A) 6 apples.
B) 7 apples.
C) 1 apple.
D) 3 apples.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Economists focus on the effect of changes in income and prices in influencing actual consumer purchases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marginal utility is the
A) Change in total utility obtained by spending one extra dollar on a good or service.
B) Change in total utility obtained by consuming one extra unit of a good or service.
C) Change in total utility obtained by selling one extra unit of a good or service.
D) Utility received from consuming the optimal combination of goods and services.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Complete Table 19.3 below.Assume the price of cola is $8 per unit and the price of pretzels is $4 per unit. Table 19.3 Michael's Utility Schedule Refer to Table 19.3.If Michael has $28 dollars to spend, why will three colas and four pretzels not be optimal?
A) This combination has less total utility.
B) This combination is affordable but does not maximize utility.
C) This combination is not affordable.
D) This combination has less marginal utility per dollar.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal utility for a good is computed as
A) Total utility divided by quantity.
B) Quantity divided by total utility.
C) The change in quantity divided by total utility.
D) The change in total utility divided by the change in quantity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic explanations of consumer behavior take into consideration
A) Ego gratification.
B) Lack of self-confidence.
C) Social status.
D) Prices and income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Consumer surplus does not exist because some consumers cannot afford to purchase the product at all.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A budget constraint line represents combinations of two goods that provide an individual the same total utility.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which industry here is unlikely to exhibit price discrimination?
A) Airlines.
B) New cars.
C) Supermarkets.
D) Colleges.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Complete Table 19.3 below.Assume the price of cola is $8 per unit and the price of pretzels is $4 per unit. Table 19.3 Michael's Utility Schedule The marginal utility per dollar of the third pretzel is
A) 4.
B) 5.
C) 6.
D) 12.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The four determinants of demand that are held constant when we consider a movement along a demand curve include all of the following except
A) Price.
B) Income.
C) Tastes.
D) Availability and price of substitute goods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Complete Table 19.3 below.Assume the price of cola is $8 per unit and the price of pretzels is $4 per unit. Table 19.3 Michael's Utility Schedule In Table 19.3, what is the total utility of two units of cola?
A) 32.
B) 40.
C) 72.
D) 96.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a good had a zero price (i.e., the good was free) , a rational person would consume
A) An infinite amount of the good.
B) The good until total utility was zero.
C) The good until the marginal utility was maximized.
D) The good until the marginal utility of the last unit was zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Utility maximization is always achieved where total revenue is maximized.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An indifference curve shows the
A) Maximum utility that can be achieved for a given consumer budget.
B) Maximum utility that can be achieved for different amounts of a good.
C) Combinations of goods giving equal utility to a consumer.
D) Optimal consumption combinations between two goods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these examples is an example of price discrimination?
A) Goods are marked down on sale.
B) Wholesale prices differ from retail prices.
C) Seniors pay one price at the movie theater and adults pay more.
D) Cereal manufacturers put discount coupons inside their cereal boxes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The farther an indifference curve is from the origin, the more total utility it yields.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An indifference map shows
A) A set of indifference curves.
B) One indifference curve.
C) A set of indifference curves and a set of budget constraints.
D) A set of budget constraints and one indifference curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Marginal utility represents the additional satisfaction obtained from one more unit of a good or service.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
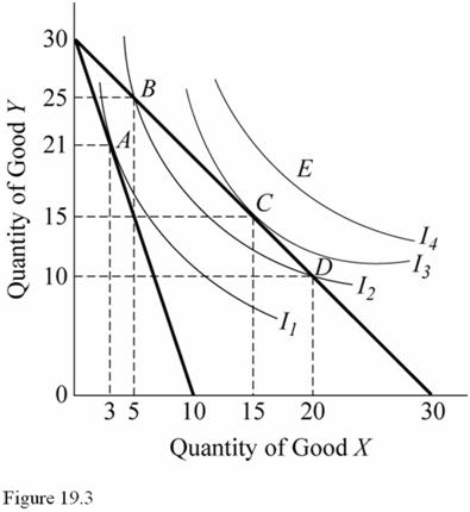 Use the indifference curves and the budget lines in Figure 19.3 to answer the indicated question.Assume the price of Y is $1 per unit.Point D on the graph
Use the indifference curves and the budget lines in Figure 19.3 to answer the indicated question.Assume the price of Y is $1 per unit.Point D on the graph
A) Is not affordable.
B) Is affordable but does not yield the highest utility possible.
C) Is affordable and is the optimal consumption bundle for this individual.
D) Lies on an indifference curve that is not obtainable.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 138
Related Exams