A) 21.2 m/s
B) 21.0 m/s
C) 21.5 m/s
D) 21.7 m/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fixed amount of ideal gas is held in a rigid container that expands negligibly when heated. At 20°C the gas pressure is p. If we add enough heat to increase the temperature from 20°C to 40°C, the pressure will be
A) impossible to determine since we do not know the number of moles of gas in the container.
B) greater than 2p.
C) less than 2p.
D) equal to 2p.
E) impossible to determine since we do not know the volume of gas in the container.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mole of oxygen (O2) molecules and a mole of carbon dioxide (CO2) molecules at the same temperature and pressure have
A) the same average molecular speeds.
B) the same number of atoms.
C) different average kinetic energy per molecule.
D) the same number of molecules.
E) different volumes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A vertical tube that is closed at the upper end and open at the lower end contains an air pocket. The open end of the tube is under the water of a lake, as shown in the figure. When the lower end of the tube is just under the surface of the lake, where the temperature is 37°C and the pressure is 1.0 × 105 Pa, the air pocket occupies a volume of 630 cm3. Suppose now that the lower end of the tube is at a depth of 86 m in the lake, where the temperature is 7.0°C. What is the volume of the air pocket under these conditions? The density of the water in the lake is 1000 kg/m3. 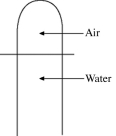
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sealed container holds 0.020 moles of nitrogen (N2) gas, at a pressure of 1.5 atmospheres and a temperature of 290 K. The atomic mass of nitrogen is 14.0 g/mol. The Boltzmann constant is 1.38 × 10-23 J/K and the ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 J/mol · K = 0.0821 L · atm/mol · K. The mass density of the gas is closest to
A) 0.90 kg/m3
B) 1.3 kg/m3
C) 1.8 kg/m3.
D) 2.2 kg/m3
E) 2.6 kg/m3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 3.2-L volume of neon gas (Ne) is at a pressure of 3.3 atm and a temperature of 330 K. The atomic mass of neon is 20.2 g/mol, Avogadro's number is 6.022 · 1023 molecules/mol, and the ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 J/mol · K = 0.0821 L · atm/mol · K. The mass of the neon gas is closest to
A) 7.9 × 10-3 kg.
B) 4.6 × 10-3 kg.
C) 3.8 kg.
D) 7.8 kg.
E) 7.8 × 102 kg.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 5.0-liter gas tank holds 1.4 moles of helium (He) and 0.70 moles of oxygen (O2) , at a temperature of 260 K. The atomic masses of helium and oxygen are 4.0 g/mol and 16.0 g/mol, respectively. Avogadro's number is 6.022 × 1023 molecules/mol and the Boltzmann constant is 1.38 × 10-23 J/K. The total random translational kinetic energy of the gas in the tank is closest to
A) 6.8 kJ.
B) 6.1 kJ.
C) 7.6 kJ.
D) 8.3 kJ.
E) 9.1 kJ.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which contains more moles of material: 80 grams of helium gas (He, having atomic weight 4.0 g/mol) or 400 grams of argon gas (Ar, having atomic weight 40 g/mol) ?
A) helium
B) argon
C) Both contain the same number of moles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the root-mean-square value of the following velocity components: 2.0 m/s, -3.0 m/s, and 4.0 m/s?
A) 5.4 m/s
B) 1.9 m/s
C) 3.1 m/s
D) 3.3 m/s
E) 1.0 m/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 0.10-m3 gas tank holds 5.0 moles of nitrogen gas (N2) , at a temperature of 370 K. The atomic mass of nitrogen is 14 g/mol, the molecular radius is 3.0 × 10-10 m, and the Boltzmann constant is 1.38 × 10-23 J/K. The root-mean-square speed (thermal speed) of the molecules is closest to
A) 570 m/s.
B) 810 m/s.
C) 410 m/s.
D) 22 m/s.
E) 99 m/s.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many moles of water (H2O) molecules are in a 4.00 m3 container at a pressure 8.00 × 105 N/m2 and temperature 600°C? The ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 J/mol•K = 0.0821 L ∙ atm/mol ∙ K.
