A) 5.3 × 102 yr
B) 7.6 × 102 yr
C) 1.1 × 103 yr
D) 9.4 × 103 yr
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rate constant for the first-order decomposition of N2O is 3.40 s-1.What is the half-life of the decomposition?
A) 0.491 s
B) 0.204 s
C) 0.236 s
D) 0.424 s
E) 0.294 s
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The half-life for the second-order decomposition of HI is 15.4 s when the initial concentration of HI is 0.67 M.What is the rate constant for this reaction?
A) 1.0 × 10-2 M-1s-1
B) 4.5 × 10-2 M-1s-1
C) 9.7 × 10-2 M-1s-1
D) 2.2 × 10-2 M-1s-1
E) 3.8 × 10-2 M-1s-1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rate constant for a zero-order reaction is 0.54 s-1.What is the half-life of this reaction if the initial concentration is 0.33 M?
A) 0.089 s
B) 1.8 s
C) 0.31 s
D) 5.6 s
E) 1.3 s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Derive an expression for a "1/3-life" for a first-order reaction.
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the CFC with the shortest atmospheric lifetime.
A) CFC-113
B) CFC-12
C) CFC-114
D) CFC-11
E) CFC-115
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Write a balanced reaction for which the following rate relationships are true. Rate = 
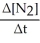 =
= 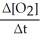 = -
= - 
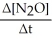
A) ![]() N2 + O2 →
N2 + O2 →
![]() N2O
N2O
B) 2 N2O → 2 N2 + O2
C) N2O → N2 + 2 O2
D) ![]() N2O →
N2O →![]() N2 + O2
N2 + O2
E) 2 N2 + O2 → 2 N2O
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nitrogen dioxide decomposes at 300°C via a second-order process to produce nitrogen monoxide and oxygen according to the following chemical equation. 2 NO2(g) → 2 NO(g) + O2(g) . A sample of NO2(g) is initially placed in a 2.50-L reaction vessel at 300°C.If the half-life and the rate constant at 300°C are 11 seconds and 0.54 M-1 s-1,respectively,how many moles of NO2 were in the original sample?
A) 0.17 mol
B) 0.42 mol
C) 5.9 mol
D) 15 mol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are the units of k in the following rate law? Rate = k[X]
A) ![]()
B) M s2
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The first-order decomposition of cyclopropane has a rate constant of 6.7 × 10-4 s-1.If the initial concentration of cyclopropane is 1.33 M,what is the concentration of cyclopropane after 644 s?
A) 0.43 M
B) 0.15 M
C) 0.94 M
D) 0.86 M
E) 0.67 M
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which rate law has a molecularity of two?
A) Rate = k[A]0
B) Rate = k[A][B]
C) Rate = k[A][B][C]
D) Rate = k[A]
E) Rate = k[A]3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many half-lives are required for the concentration of reactant to decrease to 12.5% of its original value?
A) 3
B) 2
C) 2.5
D) 2.75
E) 8
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following represents the integrated rate law for a second-order reaction?
A) ![]() = - kt
= - kt
B) ![]() -
-![]() = kt
= kt
C) [A]o - [A]t = - kt
D) k = Ae(Ea/RT)
E) ![]() =
=![]()
![]() - lnA
- lnA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The half-life for the decay of radium is 1620 years.What is the rate constant for this first-order process?
A) 4.28 × 10-4 yr-1
B) 1.12 × 10-4 yr-1
C) 2.33 × 10-4 yr-1
D) 8.91 × 10-4 yr-1
E) 6.17 × 10-4 yr-1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the following balanced equation,determine the rate of reaction with respect to [SO3]. 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g)
A) Rate = - ![]()
![]()
B) Rate = + ![]()
![]()
C) Rate = + ![]()
D) Rate = - ![]()
E) It is not possible to determine without more information.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the following proposed mechanism,predict the rate law for the overall reaction. A2 + 2 B → 2 AB (overall reaction) Mechanism A2 ⇌ 2 A fast A + B → AB slow
A) Rate = k[A]1/2[B]2
B) Rate = k[A2][B]
C) Rate = k[A2]2[B]1/2
D) Rate = k[A2]1/2
E) Rate = k[A2]1/2[B]
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the concentration of a reactant is 6.25%,how many half-lives has it gone through?
A) 7
B) 10
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the overall order of the following reaction,given the rate law? 2 NO(g) + H2(g) → N2(g) + 2 H2O(g) Rate = k[NO]2[H2]
A) 1st order
B) 2nd order
C) 3rd order
D) 4th order
E) 0th order
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are the units of k in the following rate law? Rate = k[X]2[Y]
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) M2s2
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Biological catalysts that increase the rates of biochemical reactions are known as
A) substrates.
B) inhibitors.
C) enzymes.
D) binders.
E) trumanettes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 154
Related Exams