A) The gene might be inserted into the plasmid by forming hydrogen bonds.
B) The gene might be inserted into the plasmid multiple times in a row.
C) The gene might insert into the plasmid in the proper (forward) orientation.
D) The gene might insert into the plasmid in the wrong (backward) orientation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A researcher can use BLAST for all of the following except
A) to compare gene sequences between species.
B) to compare DNA sequences within a species.
C) to compare nucleotide sequences within a species.
D) to compare carbohydrate compositions between species.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the accompanying figure to answer the following question. The bands in the ladder are in 10-base increments, starting with 10 bases at the bottom and going to 70 bases at the top. Approximately how many bases are in the DNA molecule that the arrow is pointing to? 
A) 30 bases
B) 36 bases
C) 40 bases
D) 44 bases
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease that results from a defective CFTR protein that alters ion flow through the cell membrane such that water does not cross the cell membrane. Gene therapy is being used to attempt to help cystic fibrosis patients. Which of the following steps is not needed to develop a gene therapy treatment for cystic fibrosis?
A) Clone the normal-functioning CFTR gene and make an RNA version of the gene.
B) Make antibodies to the defective CFTR protein to enhance the patient's immune system.
C) Remove cells from a patient and infect them with the recombinant virus.
D) Insert the RNA version of the CFTR gene into a virus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
"Sticky ends" are
A) produced by the action of DNA ligase.
B) another name for the 5' cap on mRNA transcripts.
C) always long sequences of a single nucleotide.
D) DNA fragments with single-stranded ends.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ________ approach to gene cloning employs a mixture of fragments from the entire genome of an organism and results in the production of thousands of different recombinant plasmids.
A) shotgun
B) genetic engineering
C) restriction
D) cloning
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The polymerase chain reaction relies upon unusual, heat-resistant ________ that were isolated from bacteria living in hot springs.
A) DNA polymerases
B) DNA ligases
C) restriction enzymes
D) plasmids
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gel electrophoresis sorts DNA molecules on the basis of their
A) nucleotide sequence.
B) ability to bind to mRNA.
C) solubility in the gel.
D) size.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Researchers are using the CRISPR-Cas9 system to genetically engineer organisms in order to study gene function and to attempt to help patients with genetic diseases. In 2016, a research team used the CRISPR-Cas9 system to genetically alter pig zygotes so that they would have muscular dystrophy, a type of genetic disease that results in muscle wasting and loss of muscle mass. This disease often results from a lack of the protein dystrophin in skeletal muscle tissue. Researchers sometimes develop animal models of diseases so that they can develop therapies to treat the human version of the disease.
The researchers compared the molecular biology and physiology of two types of pigs: healthy, normal pigs (WT) and those that were modified when they were zygotes with the CRISPR-Cas9 system (CRISPR) . The data below show the dystrophin levels in various tissues from both types of pigs.
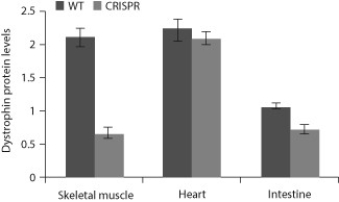 Source: Adapted from Yu, H. H., Zhao, H., Qing, Y. B., Pan, W. R., Jia, B. Y., Zhao, H. Y., Huang, X. X., et al. (2016) . Porcine zygote injection with Cas9/sgRNA results in DMD-modified pig with muscle dystrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,17(10) : 1668. MDPI AG. Retrieved from http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101668.
-In this study, what would have been true of the guide RNA that was used in the CRISPR-Cas9 system?
Source: Adapted from Yu, H. H., Zhao, H., Qing, Y. B., Pan, W. R., Jia, B. Y., Zhao, H. Y., Huang, X. X., et al. (2016) . Porcine zygote injection with Cas9/sgRNA results in DMD-modified pig with muscle dystrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,17(10) : 1668. MDPI AG. Retrieved from http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101668.
-In this study, what would have been true of the guide RNA that was used in the CRISPR-Cas9 system?
A) The guide RNA was complementary in sequence to a region of the dystrophin gene.
B) The guide RNA was injected into skeletal muscle cells, heart cells, and intestinal cells.
C) The guide RNA helped target the Cas9 enzyme to the dystrophin protein.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Genome sequence analysis suggests that Neanderthals
A) never interbred with humans.
B) are more closely related to chimpanzees than humans.
C) were lactose intolerant as adults.
D) could not speak.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ are a major source of restriction enzymes.
A) Plant cells
B) Human cells
C) Bacteria
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are setting up a PCR reaction and add a primer for one end of the target sequence, but you forget to add the primer for the other end of the target sequence. If you added the other necessary components, what do you expect to observe after running the PCR reaction for 40 cycles?
A) The PCR reaction will produce billions of copies of the target DNA.
B) The PCR reaction will produce millions of copies of the target DNA.
C) The PCR reaction will produce one copy of the target DNA.