A) 7.72 × 1026 mol
B) 641 mol
C) 441 mol
D) 3.86 × 1026 mol
E) 2.65 × 1026 mol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mean free path of an oxygen molecule is 2.0 × 10-5 m, when the gas is at a pressure of 120 Pa and a temperature of 275 K. The atomic mass of oxygen is 16.0 g/mol, the Boltzmann constant is 1.38 × 10-23 J/K, Avogadro's number is 6.02 × 1023 molecules/mole, and the ideal gas constant is J/mol•K = 0.0821 L ∙ atm/mol ∙ K. The radius of an oxygen molecule is closest to
A) 0.22 nm.
B) 0.24 nm.
C) 0.26 nm.
D) 0.28 nm.
E) 0.30 nm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At what temperature would the root-mean-square speed (thermal speed) of oxygen molecules be 13.0 m/s? Assume that oxygen approximates an ideal gas. The mass of one O2 molecule is 5.312 x 10-26 kg. The Boltzmann constant is 1.38 × 10-23 J/K.
A) 0.217 K
B) 1800 K
C) 5410 K
D) 0.0666 K
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An ideal gas is kept in a rigid container that expands negligibly when heated. The gas starts at a temperature of 20.0°C, and heat is added to increase its temperature. At what temperature will its root-mean-square speed (thermal speed) be double its value at 20.0°C?
A) 40.0°C
B) 141°C
C) 313°C
D) 400°C
E) 899°C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the temperature of a fixed amount of an ideal gas is increased, it NECESSARILY follows that
A) the pressure of the gas will increase.
B) the volume of the gas will increase.
C) the speed of the gas molecules will increase.
D) All of the above statements are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a fixed amount of gas, if the absolute temperature of the gas is doubled, what happens to the pressure of the gas?
A) The answer cannot be determined without volume information.
B) The pressure of the gas becomes double the original pressure.
C) The pressure of the gas becomes eight times the original pressure.
D) The pressure of the gas becomes one half the original pressure.
E) The pressure of the gas becomes four times the original pressure.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the mean free path of molecules in an ideal gas in which the mean collision time is 3.00 × 10-10 s, the temperature is 300 K, and the mass of the molecules is 6.00 × 10-25 kg? Assume that the molecules are moving at their root-mean-square speeds. The Boltzmann constant is 1.38 × 10-23 J/K.
A) 7.22 × 10-8 m
B) 4.32 × 10-8 m
C) 9.19 × 10-8 m
D) 1.39 × 10-8 m
E) 6.71 × 10-8 m
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dust particles are pulverized rock, which has density 2500 kg/m3. They are approximately spheres 20 μm in diameter. Treating dust as an ideal gas, what is the root-mean-square speed (thermal speed) of a dust particle at 400°C? (The Boltzmann constant is 1.38 × 10-23 J/K.)
A) 5.2 × 10-5 m/s
B) 1.7 × 10-5 m/s
C) 3.0 × 10-5 m/s
D) 7.3 × 10-5 m/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A container is filled with a mixture of helium (light molecules) and oxygen (heavy molecules) gases. A thermometer in the container reads 22°C. Which gas molecules have the greater average kinetic energy?
A) It is the same for both of the gases because the temperatures are the same.
B) The oxygen molecules do because they are diatomic.
C) The oxygen molecules do because they are more massive.
D) The helium molecules do because they are less massive.
E) The helium molecules do because they are monatomic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sometimes an experiment requires a certain pure gas to be used at reduced pressure. One way to achieve this is to purchase a sealed glass container filled with the gas, and to introduce the gas into a vacuum by attaching the glass container to the vacuum chamber and breaking the tip of the glass container using a metallic bean and a magnet. If the volume of the glass container is 1.0 L and it is at a pressure of 1.0 × 105 Pa and if the vacuum chamber has a volume of 2.0 L, what will the pressure be after the gas, which is to be assumed to be an ideal gas, is released into the vacuum chamber and the temperature has returned to its original value? (Note that the glass container remains part of the system.)
A) 33 kPa
B) 50 kPa
C) 300 kPa
D) 200 kPa
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 58
Related Exams