A) is more elastic than the monopolist's demand curve.
B) is less elastic than the monopolist's demand curve.
C) will shift outward as new firms enter the industry.
D) is more elastic than the demand curve faced by the purely competitive firm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If output is set at the kink of the kinked-demand model,then there:
A) is a strong incentive for rivals to decrease prices.
B) is a strong incentive for rivals to increase prices.
C) is one price at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D) are several prices at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the kinked-demand model,there will be a vertical break in the firm's:
A) demand curve.
B) marginal cost curve.
C) marginal revenue curve.
D) average total cost curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In long-run equilibrium,a monopolistically competitive firm achieves:
A) productive and allocative efficiency.
B) productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency.
C) allocative efficiency but not productive efficiency.
D) neither allocative efficiency nor productive efficiency.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If oligopolistic firms facing similar cost and demand conditions successfully collude,price and output results in this industry will be most accurately predicted by which of the following models?
A) Kinked-demand curve model of oligopoly
B) Price-leadership model of oligopoly
C) Pure monopoly model
D) Monopolistic competition model
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which product is made by an industry that best illustrates the concept of homogeneous oligopoly?
A) Home computers
B) Cigarettes
C) Copper
D) Cars
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a positive effect of advertising?
A) It reduces economic efficiency in the economy.
B) It promotes economic concentration in industry.
C) It is designed to persuade rather than inform consumers.
D) It provides information that reduces search costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is a likely characteristic of a differentiated oligopolistic market?
A) There are minimal barriers to entry.
B) The market demand curve is inelastic.
C) There is minimal advertising expenditure.
D) Price and output decisions of firms are interdependent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is a characteristic of monopolistic competition?
A) Standardized product
B) A relatively small number of firms
C) Absence of nonprice competition
D) Relatively easy entry
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolistically competitive industry is like a purely competitive industry in that:
A) each industry produces a standardized product.
B) nonprice competition is a feature in both industries.
C) neither industry has significant barriers to entry.
D) firms in both industries face a horizontal demand curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In imperfectly competitive industries,producers' agreements to restrict output tend to be unstable because each firm has an incentive to:
A) produce more than its output quota.
B) lower both its price and its output.
C) raise prices above the cooperative price.
D) establish competitive price and output levels.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major prediction of the kinked-demand curve model is:
A) price stability in oligopolies.
B) price instability in oligopolies.
C) stability of production costs in oligopolies.
D) stable purchasing behavior by consumers over time.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an oligopoly game,each player tries to:
A) maximize its own profits.
B) minimize the market shares of its opponents.
C) minimize the profits of its opponents.
D) maximize its own market share.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which market model is characterized by many firms,differentiated products,and relatively easy entry?
A) Pure competition
B) Pure monopoly
C) Monopolistic competition
D) Oligopoly
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long-run equilibrium position of a monopolistically competitive firm is where average costs are:
A) constant.
B) increasing.
C) decreasing.
D) at their minimum point.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under oligopoly,if one firm in an industry significantly increases advertising expenditures in order to capture a greater market share,it is most likely that other firms in that industry will:
A) pursue a strategy to reduce advertising expenditures to maintain profits.
B) decide to increase advertising expenditures even if it means a reduction in profits.
C) make no changes in advertising expenditures because advertising is effective in the short run,but not the long run.
D) increase the price of the product to improve profits and then increase advertising expenditures.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
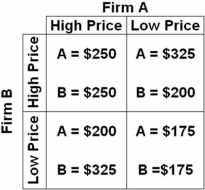 Refer to the above payoff matrix.Assume that firm B adopts a low-price strategy while firm A maintains a high-price strategy.Compared to the results from a high-price strategy for both firms,firm B will now:
Refer to the above payoff matrix.Assume that firm B adopts a low-price strategy while firm A maintains a high-price strategy.Compared to the results from a high-price strategy for both firms,firm B will now:
A) lose $75 million in profit and firm A will gain $50 million in profit.
B) gain $50 million in profit and firm A will lose $50 million in profit.
C) gain $75 million in profit and firm A will lose $50 million in profit.
D) gain $50 million in profit and firm A will lose $75 million in profit.
The high-price strategy results in $500 million profits for both.If B adopts a low-price strategy and A stays with the high-price strategy,B will gain and A will lose.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The steel industry is an example of a homogeneous oligopoly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Both collusive and noncollusive oligopoly models suggest that price changes will be relatively infrequent in these types of industries.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
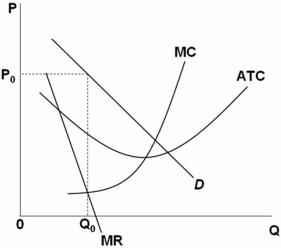 Refer to the above graph.It represents a monopolistically competitive firm in a constant-cost industry.In long-run equilibrium this firm will:
Refer to the above graph.It represents a monopolistically competitive firm in a constant-cost industry.In long-run equilibrium this firm will:
A) continue to earn economic profits because it has monopolistic power to set its price.
B) become a perfectly competitive firm because there are no significant barriers to entry.
C) break even because average total cost (ATC) and marginal cost (MC) will increase as more firms enter the market.
D) break even because its demand curve will fall and become more elastic as it loses sales to other firms entering the market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 179
Related Exams