A) the average cost of producing units of electricity by one producer in a specific region was lower than if the same quantity were produced by two or more producers in the same region.
B) the average cost of producing units of electricity by one producer in a specific region was higher than if the same quantity were produced by two or more produced in the same region.
C) the marginal cost of producing units of electricity by one producer in a specific region was higher than if the same quantity were produced by two or more producers in the same region.
D) electricity is a special non-excludable good that could never be sold in a competitive market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following can defeat the profit-maximizing strategy of price discrimination?
A) consumer surplus
B) deadweight loss
C) market power
D) arbitrage
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Customers who purchase an audio CD from Sally's Sounds are charged 20% more than customers who purchase the audio CD from the Sally's Sounds website. This is an example of
A) perfect price discrimination.
B) price discrimination.
C) deadweight loss.
D) socially inefficient output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopoly is an inefficient way to produce a product because
A) it can earn both short-run and long-run profits.
B) it faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
C) the cost to the monopolist of producing one more unit exceeds the value of that unit to potential buyers.
D) it produces a smaller level of output than would be produced in a competitive market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 15-4
A monopolist faces the following demand curve:
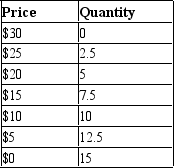 -Refer to Table 15-4. In order to maximize profits, the monopolist should produce
-Refer to Table 15-4. In order to maximize profits, the monopolist should produce
A) 7.5 units.
B) 10 units.
C) where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D) Both a and c are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a competitive market, a firm's supply curve dictates the amount it will supply. In a monopoly market the
A) same is true.
B) supply curve conceptually makes sense, but in practice is never used.
C) supply curve will have limited predictive capacity.
D) decision about how much to supply is impossible to separate from the demand curve it faces.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Name brand drugs are able to continue capitalizing on their market power even after generic drugs enter the market because (i) almost all people fear the generic drug companies are devoting too few resources to research and development. (ii) some people fear that generic drugs are inferior. (iii) some people are loyal to the name brand.
A) (i) and (ii) only
B) (ii) and (iii) only
C) (i) and (iii) only
D) (i) , (ii) , and (iii)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The simplest way for a monopoly to arise is for a single firm to
A) decrease its price below its competitors' prices.
B) decrease production to increase demand for its product.
C) make pricing decisions jointly with other firms.
D) own a key resource.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are necessary characteristics of a monopoly? (i) The firm is the sole seller of its product. (ii) The firm's product does not have close substitutes. (iii) The firm generates a large economic profit. (iv) The firm is located in a small geographic market.
A) (i) and (ii) only
B) (i) and (iii) only
C) (i) , (ii) , and (iii) only
D) (i) , (ii) , (iii) , and (iv)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Scenario 15-11
Vincent operates a scenic tour business in Boston. He has one bus which can fit 50 people per tour and each tour lasts 2 hours. His total cost of operating one tour is fixed at $450. Vincent's cost is not reduced if he runs a tour with a partially full bus. While his cost is the same for all tours, Vincent charges each passenger his/her willingness to pay: adults $18 per trip, children $10 per trip, and senior citizens $12 per trip. At those rates, on a typical day Vincent's demand is:
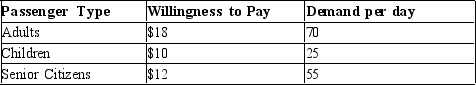 Assume that Vincent's customers are always available for the tour; therefore, he can fill his bus for each tour as long as there is sufficient total demand for the day.
-Refer to Scenario 15-11. One of Vincent's friends tells him he would be more profitable if he charged a single price of $18. Assuming no changes in consumer demand, what would Vincent's profit be if he charged every customer $18?
Assume that Vincent's customers are always available for the tour; therefore, he can fill his bus for each tour as long as there is sufficient total demand for the day.
-Refer to Scenario 15-11. One of Vincent's friends tells him he would be more profitable if he charged a single price of $18. Assuming no changes in consumer demand, what would Vincent's profit be if he charged every customer $18?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 15-7
Sally owns the only shoe store in town. She has the following cost and revenue information.
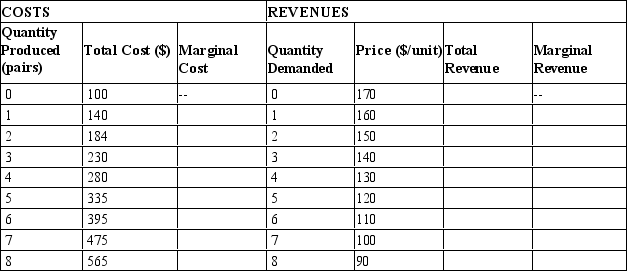 -Refer to Table 15-7. What is the total variable cost of production when Sally produces six pairs of shoes?
-Refer to Table 15-7. What is the total variable cost of production when Sally produces six pairs of shoes?
A) $100
B) $295
C) $600
D) $620
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopoly firm, which of the following equalities is always true?
A) price = marginal revenue
B) price = average revenue
C) price = total revenue
D) marginal revenue = marginal cost
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With no price discrimination, the monopolist sells every unit at the same price. Therefore
A) marginal revenue is equal to price.
B) marginal revenue is equal to average revenue.
C) price is greater than marginal revenue.
D) Both a and b are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does a competitive market compare to a monopoly that engages in perfect price discrimination?
A) In both cases, total social welfare is the same.
B) Total social welfare is higher in the competitive market than with the perfectly price discriminating monopoly.
C) In both cases, some potentially mutually beneficial trades do not occur.
D) Consumer surplus is the same in both cases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With perfect price discrimination the monopoly
A) eliminates all price discrimination by charging each customer the same price.
B) charges each customer an amount equal to the monopolist's marginal cost of production.
C) eliminates deadweight loss.
D) eliminates profits and increases consumer surplus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15-9 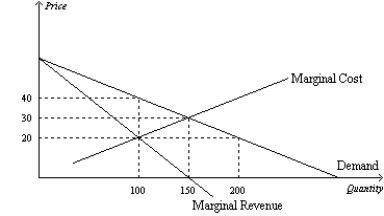 -Refer to Figure 15-9. The deadweight loss caused by a profit-maximizing monopoly amounts to
-Refer to Figure 15-9. The deadweight loss caused by a profit-maximizing monopoly amounts to
A) $250.
B) $500.
C) $750.
D) $1,000.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
During the life of a drug patent, the monopoly pharmaceutical firm maximizes profit by producing the quantity at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The deadweight loss associated with a monopoly occurs because the monopolist
A) maximizes profits.
B) produces an output level less than the socially optimal level.
C) produces an output level greater than the socially optimal level.
D) equates marginal revenue with marginal cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Copyrights and patents are examples of barriers to entry that give firms monopoly pricing powers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 15-7
Sally owns the only shoe store in town. She has the following cost and revenue information.
 -Refer to Table 15-7. What is total profit at the profit-maximizing quantity?
-Refer to Table 15-7. What is total profit at the profit-maximizing quantity?
A) $100
B) $245
C) $265
D) $395
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 637
Related Exams