Correct Answer

verified
Alpha emitters have the highest ionizing...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Positrons are similar in ionizing power and penetrating power to beta particles.
B) A positron is the antiparticle of the electron.
C) Beta decay occurs when a neutron changes into a proton while emitting an electron.
D) An alpha particle is a helium 2+ ion.
E) All of the above are true.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A hydrogen bomb has up to ________ times the explosive force of the first atomic bomb.
A) 2000
B) 1000
C) 500
D) 200
E) 100
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Beta decay of 60Co produces a beta particle and
A) (56Mn) .
B) (59Co) .
C) (60Fe) .
D) (60Ni) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The combination of two light nuclei to form a heavier nucleus is called
A) radioactive cleavage.
B) nuclear fission.
C) nuclear fusion.
D) radioactive merge.
E) half-life.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the alpha decay of 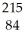 Po.
Po.
A) ![]() Po
Po
B) ![]() Hg
Hg
C) ![]() At
At
D) ![]() Pb
Pb
E) ![]() Rn
Rn
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the scientist(s) that were awarded the Nobel Prize in physics for the discovery of radioactivity in 1903.
A) Johannes Geiger, Marie Curie
B) Albert Einstein
C) Antoine-Henri Becquerel, Marie Curie, Pierre Curie
D) Ernest Rutherford, Johannes Geiger
E) Galileo Galilei
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear equation: 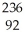 U → ? +
U → ? + 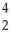 He + 2
He + 2 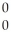 g
g
A) ![]() Th
Th
B) ![]() Ra
Ra
C) ![]() Pu
Pu
D) ![]() Th
Th
E) ![]() Ra
Ra
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the technique used to predict the age of the Shroud of Turin.
A) uranium-238 to lead-206
B) potassium-40 to argon-40
C) carbon-14 to nitrogen-14
D) none of the above
E) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the nuclide that has the longest half-life.
A) ![]() U
U
B) ![]() C
C
C) ![]() Rn
Rn
D) ![]() Th
Th
E) ![]() Th
Th
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the positron emission of 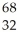 Ge.
Ge.
A) ![]() Ga
Ga
B) ![]() As
As
C) ![]() Zn
Zn
D) ![]() As
As
E) ![]() Ga
Ga
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear equation: 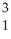 H +
H + 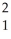 H →
H → 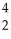 He + ? +
He + ? + 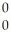 g
g
A) ![]() n
n
B) ![]() n
n
C) ![]() H
H
D) ![]() n
n
E) ![]() g
g
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the electron capture by 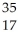 Cl.
Cl.
A) ![]() Ar
Ar
B) ![]() K
K
C) ![]() S
S
D) ![]() P
P
E) ![]() Ar
Ar
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the elements discovered by Marie Curie.
A) polonium and radium
B) radium and cesium
C) argon and xenon
D) radon and xenon
E) selenium and tungsten
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following reaction represents what nuclear process? 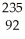 U +
U + 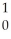 n →
n → 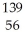 Ba +
Ba + 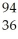 Kr + 3
Kr + 3 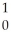 n
n
A) nuclear fission
B) nuclear fusion
C) electron capture
D) alpha capture
E) beta capture
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the mass defect in Mo-96 if the mass of a Mo-96 nucleus is 95.962 amu.The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and the mass of a neutron is 1.008665 amu.
A) 0.197 amu
B) 0.795 amu
C) 0.212 amu
D) 0.812 amu
E) 0.188 amu
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the electron capture by 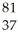 Rb.
Rb.
A) ![]() Kr
Kr
B) ![]() Sr
Sr
C) ![]() Br
Br
D) ![]() Y
Y
E) ![]() Kr
Kr
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An archaeologist graduate student found a leg bone of a large animal during the building of a new science building.The bone had a carbon-14 decay rate of 14.8 disintegrations per minute per gram of carbon.Living organisms have a decay rate of 15.3 disintegrations per minute.How old is the bone?
A) 53.3 years
B) 275 years
C) 111 years
D) 25 years
E) 83 years
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Write the nuclear equation for the alpha decay of 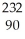 Th.
Th.
A) ![]() He +
He +![]() Th →
Th →![]() U
U
B) ![]() n +
n +![]() Th →
Th →![]() Th
Th
C) ![]() Th →
Th →![]() e +
e +![]() Ac
Ac
D) ![]() Th →
Th →![]() He +
He +![]() Ra
Ra
E) ![]() Th →
Th →![]() e +
e +![]() Pa
Pa
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify a beta particle.
A) ![]() e
e
B) ![]() n
n
C) ![]() e
e
D) ![]() n
n
E) ![]() γ
γ
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 135
Related Exams