A) below;increases
B) above;decreases
C) below;decreases
D) above;increases
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions: 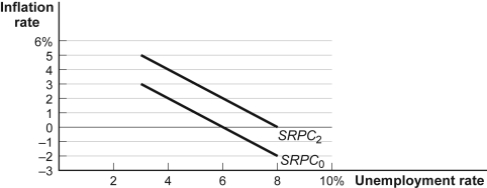 -(Figure: Expected Inflation and the Short-Run Phillips Curve)
SRPC0 is the Phillips curve with an expected inflation rate of zero;SRPC2 is the Phillips curve with an expected inflation rate of 2%.
Refer to Figure: Expected Inflation and the Short-Run Phillips Curve.Suppose that this economy has an unemployment rate of 6%,inflation of 2%,and an expectation of 2% inflation.If the central bank increases the money supply such that aggregate demand shifts to the right and unemployment falls to 4%,then inflation will:
-(Figure: Expected Inflation and the Short-Run Phillips Curve)
SRPC0 is the Phillips curve with an expected inflation rate of zero;SRPC2 is the Phillips curve with an expected inflation rate of 2%.
Refer to Figure: Expected Inflation and the Short-Run Phillips Curve.Suppose that this economy has an unemployment rate of 6%,inflation of 2%,and an expectation of 2% inflation.If the central bank increases the money supply such that aggregate demand shifts to the right and unemployment falls to 4%,then inflation will:
A) fall to -2%.
B) not change.
C) rise to 2%.
D) rise to 4%.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The main difference between the classical model of the price level and the modern understanding of the relationship between the money supply,the price level,and real GDP is that according to classical economists,_____,while today's economists _____.
A) money is neutral in the long run;do not consider money to be neutral in the long run
B) the adjustment of prices takes some time;expect changes in the money supply to be instantaneous
C) who did not consider money to be neutral in the long run;consider money neutral in the long run
D) the adjustment of prices to changes in the money supply is instantaneous;argue that this adjustment process takes some time
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During hyperinflation in Germany in 1922-1923,prices rose at _____% per day.
A) 0.1
B) 16
C) 50
D) 100
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Policies that reduce inflation are popular with voters because they lead to higher output and lower unemployment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions: 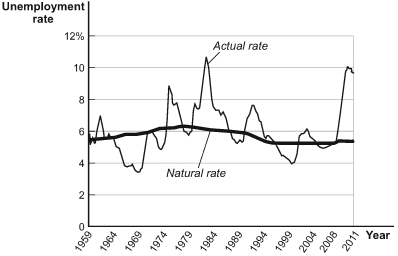 -(Figure: Actual and Natural Rates of Unemployment) Refer to Figure: Actual and Natural Rates of Unemployment.In 2000,the output gap was:
-(Figure: Actual and Natural Rates of Unemployment) Refer to Figure: Actual and Natural Rates of Unemployment.In 2000,the output gap was:
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) zero.
D) impossible to determine without more information.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the money supply grows by 4% and the real money supply is $100 billion,real seigniorage is:
A) $4 billion.
B) $25 billion.
C) $400 billion.
D) $2.5 trillion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When economists state that there is a zero bound on nominal interest rates,they mean that the:
A) real interest rate cannot go below zero.
B) nominal interest rate cannot go below zero.
C) real interest rate can very well be negative.
D) nominal interest rate can always go below zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The short-run Phillips curve represents the relationship between the unemployment rate and the rate of change in:
A) the interest rate.
B) output.
C) wages only.
D) the aggregate price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question : 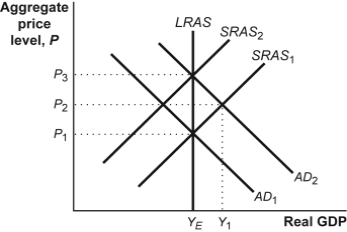 -(Figure: AD-AS Model) Refer to Figure: AD-AS Model.Suppose that the economy is at YE with a price level of P1. Which of the following would represent the new long-run equilibrium position if the aggregate demand curve shifted to the right from AD1 to AD2 as a result of an increase in the money supply?
-(Figure: AD-AS Model) Refer to Figure: AD-AS Model.Suppose that the economy is at YE with a price level of P1. Which of the following would represent the new long-run equilibrium position if the aggregate demand curve shifted to the right from AD1 to AD2 as a result of an increase in the money supply?
A) YE and P2
B) YE and P1
C) Y1 and P2
D) YE and P3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a central bank pursues an expansionary monetary policy:
A) the aggregate price level and level of real GDP will increase in the short run.
B) the level of real GDP will increase,but the aggregate price level will stay the same in the long run.
C) nominal prices and nominal wages will be unaffected in the long run.
D) the aggregate price level will increase and the level of real GDP will decrease in the short run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If actual output growth is 5% when potential output growth is 5%,then the unemployment rate will:
A) not change.
B) rise.
C) fall.
D) be zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The debt is monetized when:
A) the budget is approved by the federal government.
B) the Bank of Canada buys back debt via open-market purchases.
C) the government raises taxes.
D) transfer payments are decreased.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An inflation tax is the effect on the public of a reduction in the value of money caused by inflation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To bring disinflation to an economy,policy makers must:
A) slow down labour productivity growth.
B) increase the money supply to release the economy from the liquidity trap.
C) keep unemployment below its natural rate for an extended period.
D) announce and commit to a credible policy of disinflation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When inflation is high:
A) people will increase their level of real-money holdings.
B) people will save more.
C) lenders gain at the expense of borrowers.
D) people will decrease their level of real-money holdings.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Workers in country A have wage contracts for cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs) ,which adjust wages to offset the effect of inflation,and workers in country B do not.When the central banks of countries A and B increase the money supply:
A) prices in country A increase faster than prices in country B.
B) prices in country B increase faster than prices in country A.
C) prices in countries A and B will change at the same rate.
D) COLAs have no effect on the speed of price changes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The inflation tax is the effect on the public of:
A) the increase in the real value of money caused by inflation.
B) the decrease in the real value of money caused by inflation.
C) the result of indexing wages to inflation.
D) cost of living adjustments.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy finds itself in a liquidity trap:
A) consumers are trapped by an abundance of liquidity and are spending abundantly.
B) the economy is trapped by the inability of monetary policy to reduce nominal interest rates further.
C) money markets are trapped in a state of continuous disequilibrium.
D) monetary authorities cannot stop nominal interest rates from rising.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Deflation:
A) hurts borrowers and helps lenders.
B) helps borrowers and hurts lenders.
C) unlike inflation,affects neither borrowers nor lenders.
D) affects only lenders.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 221
Related Exams