A) cellulose
B) polypeptides
C) starch
D) amylopectin
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an RNA sample, ________.
A) the number of thiamine may or may not equal the number of adenine
B) the number of purine always equals the number of pyrimidine
C) the number of thiamine always equals the number of uracil
D) the number of purine may or may not equal the number of and pyrimidine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What component of amino acid structure varies among different amino acids?
A) The long carbon-hydrogen tails of the molecule.
B) The presence of a central C atom.
C) The components of the R group.
D) The glycerol molecule that forms the backbone of the amino acid.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What makes lipids/fats hydrophobic?
A) Their long carbon skeleton.
B) The carboxyl group at one end of the molecule.
C) The glycerol moiety.
D) The presence of relatively nonpolar C-H bonds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following descriptions best fits the class of molecules known as nucleotides?
A) a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group
B) a nitrogenous base and a sugar
C) a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a sugar
D) a sugar and a purine or pyrimidine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the major structural difference between starch and glycogen?
A) The types of monosaccharide subunits in the molecules.
B) The type of glycosidic linkages in the molecule.
C) Whether glucose is in the α or β form.
D) The amount of branching that occurs in the molecule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a major difference between RNA and DNA?
A) type of sugar
B) type of phosphate
C) type of purines
D) type of glycosidic bond
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
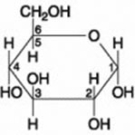 The molecule shown is ________.
The molecule shown is ________.
A) a hexose
B) a pentose
C) fructose
D) maltose
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The molecular formula for glucose is C₆H₁₂O₆. What would be the molecular formula for a molecule made by linking three glucose molecules together by dehydration reactions?
A) C18H36O18
B) C18H32O16
C) C6H10O5
D) C18H30O15
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true about proteins?
A) Denaturation leads to bond disruption, and the molecule turns into liquid.
B) Denaturation is always irreversible.
C) Final folded structure can reveal the steps of protein folding.
D) Some proteins form a complete 3-D structure only when they interact with their targets.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best summarises the relationship between dehydration reactions and hydrolysis?
A) Dehydration reactions assemble polymers; hydrolysis reactions break polymers apart.
B) Dehydration reactions eliminate water from membranes; hydrolysis reactions add water to membranes.
C) Dehydration reactions and hydrolysis reactions assemble polymers from monomers.
D) Hydrolysis reactions create polymers, and dehydration reactions create monomers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In sickle-cell disease, as a result of a single amino acid change, the mutant haemoglobin tetramers associate with each other and assemble into large fibres. Based on this information alone, we can conclude that sickle-cell haemoglobin exhibits ________.
A) only altered primary structure
B) only altered tertiary structure
C) only altered quaternary structure
D) altered primary structure and altered quaternary structure; the secondary and tertiary structures may or may not be altered
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
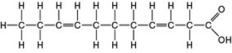 The molecule illustrated in the figure ________.
The molecule illustrated in the figure ________.
A) is a saturated fatty acid
B) stores genetic information
C) will be liquid at room temperature
D) is a carbohydrate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Homo sapiens have 23 pairs of chromosomes. This implies that ________.
A) 46 double-stranded DNA molecules are present in each somatic cell
B) 23 single-stranded DNA molecules are present in each somatic cell
C) 23 double-stranded DNA molecules are present in each somatic cell
D) several hundreds of genes are present on DNA but not on the chromosomes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
"The native structure of h[a]emoglobin (Hb) comprises of two α and two β subunits, each of which carries a h[a]eme group. There appear to be no previous studies that report the in-vitro folding and assembly of Hb from highly unfolded α and β globin in a 'one-pot' reaction. One difficulty that has to be overcome for studies of this kind is the tendency of Hb to aggregate during refolding. This work demonstrates that denaturation of Hb in 40% acetonitrile at pH 10.0 is reversible." (J Am Soc Mass Spectrum 2007, 18, 8-16) -Haemoglobin, when subjected to 40% acetonitrile at pH 10.0, loses its quaternary structure, which means the ________.
