A) rational economics.
B) neuroeconomics.
C) environmental economics.
D) developmental economics.
E) scientific economics.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When a firm is operating at its minimum efficient scale,its short-run marginal cost of production is minimized.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the situations described below is the principal-agent problem least likely to occur?
A) a patient using hospital services
B) a doctor visiting a patient at home
C) a bartender serving an individual at a bar
D) a mechanic repairing a television set
E) a stockbroker offering financial advice to a client
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 14.2
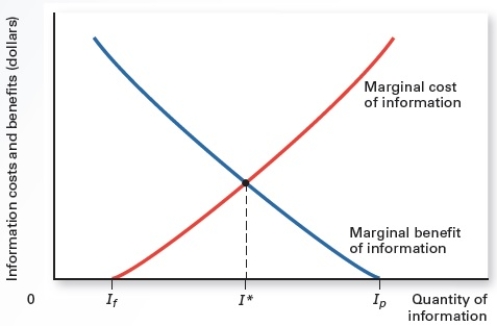 -Refer to Exhibit 14.2,which shows the marginal cost and the marginal benefit of information curves.I* reflects _____
-Refer to Exhibit 14.2,which shows the marginal cost and the marginal benefit of information curves.I* reflects _____
A) that marginal benefit equals marginal cost.
B) that the value of additional information is zero.
C) that the marginal cost is zero.
D) adverse selection.
E) that all information is costly.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
One result of asymmetric information in the market for used cars is that buyers benefit at the expense of sellers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Screening is the attempt by the uninformed party to select the best workers based on observable characteristics of the informed party.
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person or firm who hires an agent to act on their behalf is called the _____
A) principal.
B) agent.
C) buyer.
D) seller.
E) winner.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 14.2
 -Refer to Exhibit 14.2,which shows the marginal cost and the marginal benefit of information curves.If reflects _____
-Refer to Exhibit 14.2,which shows the marginal cost and the marginal benefit of information curves.If reflects _____
A) that marginal benefit equals the marginal cost.
B) that the value of additional information is zero.
C) that the marginal cost is zero.
D) adverse selection.
E) that all information is costly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At Tony's Car Wash,a team of four workers washes and rinses each car by hand and one worker dries the car by hand.Which of the following is true?
A) Tony will not face any principal-agent problem in performance evaluation.
B) Tony will face more problems in performance evaluation in washing and rinsing than in drying the cars.
C) Tony will face more problems in performance evaluation in drying than in washing and rinsing the cars.
D) Tony will face similar problems in performance evaluation in washing, rinsing, and drying.
E) Tony will not have an incentive to monitor the car wash, as the productivity of the workers is same.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 14.3
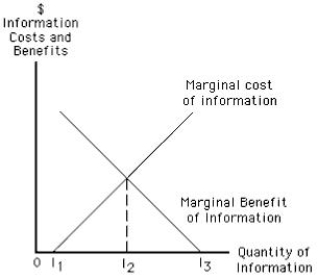 -Refer to Exhibit 14.3,which shows the marginal cost and the marginal benefit of information curves.If a consumer gathers an amount of information equal to I2,it implies that _____
-Refer to Exhibit 14.3,which shows the marginal cost and the marginal benefit of information curves.If a consumer gathers an amount of information equal to I2,it implies that _____
A) she has made the optimal search.
B) she has avoided the cost of acquiring information.
C) she has searched too much.
D) further information will be costless to her.
E) she should increase her search.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the market for used cars,car owners have abundant personal experience with the important characteristics of the vehicle that they are selling.However,a prospective buyer can only guess the characteristics based on each car's appearance.Which of the following problems arises because of this information mismatch?
A) the principal-agent problem
B) the problem of the winner's curse
C) the problem of adverse selection
D) the problem of common resources
E) the problem of unbounded rationality
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 14.3
 -Refer to Exhibit 14.3,which shows the marginal cost and the marginal benefit of information curves.Identify a likely impact of a new technology that requires consumers to spend less time searching for information.
-Refer to Exhibit 14.3,which shows the marginal cost and the marginal benefit of information curves.Identify a likely impact of a new technology that requires consumers to spend less time searching for information.
A) a rightward shift of the marginal cost of information curve
B) a rightward shift of the marginal benefit of information curve
C) a leftward shift of the marginal cost of information curve
D) a leftward shift of the marginal benefit of information curve
E) an increase in common knowledge
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Darryl graduated from college with outstanding grades.However,he obtained his outstanding grades by cheating on every final exam with help from his best friend.Nevertheless,he gets a job with a top accounting firm in Boston.The fact that he is hired illustrates a failure of _____
A) the efficiency wage theory.
B) signaling and screening.
C) the marginal productivity theory.
D) the supply and demand theory.
E) outsourcing and specialization.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Imperfect information among the potential bidders of a cable TV franchise results in a final bid that is more than the market value of a franchise.This situation is an example of _____
A) moral hazard.
B) an authority relation.
C) the winner's curse.
D) the tragedy of the commons.
E) adverse selection.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A situation in which one party makes a contractual agreement with a second party in the expectation that the second party will act on its behalf is known as _____
A) collusion.
B) a horizontal agreement.
C) an authority relation.
D) a principal-agent problem.
E) a vertical agreement.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the quality of an input is easily determined at the time of purchase,then it is likely to _____
A) result in high transaction costs of using markets.
B) encourage horizontal integration of the production process.
C) encourage supplier firms to produce low-quality inputs.
D) be produced internally by a firm.
E) be purchased in the market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bounded rationality _____
A) borrows insights from psychology to help explain economic choices.
B) maps brain activity while subjects make economic choices.
C) describes a more realistic conception of human problem-solving ability.
D) assumes that people act rationally.
E) assumes that people pursue their rational self-interest.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neuroeconomics _____
A) borrows insights from psychology to help explain economic choices.
B) maps brain activity while subjects make economic choices.
C) describes a more realistic conception of human problem-solving ability.
D) assumes that people act rationally.
E) assumes that people pursue their rational self-interest.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 14.3
 -Refer to Exhibit 14.3,which shows the marginal cost and the marginal benefit of information curves.The marginal benefit curve shows that _____
-Refer to Exhibit 14.3,which shows the marginal cost and the marginal benefit of information curves.The marginal benefit curve shows that _____
A) as consumers become more familiar with a market, additional information yields less and less marginal utility.
B) the marginal benefit of information increases as a consumer spends more and more time acquiring information.
C) greater and greater distances must be covered to acquire a marginal piece of information.
D) the cost of gathering information diminishes as more of it is gathered.
E) common knowledge alone is enough to decide consumer choice.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these problems is encountered in labor markets where the abilities of the workers are intangible or unmeasurable?
A) the problem of increasing opportunity cost
B) the adverse selection problem
C) the moral hazard problem
D) the winner's curse problem
E) the problem of diminishing marginal productivity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 199
Related Exams