Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Centrosomes
A) are constricted regions of prophase chromosomes.
B) determine the plane of cell division.
C) are the central region of the cell.
D) are the region where the membrane constricts during cytokinesis.
E) are part of cilia.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an organism with a haplontic life cycle, the adult multicellular organism is _______, and the time spent between fertilization and meiosis is _______ the time spent between meiosis and fertilization.
A) haploid; longer than
B) haploid; shorter than
C) diploid; longer than
D) diploid; equal to
E) diploid; shorter than
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The activity of oncogenes
A) increases the rate of growth of cancer cells.
B) retards the growth of cancer cells.
C) is derived from normal regulators of cell division.
D) can include inhibition of the cell cycle.
E) Both a and c
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The haploid chromosome number of a cell is 32.How many chromosomes will a trisomic individual have?
A) 31
B) 32
C) 63
D) 65
E) 96
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When does a cell make the commitment for another cell cycle?
A) Early in G1
B) Late in G2
C) At the transition between G1 and G2
D) At the transition between S and G2
E) At the transition between G1 and S
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The event in the cell division process that clearly involves microfilaments is
A) chromosome separation during anaphase.
B) movement of chromosomes to the metaphase plate.
C) chromosome condensation during prophase.
D) disappearance of the nuclear envelope during prophase.
E) cytokinesis in animal cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you were interested in determining the rates of recombination in an organism, what feature of meiosis would you observe?
A) Synapsis
B) Aneuploidy
C) Nondisjunction
D) Chiasmata
E) Chromatin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which phenomenon will most likely lead to aneuploidy?
A) Crossing over
B) Independent assortment
C) Nondisjunction
D) Autopolyploidy
E) Allopolyploidy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does a nucleus in G2 differ from a nucleus in G1?
A) The G2 nucleus has double the amount of DNA as the G1 nucleus.
B) DNA synthesis occurs only in G1 phase.
C) Inactive cells are arrested only in G2 phase.
D) During G2 the cell prepares for S phase.
E) None of the above; there is no difference in the nucleus between G1 and G2.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure showing crossing over. 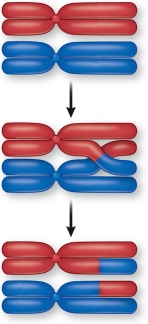 This figure depicts
This figure depicts
A) prophase I.
B) prophase II.
C) metaphase I.
D) metaphase II.
E) anaphase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bacterial colony grows steadily by rapid cell division in a medium that is rich in the amino acid alanine.If the alanine concentration drops, cell division slows.Supplying more alanine results in resumed cell division.Alanine is thus
A) a fertilization signal.
B) a ter site.
C) a reproductive signal.
D) an oncogene.
E) an ori site.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Genetic recombination occurs during
A) prophase of meiosis I.
B) the interphase preceding meiosis II.
C) the mitotic telophase.
D) fertilization.
E) the formation of somatic cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which situation would be the most likely result of a mutation in a eukaryotic organism that causes it to produce less p21 protein than normal?
A) Cell replication would be slowed if the organism receives radiation.
B) Cells with radiation-induced DNA damage would continue through the cell cycle without repairing the damaged DNA.
C) Cells with incomplete DNA replication would continue through the checkpoint.
D) Cells would not respond to growth factors.
E) Cells would have a hypersensitive response to growth factors.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which eukaryotic process has no analogue in prokaryotes?
A) Response to reproductive signals
B) DNA replication
C) Segregation of DNA to new cells
D) Meiosis
E) Cytokinesis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The DNA of a eukaryotic cell is
A) double-stranded and linear.
B) single-stranded and linear.
C) double-stranded and circular.
D) single-stranded and circular.
E) conservative.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
If a cell in G1 has 1.2 pg of DNA, it will have _______ pg of DNA in G2.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chromosome number is reduced during meiosis because the process consists of
A) two cell divisions without any chromosome replication.
B) a single cell division without any chromosome replication.
C) two cell divisions in which half of the chromosomes are destroyed.
D) two cell divisions and only a single round of chromosome replication.
E) None of the above; chromosome number is not reduced during meiosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the essential difference between necrosis and apoptosis?
A) In apoptosis, the cell death is part of the normal developmental process; in necrosis, by contrast, the cell death is the result of something gone wrong.
B) Necrosis occurs in animals, while apoptosis occurs in plants.
C) In necrosis, the cells actually die. In apoptosis, they are just dormant.
D) In apoptosis, the cells actually die. In necrosis, they are just dormant.
E) There is no difference; they are different words to describe the same phenomenon.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Necrosis
A) is the same as apoptosis.
B) is a form of cell death that can occur due to an environmental insult.
C) involves the production of caspases.
D) is a form of polyploidy.
E) is a type of cell division.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 260
Related Exams