A) four α and β polypeptides dissociate
B) peptide bonds between amino acids break
C) α and β polypeptides lose their 3-D structure
D) four α and β polypeptides dissociate, peptide bonds between amino acids, and α and β polypeptides lose their 3-D structure
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between an aldose sugar and a ketose sugar is ________.
A) the number of carbon atoms
B) the position of the hydroxyl groups
C) the position of the carbonyl group
D) the ring form and the linear chain
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cooking oil and petrol (a hydrocarbon) are not amphipathic molecules because they ________.
A) do not have a polar or charged region
B) do not have a nonpolar region
C) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
D) are highly reduced molecules
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Absorbance at Various pH Levels
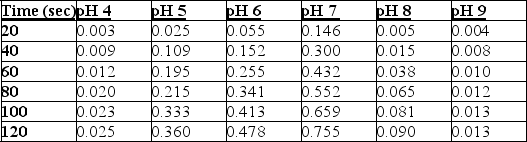 The table represents the results of an experiment where the effects of pH buffers on an enzyme found in saliva (amylase) were studied. A spectrophotometer set at 500 nm was used to measure absorbance at the various pH levels every 20 seconds for 2 minutes. The higher absorbance values would indicate greater enzyme activity. All experiments were conducted at the same temperature.
Which statement correctly identifies the result that the optimum pH for amylase function is 7?
The table represents the results of an experiment where the effects of pH buffers on an enzyme found in saliva (amylase) were studied. A spectrophotometer set at 500 nm was used to measure absorbance at the various pH levels every 20 seconds for 2 minutes. The higher absorbance values would indicate greater enzyme activity. All experiments were conducted at the same temperature.
Which statement correctly identifies the result that the optimum pH for amylase function is 7?
A) The pH with the lowest absorbance values would indicate the optimum pH for amylase since this pH does not affect the structure or function of the protein.
B) The pH with the highest absorbance values would indicate the optimum pH for amylase since this pH does not affect the structure or function of the protein.
C) At pH 9, the enzyme is denatured and will lose its function, but not its structure.
D) At pH 4, the structure of the enzyme will be altered, and the enzyme would not be able to catalyse the reaction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
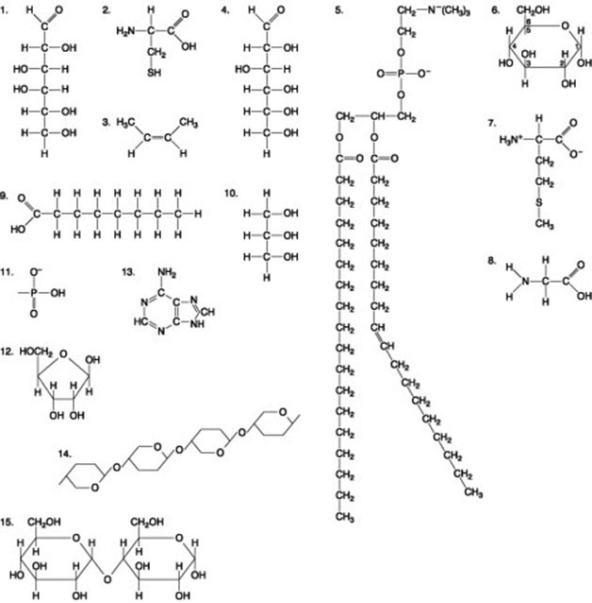 -Which molecule is a saturated fatty acid?
-Which molecule is a saturated fatty acid?
A) 1
B) 5
C) 8
D) 9
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -Which of the following pairs of molecules could be joined together by a peptide bond in a dehydration reaction?
-Which of the following pairs of molecules could be joined together by a peptide bond in a dehydration reaction?
A) 2 and 3
B) 7 and 8
C) 8 and 9
D) 12 and 13
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 70
Related Exams