A) Barriers to entry.
B) Economies of scale.
C) Negative economic profit.
D) Price discrimination.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In Table 24.1, according to the profit maximization rule, at the profit-maximizing level of output marginal, cost is
A) $200.
B) $250.
C) $300.
D) $350.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reductions in minimum average costs that come about through increases in the size of plants and equipment are called
A) Barriers to entry.
B) Economies to monopoly power.
C) Economies of scale.
D) Diseconomies of entry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopoly
A) Maximizes profits at the output level where MR > MC.
B) Produces less output than a competitive industry, ceteris paribus.
C) Charges the same price as a competitive industry, ceteris paribus.
D) Maximizes profits at the output where P = MR.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Federal Trade Commission was created to study industry structures and behavior and identify anticompetitive practices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopoly realizes larger profits than a comparable competitive market by
A) Setting a higher price at the competitive level of output, thereby increasing total revenue.
B) Producing a greater quantity at the competitive price, thereby increasing profits.
C) Producing at output levels with more favorable cost structures and charging the competitive market price, thereby increasing profits per unit.
D) Reducing production and pushing prices up.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would definitely not be used by any unregulated monopolist?
A) Marginal cost pricing.
B) The profit-maximizing rule.
C) Price discrimination.
D) Economies of scale.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patent gives a firm the exclusive right to produce a product for
A) 6 months.
B) 2 years.
C) 20 years.
D) Forever.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an accurate argument in support of market power?
A) It restricts output and raises prices, contributing to more efficient use of resources.
B) It contributes to efficient production when there are diseconomies of scale.
C) It provides the economic profit necessary for survival and efficient production in a market.
D) It provides greater ability to fund research and development.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An In the News article titled "Jury Rules Magnetek Unit Is Liable for Keeping Technology off Market" reported, "A county superior court jury in Oakland ordered a unit of Magnetek Inc.to pay $25.8 million to two California entrepreneurs ...the unit had failed to bring the pair's energy-saving fluorescent-light technology to market in a profitable manner ...in favor of an outmoded technology." The most correct implication of this quotation is that Magnetek
A) Attempted to suppress Ramp;D.
B) Is a highly efficient, high-tech industry.
C) Makes zero economic profits.
D) Charges lower prices than might be expected in a competitive market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following can be used to increase monopoly power except
A) Acquisitions.
B) Lawsuits.
C) Antitrust laws.
D) Discounts for customer loyalty.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A monopoly is considered more desirable to society than a perfectly competitive firm because a monopoly has the incentive to pursue research and development.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The World View article "Foxy Soviets Pelt the West: Sable Monopoly Traps Hard Currency, Coats Capitalists" provides evidence that the Soviets would
A) Experience zero long-run profits in the sable market.
B) Practice marginal cost pricing.
C) Charge a price greater than marginal revenue.
D) Practice price discrimination.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal revenue of a monopolist
A) Is equal to price at all output levels.
B) Is above a downward-sloping demand curve.
C) Is positive up to the rate of output that maximizes total revenue.
D) Is negative up to the rate of output that maximizes total revenue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopoly can have a high degree of market power because of all but
A) Control over key inputs.
B) Government-bestowed franchise rights.
C) A downward-sloping demand curve for its product.
D) The presence of many close substitutes for its product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the entire output of a market is produced by a single seller, the firm
A) Is a monopoly.
B) Faces perfectly inelastic demand.
C) Can charge any price it wants and not lose customers.
D) Is producing a new product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a monopolist is producing a level of output where MR is less than MC, then it should
A) Shift its marginal cost curve upward.
B) Increase its output.
C) Lower its output.
D) Lower its price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
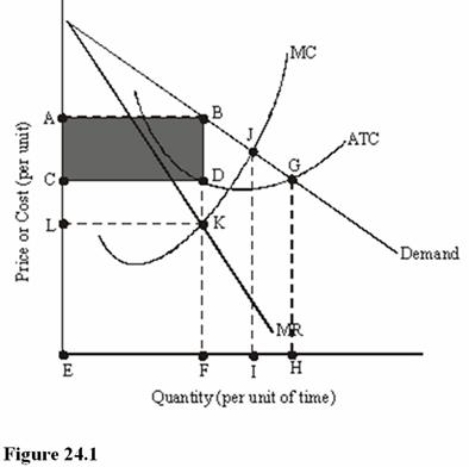 In Figure 24.1, the profit-maximizing monopolist will charge a price of
In Figure 24.1, the profit-maximizing monopolist will charge a price of
A) J.
B) L.
C) C.
D) A.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
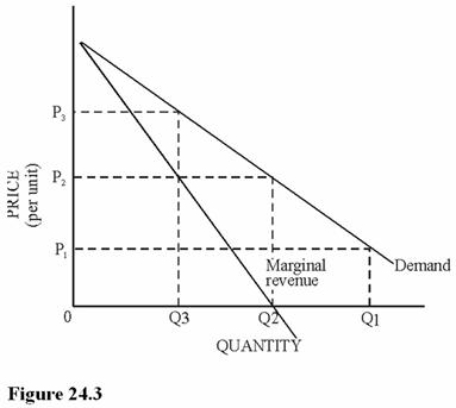 Refer to Figure 24.3.Which of the following statements is true about the price elasticity of demand at price P3?
Refer to Figure 24.3.Which of the following statements is true about the price elasticity of demand at price P3?
A) The price elasticity is elastic.
B) The price elasticity is unitary.
C) The price elasticity is inelastic.
D) The price elasticity is zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm can change market prices by altering its output, then it
A) Has market power.
B) Faces a flat demand curve.
C) Is a price taker.
D) Engages in marginal cost pricing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 153
Related Exams