A) A substitution effect
B) A real-balances effect
C) An interest-rate effect
D) A foreign-purchases effect
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The shape of the short-run aggregate supply curve indicates that as the general price level rises, output will expand but not by much when the economy reaches full employment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When the stock market crashed in 2008, the so-called reverse wealth effect caused consumer spending to decrease.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in real interest rates will increase investment and aggregate demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aggregate demand decreases and real output falls but the price level remains the same. Which of the following factors most likely contributes to downward price inflexibility in the immediate short run?
A) The multiplier effect
B) The wealth effect
C) Fear of price wars
D) Business taxes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If personal income taxes and business taxes increase, then this will:
A) Increase aggregate demand and aggregate supply
B) Decrease aggregate demand and aggregate supply
C) Decrease aggregate demand and increase aggregate supply
D) Increase aggregate demand and decrease aggregate supply
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
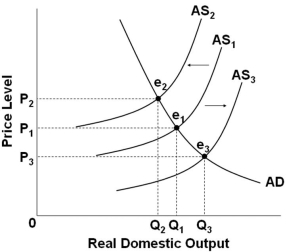 Refer to the graph above. A shift from AS1 to AS2 would be consistent with what economic event in U.S. history?
Refer to the graph above. A shift from AS1 to AS2 would be consistent with what economic event in U.S. history?
A) Demand-pull inflation in the late 1960s
B) Cost-push inflation in the mid-1970s
C) Full-employment in the late 1990s
D) Great Recession in 2007-2009
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The long-run aggregate supply curve is upward-sloping.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in expected returns on investment will most likely shift the AD curve to the:
A) Right because C will increase
B) Left because C will decrease
C) Right because Ig will increase
D) Left because Ig will decrease
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The real-balance effect pertains to the effect of:
A) Consumer spending on the price level, while the wealth effect refers to the impact of changes in wealth on consumer spending
B) Wealth-changes on aggregate demand, while the wealth effect refers to the impact of changes in the price level on the real value of wealth
C) Changes in interest rate on aggregate demand, while the wealth effect refers to the impact of changes aggregate demand on people's wealth
D) Price-changes on aggregate demand, while the wealth effect refers to the impact of changes in wealth on aggregate demand
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the general price level in our economy increases, the following effects occur except:
A) The purchasing power of people's savings will increase
B) The interest rate will also tend to increase
C) Foreign buyers will buy less of our output, and we tend to import more
D) Our net exports will tend to decrease
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that an economy produces 500 units of output. It takes 10 units of labor at $15 a unit and 4 units of capital at $50 a unit to produce this amount of output. The per unit cost of production is:
A) $1.42
B) $1.24
C) $0.70
D) $0.40
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
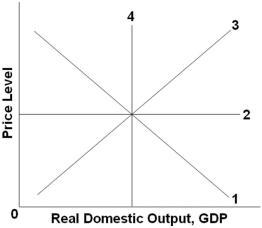 Refer to the graph above. The long-run aggregate supply curve would be represented by which line?
Refer to the graph above. The long-run aggregate supply curve would be represented by which line?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in interest rates caused by a change in the price level would cause a(n) :
A) Decrease (or shift left) in aggregate demand
B) Increase (or shift right) in aggregate demand
C) Decrease in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement up along AD)
D) Increase in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement down along AD)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The real-balance and interest-rate effects help explain why aggregate demand might shift to the right or to the left.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Deflation refers to a situation where:
A) Price level falls, and could be caused by a shift of AD to the left
B) Price level falls, and could be caused by a decrease in aggregate supply
C) The rate of inflation falls, and could be caused by a shift of AS to the right
D) The rate of inflation rises, and could be caused by an decrease in aggregate demand
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows the aggregate demand and aggregate supply schedules for a hypothetical economy. 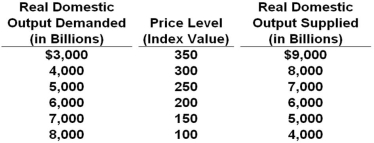 Refer to the table above. At the price level of 150, there will be a general:
Refer to the table above. At the price level of 150, there will be a general:
A) Surplus in the economy, and output supplied will decrease as the price level falls
B) Shortage in the economy, and output demanded will decrease as the price level rises
C) Surplus in the economy, and output supplied will increase as the price level rises
D) Shortage in the economy, and output demanded will increase as the price level falls
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
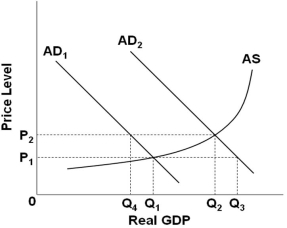 Refer to the figure above. If aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD1, the full multiplier effect on real GDP will be a decrease from:
Refer to the figure above. If aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD1, the full multiplier effect on real GDP will be a decrease from:
A) Q3 to Q1
B) Q2 to Q4
C) Q2 to Q1
D) Q3 to Q4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model, the economy's price level is assumed to be:
A) Constant, just like in the aggregate expenditures model
B) Variable, just like in the aggregate expenditures model
C) Constant, unlike in the aggregate expenditures model
D) Variable, unlike in the aggregate expenditures model
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aggregate demand curve shows the:
A) Inverse relationship between the price level and the quantity of real GDP purchased
B) Direct relationship between the price level and the quantity of real GDP produced
C) Inverse relationship between interest rates and the quantity of real GDP produced
D) Direct relationship between real-balances and the quantity of real GDP purchased
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 152
Related Exams