A) mutations.
B) single nucleotide polymorphisms.
C) gentoypes.
D) gene pools.
E) heterozygotes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following did Darwin suggest was the mechanism for evolution?
A) Natural selection
B) Analogous selection
C) Artificial selection
D) Founder selection
E) Bottleneck selection
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lamarck's theory of evolution included the idea that
A) the continual stretching of a giraffe's neck to reach leaves led to longer necks.
B) local catastrophes cause mass extinctions.
C) species are only produced through special creation.
D) species are unchanged over time.
E) natural selection is the driving force behind evolution.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following most clearly reflects the thought of Lamarck rather than that of Darwin?
A) A population is able to produce more offspring than the environment can support.
B) Only certain members of a population survive and reproduce.
C) The members of a population have inheritable variations.
D) Any acquired change an organism gains over its life can be passed on to its offspring.
E) Natural selection results in a population adapting to the local environment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following was a geologist who wrote The Principles of Geology,a very important book in helping Darwin shape the theory of natural selection?
A) Cuvier
B) Lamarck
C) Fitzroy
D) Lyell
E) Wallace
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When only a few individuals survive unfavorable times,thereby losing a majority of genotypes in the next generation,it is referred to as
A) artificial selection.
B) the bottleneck effect.
C) the founder effect.
D) the transition effect.
E) coevolution.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure: 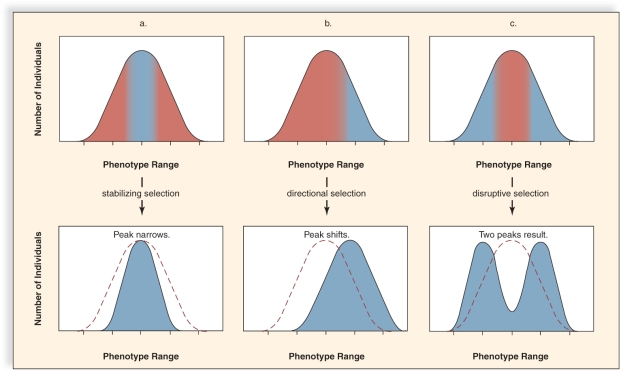 -This figure shows the three different types of natural selection.What does "C" represent?
-This figure shows the three different types of natural selection.What does "C" represent?
A) disruptive selection
B) directional selection
C) genetic drift selection
D) stabilizing selection
E) adaptive selection
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Structures which are fully developed in one group of organisms but reduced or possibly nonfunctional in a similar group are referred to as
A) vestigial structures.
B) analogous structures.
C) transitional structures.
D) directional structures.
E) homologous structures.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Besides mutation,which of the following is important in generating phenotypic differences?
A) sexual reproduction
B) genetic drift
C) gene flow
D) stabilizing selection
E) microevolution
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Structures that are anatomically similar because they are inherited from a recent common ancestor are called
A) vestigial structures.
B) analogous structures.
C) transitional structures.
D) directional structures.
E) homologous structures.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A type of nonrandom mating that occurs when individuals tend to mate with those having the same phenotype with respect to certain characteristics is referred to as
A) disruptive mating.
B) directional mating.
C) artificial mating.
D) assortative mating.
E) homologous mating.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If two adjacent populations of the same species show gene flow,then the two populations will
A) become more similar in their gene pools.
B) become isolated from each other.
C) develop into different species.
D) adapt to different conditions and become separate.
E) develop into a species and a sub-species.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The raw material for evolutionary change is
A) gene flow.
B) genetic drift.
C) mutation.
D) nonrandom reproduction.
E) natural selection.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which line of evidence developed since the time of Darwin has strengthened support for his theory of natural selection?
A) comparative anatomy
B) biogeography
C) fossil record
D) comparative embryology
E) comparative biochemistry
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When one group of organisms gives rise to several other groups of organisms,the original group is referred to as
A) a transitional ancestor.
B) a common ancestor.
C) a homologous ancestor.
D) an analogous ancestor.
E) a vestigial ancestor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fossils that have characteristics of two different groups of organisms are called
A) vestigial fossils.
B) analogous fossils.
C) homologous fossils.
D) transitional fossils.
E) founder fossils.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The equation p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 describes
A) the process of evolution.
B) the size of a population.
C) the rate of speciation of species p and q.
D) the genotype and allele frequency of a population.
E) the phenotypic frequency of a population.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a population of pepper moths,the frequency of the DD genotype (dark-colored) is 0.25,and the frequency of the dd genotype (light-colored) is 0.25.What would be the frequency of the Dd genotype (dark-colored) in the next generation,assuming a Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A) 0.25
B) 0.5
C) 0.75
D) 0.1
E) 1.0
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you were a biologist studying the type of natural selection where an extreme phenotype is favored and the distribution curve shifts toward that phenotype,what would you be studying?
A) disruptive selection
B) directional selection
C) genetic drift selection
D) stabilizing selection
E) adaptive selection
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Africa,Asia,South America,and Antarctica share some patterns of primitive (fossil) plants and early reptiles,but do not have similar mammal populations.This,therefore
A) casts serious doubts upon the theory of continental drift and fused land masses.
B) is an unsolved puzzle,probably due to the random nature of biological evolution.
C) suggests that a pattern of land bridges existed at different times in geological history.
D) suggests that the earlier plants and reptiles evolved while continents were joined,but mammals radiated into diverse groups after separation.
E) suggests that mammals evolved earlier while continents were joined,but plants and reptiles radiated into diverse groups after separation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 53
Related Exams