D) The PCR reaction will produce zero copies of the target DNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which step in this process requires use of restriction enzymes? 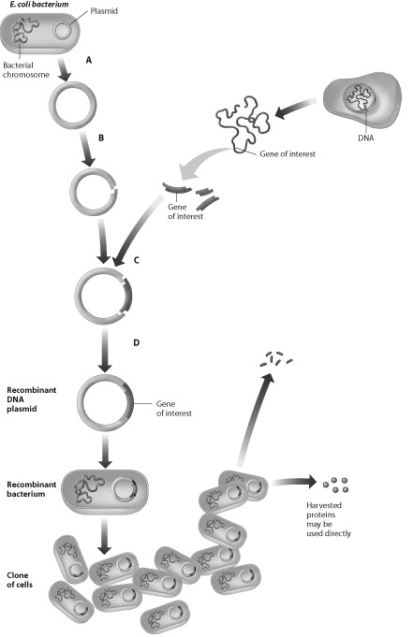
A) step A
B) step B
C) step C
D) step D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about nucleic acid probes is false?
A) A nucleic acid probe is a double-stranded DNA molecule.
B) A nucleic acid probe can be used to find a specific gene.
C) A nucleic acid probe binds to a complementary sequence in the gene of interest.
D) A nucleic acid probe is usually labeled with a radioactive isotope or fluorescent tag to help identify its location.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Four decades after the end of the Vietnam War, the remains of an Air Force pilot were discovered and returned to the United States. A search of Air Force records identified three families to which the remains might possibly belong. Each family had a surviving twin of a missing service member. The following STR profiles were obtained from the remains of the pilot and the surviving twins from the three families.
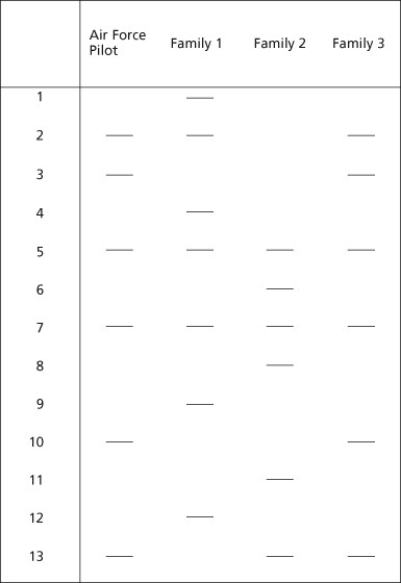 -Based on analysis of the STR sites shown, does the missing pilot belong to any of these three families?
-Based on analysis of the STR sites shown, does the missing pilot belong to any of these three families?
A) No, none of the families match.
B) Yes, family 1 matches.
C) Yes, family 2 matches.
D) Yes, family 3 matches.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the preferred name of the technique used to determine if DNA comes from a particular individual?
A) DNA technology
B) DNA profiling
C) DNA microarrays
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder that most severely affects the lungs and respiratory tract. Cystic fibrosis is caused by a mutation in the gene for the protein cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR) , which regulates the movement of chloride and sodium ions across epithelial cell membranes. When the CFTR gene is mutated in cystic fibrosis, the defective CFTR protein cannot transport ions properly, which results in too little water drawn across the membrane and the buildup of thick and sticky (viscous) mucus, especially in the airways. This leads to difficulty of breathing, frequent lung infections, and ultimately death. Research has shown that some of the increased thickness and viscosity of the mucus in the respiratory tract is due to the presence of human DNA. If DNA is present in high concentrations in solution, the DNA molecules can get entangled and lead to a thick, viscous solution. To combat this, pharmaceutical companies have developed recombinant forms of the human deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I) protein. DNase I, after being translated and modified with sugar groups, is normally produced in human cells and possibly plays a role in DNA breakdown during apoptosis (programmed cell death) . -If recombinant DNase I is added to a vial of respiratory secretions from a cystic fibrosis patient, which of the following results would indicate that the recombinant DNase I is functional?
A) The secretions become thicker and more viscous.
B) The secretions become less viscous.
C) There is no effect on the secretions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type of repetitive DNA composed of sequences of large repeated units is often associated with
A) tandem repeats.
B) transposable elements.
C) sex-linked genes.
D) transcription factors.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When cloning a gene, one of the steps is to use restriction enzymes to insert the gene of interest into a vector. If you separated the empty vector (the vector without the gene of interest) and the cloned vector (the vector that has the gene of interest added) using agarose gel electrophoresis, what do you expect to observe on the agarose gel if both vectors are loaded at the same position at the top of the gel?
A) The empty vector would migrate farther down than the cloned vector.
B) The cloned vector would migrate farther down than the cloned vector.
C) The empty vector would migrate the same distance as the cloned vector.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the process of human gene cloning using plasmids, the bacterial plasmid is
A) used as the vector.
B) the source of the gene to be cloned.
C) cultured inside the human cell, which contains the gene to be cloned.
D) used to insert the human gene into the bacterial chromosome.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 80
Related Exams