A) first-order in both A and B.
B) zero-order in both A and B.
C) second-order in A and first-order in B.
D) first-order in A and second-order in B.
E) second-order in both A and B.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rate constant for a particular reaction is 0.0070 M-1·s−1.What is the overall order of this reaction?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 0
E) 1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mechanism that explains the rate law,Rate = k[(CH3) 3CO2C(CH3) 3],for the gas-phase thermal decomposition of di-tert-butyl peroxide is given below. ![A mechanism that explains the rate law,Rate = k[(CH<sub>3</sub>) <sub>3</sub>CO<sub>2</sub>C(CH<sub>3</sub>) <sub>3</sub>],for the gas-phase thermal decomposition of di-tert-butyl peroxide is given below. For this proposed mechanism,the rate-determining step(s) must be A) step 1. B) step 3. C) step 2. D) step 1 + step 2 + step 3. E) 2 times step 2.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2288/11ea7a3a_9f0f_40b3_a82d_45143283fd5e_TB2288_00.jpg) For this proposed mechanism,the rate-determining step(s) must be
For this proposed mechanism,the rate-determining step(s) must be
A) step 1.
B) step 3.
C) step 2.
D) step 1 + step 2 + step 3.
E) 2 times step 2.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Below is a proposed mechanism for the decomposition of H2O2. H2O2 + I- → H2O + IO- Slow H2O2 + IO- → H2O + O2 + I- Fast Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) IO- is a catalyst.
B) I- is a catalyst.
C) The net reaction is 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2.
D) The reaction is first-order with respect to [I-].
E) The reaction is first-order with respect to [H2O2].
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One mechanism for the depletion of ozone in the stratosphere is proposed as follows: Cl + O3 → ClO + O2 ClO + O → Cl + O2 Identify any catalysts and intermediates in the reaction.
A) Cl is a catalyst,there are no intermediates
B) O is an intermediate,ClO is a catalyst
C) O2 is a catalyst,O is an intermediate
D) ClO is a catalyst,there are no intermediates
E) Cl is a catalyst,ClO is an intermediate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The complete mechanism for a reaction is considered to occur in two steps,one of which is slow and the other fast: A + 2B → C + D slow A + C → E + F fast What is the rate law predicted by this mechanism?
A) Rate = k[A]2[B]
B) Rate = k[A]2[B][C]
C) Rate = k[A][C]
D) Rate = k[A][B][C]
E) Rate = k[A][B]2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The gas-phase decomposition of N2O5 is a first-order process with a rate constant of 1.50 × 10-3 s-1 at 55°C.The decomposition reaction is
N2O5(g) → 2NO2(g) + 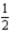 O2(g)
If 8.0 g of N2O5 is placed in vessel 1 and 16.0 g of N2O5 in vessel 2 and the vessels are at the same temperature (55°C) and the same pressure,how much time is required for half of the N2O5 to decompose in each vessel?
O2(g)
If 8.0 g of N2O5 is placed in vessel 1 and 16.0 g of N2O5 in vessel 2 and the vessels are at the same temperature (55°C) and the same pressure,how much time is required for half of the N2O5 to decompose in each vessel?
A) Vessel 1 requires the same amount of time as vessel 2.
B) Vessel 1 requires twice as much time as vessel 2.
C) Vessel 1 requires three times as much time as vessel 2.
D) Vessel 1 requires four times as much time as vessel 2.
E) Vessel 2 requires twice as much time as vessel 1.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the Arrhenius equation from the following.
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rate constant for a reaction at 40.0°C is exactly 5 times that at 20.0°C.Calculate the Arrhenius energy of activation for the reaction.
A) 5.00 kJ/mol
B) 7.38 kJ/mol
C) 61.4 kJ/mol
D) 13.4 kJ/mol
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the Arrhenius equation,the symbol A is called _____ and the symbol R is called _____.
A) Avogadro's number,Coulomb's constant
B) Bohr's radius,gravitational constant
C) bond length,atomic mass unit
D) frequency factor,gas constant
E) bond strength,neutron mass
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a postulate of collision theory?
A) Reactant molecules must collide to react.
B) Reactant molecules must collide with a certain minimum energy in order to form products.
C) Reactant molecules must collide with the correct orientation in order to form products.
D) The rate constant is directly proportional to the energy of activation.
E) The maximum in the potential energy curve,the activation energy,is determined by the structure of the activated complex or transition state.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the rate law for a reaction is Rate = k[ClO3-][I-][H+]2 What are the units of k when the unit of time is seconds and the unit of concentration is moles per liter?
A) (L ∙ s) /mol
B) mol2/(L2 ∙ s)
C) mol/(L ∙ s)
D) L2/(mol2 ∙ s)
E) L3/(mol3 ∙ s)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The main reason for the increase in reaction rate with temperature is that
A) the fraction of high-energy molecules increases exponentially with temperature.
B) the activation energy increases rapidly with temperature.
C) a 10°C temperature rise results in the rate doubling.
D) there is a dramatic increase in the number of collisions.
E) heat acts as a catalyst.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the following fast equilibrium (below) proposed for the gas phase reaction between NO and O2,what is the expression for the equilibrium concentration of the intermediate NO3?
NO + O2 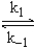 NO3
NO3
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The balanced chemical equation and rate law for the reaction between NO(g) and H2(g) at a particular temperature are 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g) Rate = k[NO]2[H2] What is the reaction order with respect to nitric oxide?
A) 4
B) 0
C) 1
D) 3
E) 2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A second-order reaction starts with an initial concentration of 0.100 mol/L of the reactant.If the rate constant is 2.4× 10-2 L/(mol ∙ s) ,what is the time required to decrease the initial concentration to 0.050 mol/L?
A) 410 s
B) 620 s
C) 28.9 s
D) 2.08 s
E) 1200 s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not a requirement for a valid reaction mechanism?
A) Each elementary reaction must be bimolecular.
B) There must not be net production of any intermediates.
C) The elementary reactions of a mechanism must add up to the net chemical reaction.
D) A mechanism must have only one rate-determining step.
E) The rate law predicted by a mechanism must agree with the experimental rate law.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning the experimental determination of reaction rates is incorrect?
A) To determine reaction rates one of the reactants must be colored.
B) Monitoring changes in reactant or product physical properties is a convenient way to determine reaction rates.
C) Analysis of samples withdrawn from the reaction solution at varying times is useful for slow reactions.
D) Instrumental methods,such as visible spectroscopy,may be used to continuously measure changes in reactants or products.
E) Any method of analysis that can determine product or reactant concentrations during the course of the reaction can potentially be used to determine reaction rates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A first-order chemical reaction is observed to have a rate constant of 24 min-1.What is the corresponding half-life for the reaction?
A) 1.7 s
B) 1.7 min
C) 35 min
D) 2.5 s
E) 34.3 s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rate constants for the first-order decomposition of a compound are 5.22× 10-4 s-1 at 43°C and 2.91 × 10-3 s-1 at 62°C.What is the value of the activation energy for this reaction? (R = 8.31 J/(mol · K) )
A) 0.87104 kJ/mol
B) 34.5 kJ/mol
C) 0.751 kJ/mol
D) 79.5 kJ/mol
E) 2 kJ/mol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 113
Related Exams