflect the value to society of the good.
B) too much of the good is being produced.
C) the government can internalize the externality by imposing a tax on the product.
D) the private value is greater than the social value.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
To determine the optimal level of output in a market with negative externalities, a benevolent social planner would look for the level of output at which private cost equals private value.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Coase theorem asserts that, in the presence of externalities,
A) private economic actors sometimes can reach a bargain that produces an efficient outcome.
B) private economic actors always can reach a bargain that makes everyone better off.
C) private solutions cannot be very effective.
D) corrective taxes cannot be very effective.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With pollution permits, the supply curve for pollution rights is
A) perfectly elastic.
B) perfectly inelastic.
C) upward sloping.
D) downward sloping.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-2. The graph depicts the market for plastic. 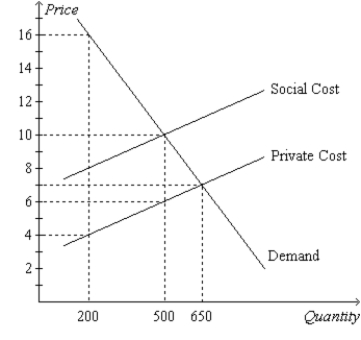 -Refer to Figure 10-2. The private value of the 200th unit of plastic exceeds the social cost of the 200th unit of plastic by
-Refer to Figure 10-2. The private value of the 200th unit of plastic exceeds the social cost of the 200th unit of plastic by
A) $4.
B) $8.
C) $12.
D) $16.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A) Private markets tend to over-produce products with negative externalities.
B) Private markets tend to under-produce products with positive externalities.
C) Private parties can bargain to efficient outcomes even in the presence of externalities.
D) Private parties are usually more successful in achieving efficient outcomes than government policies.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the government were to impose a fine of $4,000 for each unit of air-pollution released by a fertilizer plant, the policy would be considered
A) a subsidy.
B) a regulation.
C) a corrective tax.
D) an application of the Coase theorem.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Education yields positive externalities. For example,
A) colleges and universities have benefited, in recent years, from increases in tuition paid by students.
B) as a result of earning a college degree, a person becomes a more productive worker and benefits by earning higher wages.
C) a more educated population tends to result in lower crime rates.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Employing a lawyer to draft and enforce a private contract between parties wishing to solve an externality problem is an example of
A) an opportunity cost.
B) an implicit cost.
C) a sunk cost.
D) a transaction cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the case of a technology spillover, the government can encourage firms to internalize a positive externality by
A) taxing production, which would decrease supply.
B) taxing production, which would increase supply.
C) subsidizing production, which would decrease supply.
D) subsidizing production, which would increase supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a sawmill creates too much noise for local residents,
A) noise restrictions will force residents to move out of the area.
B) a sense of social responsibility will cause owners of the mill to reduce noise levels.
C) the government can raise economic well-being through noise-control regulations.
D) the government should avoid intervening because the market will allocate resources efficiently.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Many charities like the Sierra Club are established to deal with externalities.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to Figure 10-12. The graph, as drawn, could apply to the market for
A) automobiles.
B) aluminum.
C) industrial robots.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a way to address an externality problem?
A) command and control solution
B) corrective tax
C) corrective subsidy
D) all of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-12 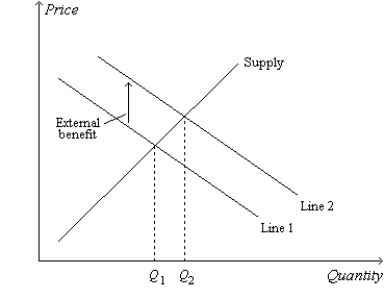 -Refer to Figure 10-12. An alternative label for the line labeled "Supply" would be
-Refer to Figure 10-12. An alternative label for the line labeled "Supply" would be
A) private value.
B) external value.
C) private cost.
D) external cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 281 - 300 of 524
Related Exams