A) 43.2 kcal are consumed when 1.00 g of N2 reacts.
B) 43.2 kcal are consumed when 1.00 g of O2 reacts.
C) 43.2 kcal are consumed when 1.00 mole of O2 reacts.
D) 43.2 kcal are produced when 1.00 mole of NO is produced.
E) 43.2 kcal are consumed when 1.00 g of NO is produced.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction below if a tank was found to contain 0.106 M O2,0.00652 M SO3 and 0.00129 M SO2.
2 SO3 (g) 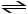 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
A) 6.78 × 10-2
B) 1.34 × 10-2
C) 4.15 × 10-3
D) 4.35 × 10-2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If we add a catalyst to the following equation,CO + H2O + heat 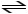 CO2 + H2,which way will the equilibrium shift?
CO2 + H2,which way will the equilibrium shift?
A) to the left
B) no effect
C) to the right
D) not enough information
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Select the correct figure to match the description. -A fast reaction with a small positive free energy change
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes involve an increase in entropy of the system? I.Mothballs vaporize in a closet. II.Blocks are assembled into a house. III.Crystals grow from a sugar solution. IV.Recyclable plastics are sorted. V.Cake mix is manufactured from five basic ingredients.
A) II,IV
B) I,II,III
C) II,III,IV
D) I,V
E) I,III,V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the reaction given below,what quantity of heat will be produced if 90.0 g of C3H8 are consumed in the reaction? C3H8 + 5 O2 → 3 CO2 + 4 H2O + 488 kcal
A) 996 kcal
B) 488 kcal
C) 332 kcal
D) 239 kcal
E) 976 kcal
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solid sample at room temperature spontaneously sublimes forming a gas.This change in state is accompanied by which of the changes in the sample?
A) Entropy and energy decrease.
B) Entropy and energy increase.
C) Entropy decreases and energy increases.
D) Entropy increases and energy decreases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A reaction which is unfavorable with respect to entropy,but favorable with respect to enthalpy
A) could occur at any temperature.
B) could not occur regardless of temperature.
C) could occur at low temperatures but not at higher temperatures.
D) could occur at high temperatures but not at lower temperatures.
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which process is not likely to be considered reversible?
A) a round trip to Las Vegas
B) melting wax to make candles
C) a reaction using the symbol "↔"
D) cutting down a tree
E) dissolving salt in water
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following. -A state in which the rate of the forward reaction is exactly equal to the rate of the reverse reaction
A) exergonic
B) endergonic
C) exothermic
D) endothermic
E) activation energy
F) chemical equilibrium
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following. -A process or reaction that has a positive value of ΔG
A) exergonic
B) endergonic
C) exothermic
D) endothermic
E) activation energy
F) chemical equilibrium
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g) 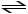 2 SO3 (g) + heat K = 4.8 × 1027
Which statement about this system is not true?
2 SO3 (g) + heat K = 4.8 × 1027
Which statement about this system is not true?
A) At equilibrium SO3 is the predominant substance.
B) Heating the system will cause breakdown of SO3.
C) Adding SO2 will cause an increase in the amount of SO3.
D) Removing O2 will cause an increase in the amount of SO3.
E) The large value of K means that the reaction essentially goes to completion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A reaction that is spontaneous can be described as
A) proceeding in both the forward and reverse directions.
B) having the same rate in both the forward and reverse directions.
C) releasing heat to the surroundings.
D) proceeding without external influence once it has begun.
E) increasing in disorder.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If heat is consumed during a reaction,the reaction is said to be ________.
A) endothermic
B) exothermic
C) endergonic
D) exothermic.
E) can't tell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the reaction:
A + 2 B 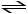 2 C + D
The equilibrium expression for this reaction is:
2 C + D
The equilibrium expression for this reaction is:
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the statements regarding the symbol "ΔH" are correct except
A) it represents the difference between the energy used in breaking bonds and the energy released in forming bonds in a chemical reaction.
B) it can be called heat of reaction.
C) it can be called enthalpy change.
D) it can be called entropy change.
E) it has a negative value for an exothermic reaction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
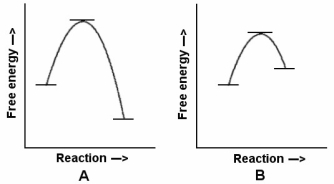 -In the reaction energy diagrams shown,reaction A is ________,and it occurs ________ reaction B.
-In the reaction energy diagrams shown,reaction A is ________,and it occurs ________ reaction B.
A) endergonic; faster than
B) exergonic; faster than
C) endergonic; slower than
D) exergonic; slower than
E) exergonic; at the same rate as
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Activation energy can best be described as
A) the energy level of the products.
B) the maximum energy level of the reaction.
C) the energy level of the reactants.
D) the difference in energy between reactants and products.
E) the difference in energy between reactants and the maximum energy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following conditions characterizes a system in a state of chemical equilibrium?
A) Concentrations of reactants and products are equal.
B) Rate of forward reaction has dropped to zero.
C) Reactants are being consumed at the same rate they are being produced.
D) Reactant molecules no longer react with each other.
E) Product concentrations are greater than reactant concentrations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
P4 (s) + 10 Cl2 (g) → 4 PCl5 (s) ΔH = -435.2 kcal Based on the reaction shown,which statement is true?
A) When 1 mol P4 (s) reacts,435.2 kcal are released.
B) When 1 mol PCl5 (s) is produced,435.2 kcal are released.
C) When 30.97 g P4 (s) react,435.2 kcal are released.
D) When 123.88 g P4 (s) react,435.2 kcal are consumed.
E) When 208.22 g PCl5 (s) are produced,435.2 kcal are consumed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 73
Related Exams