A) The structure of a market is competitive.
B) Antitrust regulations are enforced.
C) Firms can exit from the market.
D) Potential competition exists.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
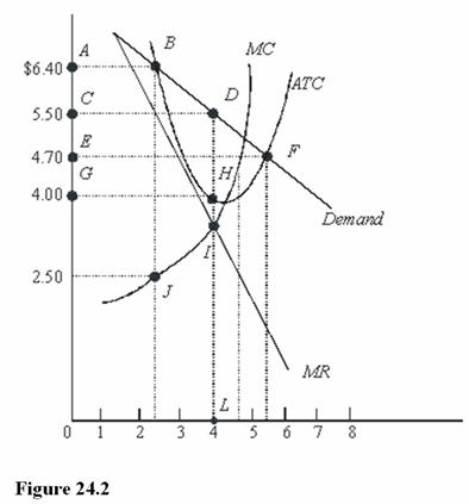 In Figure 24.2, the profit-maximizing level of output is
In Figure 24.2, the profit-maximizing level of output is
A) Between 2 and 3 units.
B) Between 4 and 5 units.
C) 4 units.
D) Between 5 and 6 units.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal revenue of a monopolist falls below price because the firm
A) Is not limited by market demand.
B) Faces a market demand curve that is inelastic.
C) Confronts a downward-sloping demand curve.
D) Has an upward-sloping marginal cost curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would definitely not be used by any unregulated monopolist?
A) Marginal cost pricing.
B) The profit-maximizing rule.
C) Price discrimination.
D) Economies of scale.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reductions in minimum average costs that come about through increases in the size of plants and equipment are called
A) Barriers to entry.
B) Economies to monopoly power.
C) Economies of scale.
D) Diseconomies of entry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sky-High Skywriters charges competitive prices for its skywriting services even though it has no competition.This is most likely because
A) There are no economies of scale in this industry.
B) It operates in a contestable market.
C) It is a natural monopoly.
D) It cares more about customers'well-being than its own well-being.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Price-discriminating firms that sell in two markets will charge higher prices in the market, ceteris paribus,
A) With a higher positive cross-price elasticity of demand with respect to substitutes.
B) With the more price-inelastic demand.
C) With the more income-elastic demand.
D) With lower incomes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist will not use marginal cost pricing because at that output
A) MR is greater than MC.
B) MR is below the ATC curve.
C) MC is greater than MR.
D) MC is greater than the monopolist's price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopolist, marginal revenue equals
A) Price.
B) Price times quantity.
C) The change in quantity divided by the change in total revenue.
D) The change in total revenue divided by the change in quantity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
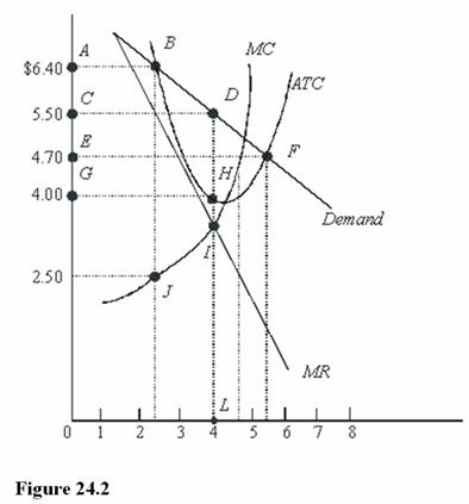 In Figure 24.2, total revenue at the profit-maximizing rate of output is
In Figure 24.2, total revenue at the profit-maximizing rate of output is
A) $22.00.
B) $6.40.
C) $4.00.
D) $16.00.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Based on the headline "Russia's Sable Monopoly Persists" you could predict that
A) Output is more than it would be in a competitive sable market.
B) Long-run economic profit is positive in the sable market.
C) The sable market is contestable.
D) Sable producers are franchise monopolists.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist has market power because it
A) Faces a downward-sloping demand curve for its own output.
B) Can raise price as much as it wishes and not lose any customers.
C) Is a price taker.
D) Is regulated by the government.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
For a monopoly, the marginal revenue from selling an extra unit of output is less than the price of that unit.
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is likely to be a monopolist?
A) A drug firm that has a patent granting it the exclusive right to produce a drug.
B) A large firm like GM, which has a substantial portion of the car market.
C) The Boeing Company, which is one of the largest producers of airplanes.
D) An Indonesian restaurant in a large city.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Price discrimination allows a producer to
A) Reap the highest possible average price for the quantity supplied.
B) Increase the elasticity of consumer demand.
C) Minimize marginal costs.
D) Decrease total costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal revenue curve is below the demand curve
A) If a firm must lower its price to sell additional output.
B) For a competitive firm.
C) When a market is characterized by economies of scale.
D) For all firms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 24.1 Hypothetical Monopoly Costs and Revenue In Table 24.1, using the profit maximization rule, a monopolist will charge a price of
A) $450.
B) $400.
C) $350.
D) $300.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist that does not practice price discrimination should never produce in the
A) Elastic portion of its demand curve because it can increase total revenue and reduce total costs by lowering the price.
B) Inelastic portion of its demand curve because it can increase total revenue and reduce total costs by increasing the price.
C) Inelastic portion of its demand curve because it can increase total revenue by more than it increases total cost by reducing the price.
D) Segment of its demand curve where the price elasticity of demand is greater than 1.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following contributes to a firm maintaining a monopoly?
A) Exclusive franchises.
B) The existence of substitute goods.
C) A large number of firms in the industry.
D) Homogeneous products in the market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist will find that its marginal revenue curve
A) Is the same as its demand curve.
B) Lies above its demand curve and is flatter than its demand curve.
C) Lies below its demand curve and is steeper than its demand curve.
D) Lies below its demand curve and has the same slope as its demand curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 153
Related Exams